ddrescue和dd
区别:
-
GNU ddrescue不是dd的衍生物,也与dd没有任何关系 除了两者都可用于将数据从一台设备复制到另一台设备。 关键的区别在于 ddrescue 使用复杂的算法来复制 来自故障驱动器的数据,尽可能少地造成额外的损坏。 -
ddrescue具备更强大的错误处理和恢复机制,可以更好地处理损坏的数据。 -
ddrescue可以逐渐恢复数据,首先尝试读取易读的部分,然后再处理更难访问的区域。 -
dd是一个基础的命令,用于一般的数据复制任务,而ddrescue专注于数据恢复,因此在某些方面更复杂。 - 如果你的任务是简单的数据复制,可能选择
dd足够了。但如果你处理的是受损的硬盘或需要更复杂的数据恢复操作,ddrescue可能更适合。
dd命令:
-
dd是一个用于复制文件和设备的基本命令。它以块为单位操作数据,可以用于复制整个磁盘、分区或文件。dd对于数据恢复来说非常基础,它简单粗暴,没有内建的错误处理机制。dd命令是一种直接复制和写入数据的工具,而不会考虑目标设备上是否已有数据。因此,在执行这个命令之前,请确保/dev/sdb上的所有数据都是你可以丢弃的,或者在执行之前进行备份。
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
sudo dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/sdb bs=4M |
从 /dev/sda 复制整个设备的内容到 /dev/sdb,块大小为4兆字节。这将覆盖 /dev/sdb 上的所有数据。较大的块大小可以提高性能,但也可能导致更多的浪费,特别是在尝试恢复数据时。 |
sudo dd if=/dev/sda of=backup.img bs=1G count=1 |
创建一个名为 backup.img 的映像文件,其中包含 /dev/sda 的前1个千兆字节的数据。 |
sudo dd if=source.img of=/dev/sdb bs=8M |
将名为 source.img 的映像文件的内容写入到 /dev/sdb,块大小为8兆字节。这会覆盖 /dev/sdb 上的所有数据。 |
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdb bs=1M count=10 |
使用 /dev/zero 中的数据(全0)覆盖 /dev/sdb 的前10兆字节。这可以用于擦除设备上的前几个块。 |
sudo dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/sdb bs=512 count=100 |
bs=512:指定块大小为512字节,即一个扇区的大小。 count=100:指定要拷贝的扇区数目。 |
sudo dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/sdb bs=4M seek=1 |
|
sudo dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/sdb bs=4M seek=100 |
从 /dev/sda 复制数据到 /dev/sdb,但从 /dev/sdb 的第100个块之后开始写入。这是一个在目标设备上追加数据。 |
- linux下dd命令的简单图形界面工具easydd
ddrescue命令:
-
ddrescue是专门设计用于数据恢复的命令。它被设计成能够处理磁盘上的坏块(损坏的数据区域)并尽量从损坏的地方恢复尽可能多的数据。ddrescue会首先尝试读取易读的部分,然后在后续尝试中逐渐尝试读取更难访问的区域。
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
sudo ddrescue /dev/sda /dev/sdb logfile |
这个例子将源设备 /dev/sda 的内容复制到目标设备 /dev/sdb,并将恢复的信息记录到 logfile 中。 |
sudo ddrescue /dev/sda /dev/sdb rescued.img |
尝试从 /dev/sda 复制数据到 /dev/sdb,并将已恢复的数据写入 rescued.img。这个命令默认尝试从容易读取的部分开始,逐渐处理难以读取的部分。 |
sudo ddrescue -n /dev/sda /dev/sdb rescued.img |
使用 ddrescue 的快速模式,只复制容易读取的数据。这个命令只进行一次尝试,不尝试处理难以读取的部分。 |
sudo ddrescue -r 3 /dev/sda /dev/sdb rescued.img |
在复制时,尝试最多 3 次从难以读取的部分恢复数据。 |
sudo ddrescue -d -r 3 /dev/sda /dev/sdb rescued.img |
在尝试读取时显示调试信息,并且最多尝试 3 次。 |
sudo ddrescue -b 4096 /dev/sda /dev/sdb rescued.img |
设置块大小为 4096 字节。这允许更精细的控制读取和写入的数据块大小。 |
sudo ddrescue -c 1M /dev/sda /dev/sdb rescued.img |
设置聚类大小为 1 兆字节,这有助于加快处理速度,特别是在处理大容量存储设备时。 |
sudo ddrescue --fill-mode=+ /dev/sda /dev/sdb rescued.img |
使用 + 填充模式,在写入时填充已损坏的区域。 |
sudo ddrescue --retry-passes=3 /dev/sda /dev/sdb rescued.img |
设置最大重试次数为 3 次。在每个重试阶段结束时,ddrescue 将记录已经复制的数据并尝试恢复尽可能多的数据。 |
sudo ddrescue --timeout=10s /dev/sda /dev/sdb rescued.img |
设置超时时间为 10 秒,在此时间内尝试读取数据。如果在规定的时间内未能读取数据,则放弃当前尝试。 |
Android 设备
-
Android 调试桥(Android Debug Bridge,简称 adb)是一种用于在计算机和 Android 设备之间进行通信的命令行工具。它允许开发者通过 USB 或网络连接在计算机和 Android 设备之间传输文件、执行命令和调试应用程序。
-
Copy full disk image from Android to computer:在某些情况下,你可能不需要使用
dd命令来直接复制设备的数据。相反,你可以确保 Android 调试桥(adb)以 root 权限运行,然后使用adb pull命令直接获取分区的块设备文件。
-
安装 ADB:
- ADB 包含在 Android SDK(软件开发工具包)中。下载并安装 Android Studio,或者只下载并安装 SDK 工具,其中包含了 adb。
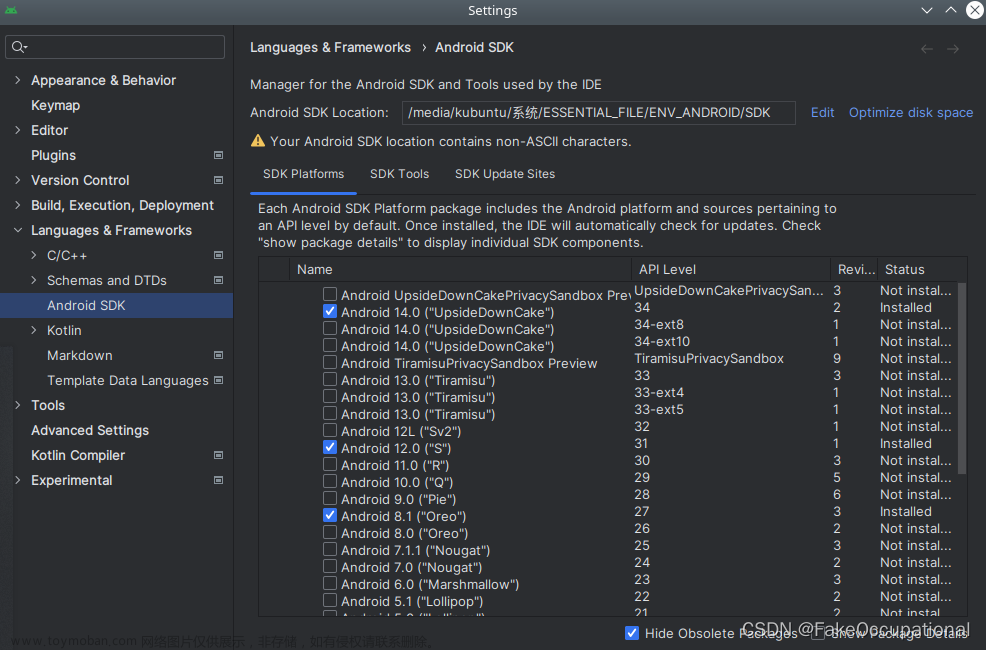
-
启用 USB 调试:
- 在 Android 设备上使用 adb 之前,你需要确保 USB 调试已经启用。在设备的设置中,进入 “开发者选项” 并启用 “USB 调试”。
-
连接设备:
- 使用 USB 数据线将 Android 设备连接到计算机。确保设备以 MTP(媒体传输协议)或 PTP(图片传输协议)模式连接。
-
运行 ADB 命令:
- 打开终端或命令提示符,导航到 Android SDK 的
platform-tools目录,并运行 adb 命令。
- 打开终端或命令提示符,导航到 Android SDK 的
kubuntu@kubuntu:/media/kubuntu/系统/ESSENTIAL_FILE/ENV_ANDROID/SDK/platform-tools$ ./adb --version
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41
Version 34.0.5-10900879
Installed as /media/kubuntu/系统/ESSENTIAL_FILE/ENV_ANDROID/SDK/platform-tools/adb
Running on Linux 5.15.0-67-generic (x86_64)
./adb --help
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41
Version 34.0.5-10900879
Installed as /media/kubuntu/系统/ESSENTIAL_FILE/ENV_ANDROID/SDK/platform-tools/adb
Running on Linux 5.15.0-67-generic (x86_64)
global options:
-a listen on all network interfaces, not just localhost
-d use USB device (error if multiple devices connected)
-e use TCP/IP device (error if multiple TCP/IP devices available)
-s SERIAL use device with given serial (overrides $ANDROID_SERIAL)
-t ID use device with given transport id
-H name of adb server host [default=localhost]
-P port of adb server [default=5037]
-L SOCKET listen on given socket for adb server [default=tcp:localhost:5037]
--one-device SERIAL|USB only allowed with 'start-server' or 'server nodaemon', server will only connect to one USB device, specified by a serial number or USB device address.
--exit-on-write-error exit if stdout is closed
general commands:
devices [-l] list connected devices (-l for long output)
help show this help message
version show version num
networking:
connect HOST[:PORT] connect to a device via TCP/IP [default port=5555]
disconnect [HOST[:PORT]]
disconnect from given TCP/IP device [default port=5555], or all
pair HOST[:PORT] [PAIRING CODE]
pair with a device for secure TCP/IP communication
forward --list list all forward socket connections
forward [--no-rebind] LOCAL REMOTE
forward socket connection using:
tcp:<port> (<local> may be "tcp:0" to pick any open port)
localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
dev:<character device name>
jdwp:<process pid> (remote only)
vsock:<CID>:<port> (remote only)
acceptfd:<fd> (listen only)
forward --remove LOCAL remove specific forward socket connection
forward --remove-all remove all forward socket connections
reverse --list list all reverse socket connections from device
reverse [--no-rebind] REMOTE LOCAL
reverse socket connection using:
tcp:<port> (<remote> may be "tcp:0" to pick any open port)
localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
reverse --remove REMOTE remove specific reverse socket connection
reverse --remove-all remove all reverse socket connections from device
mdns check check if mdns discovery is available
mdns services list all discovered services
file transfer:
push [--sync] [-z ALGORITHM] [-Z] LOCAL... REMOTE
copy local files/directories to device
--sync: only push files that are newer on the host than the device
-n: dry run: push files to device without storing to the filesystem
-z: enable compression with a specified algorithm (any/none/brotli/lz4/zstd)
-Z: disable compression
pull [-a] [-z ALGORITHM] [-Z] REMOTE... LOCAL
copy files/dirs from device
-a: preserve file timestamp and mode
-z: enable compression with a specified algorithm (any/none/brotli/lz4/zstd)
-Z: disable compression
sync [-l] [-z ALGORITHM] [-Z] [all|data|odm|oem|product|system|system_ext|vendor]
sync a local build from $ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT to the device (default all)
-n: dry run: push files to device without storing to the filesystem
-l: list files that would be copied, but don't copy them
-z: enable compression with a specified algorithm (any/none/brotli/lz4/zstd)
-Z: disable compression
shell:
shell [-e ESCAPE] [-n] [-Tt] [-x] [COMMAND...]
run remote shell command (interactive shell if no command given)
-e: choose escape character, or "none"; default '~'
-n: don't read from stdin
-T: disable pty allocation
-t: allocate a pty if on a tty (-tt: force pty allocation)
-x: disable remote exit codes and stdout/stderr separation
emu COMMAND run emulator console command
app installation (see also `adb shell cmd package help`):
install [-lrtsdg] [--instant] PACKAGE
push a single package to the device and install it
install-multiple [-lrtsdpg] [--instant] PACKAGE...
push multiple APKs to the device for a single package and install them
install-multi-package [-lrtsdpg] [--instant] PACKAGE...
push one or more packages to the device and install them atomically
-r: replace existing application
-t: allow test packages
-d: allow version code downgrade (debuggable packages only)
-p: partial application install (install-multiple only)
-g: grant all runtime permissions
--abi ABI: override platform's default ABI
--instant: cause the app to be installed as an ephemeral install app
--no-streaming: always push APK to device and invoke Package Manager as separate steps
--streaming: force streaming APK directly into Package Manager
--fastdeploy: use fast deploy
--no-fastdeploy: prevent use of fast deploy
--force-agent: force update of deployment agent when using fast deploy
--date-check-agent: update deployment agent when local version is newer and using fast deploy
--version-check-agent: update deployment agent when local version has different version code and using fast deploy
--local-agent: locate agent files from local source build (instead of SDK location)
(See also `adb shell pm help` for more options.)
uninstall [-k] PACKAGE
remove this app package from the device
'-k': keep the data and cache directories
debugging:
bugreport [PATH]
write bugreport to given PATH [default=bugreport.zip];
if PATH is a directory, the bug report is saved in that directory.
devices that don't support zipped bug reports output to stdout.
jdwp list pids of processes hosting a JDWP transport
logcat show device log (logcat --help for more)
security:
disable-verity disable dm-verity checking on userdebug builds
enable-verity re-enable dm-verity checking on userdebug builds
keygen FILE
generate adb public/private key; private key stored in FILE,
scripting:
wait-for[-TRANSPORT]-STATE...
wait for device to be in a given state
STATE: device, recovery, rescue, sideload, bootloader, or disconnect
TRANSPORT: usb, local, or any [default=any]
get-state print offline | bootloader | device
get-serialno print <serial-number>
get-devpath print <device-path>
remount [-R]
remount partitions read-write. if a reboot is required, -R will
will automatically reboot the device.
reboot [bootloader|recovery|sideload|sideload-auto-reboot]
reboot the device; defaults to booting system image but
supports bootloader and recovery too. sideload reboots
into recovery and automatically starts sideload mode,
sideload-auto-reboot is the same but reboots after sideloading.
sideload OTAPACKAGE sideload the given full OTA package
root restart adbd with root permissions
unroot restart adbd without root permissions
usb restart adbd listening on USB
tcpip PORT restart adbd listening on TCP on PORT
internal debugging:
start-server ensure that there is a server running
kill-server kill the server if it is running
reconnect kick connection from host side to force reconnect
reconnect device kick connection from device side to force reconnect
reconnect offline reset offline/unauthorized devices to force reconnect
usb:
attach attach a detached USB device
detach detach from a USB device to allow use by other processes
environment variables:
$ADB_TRACE
comma/space separated list of debug info to log:
all,adb,sockets,packets,rwx,usb,sync,sysdeps,transport,jdwp
$ADB_VENDOR_KEYS colon-separated list of keys (files or directories)
$ANDROID_SERIAL serial number to connect to (see -s)
$ANDROID_LOG_TAGS tags to be used by logcat (see logcat --help)
$ADB_LOCAL_TRANSPORT_MAX_PORT max emulator scan port (default 5585, 16 emus)
$ADB_MDNS_AUTO_CONNECT comma-separated list of mdns services to allow auto-connect (default adb-tls-connect)
Online documentation: https://android.googlesource.com/platform/packages/modules/adb/+/refs/heads/master/docs/user/adb.1.md
$ ./adb devices
List of devices attached
SJQ4C19325004095 unauthorized
========》手机上选择“允许调试”========》
$ ./adb devices
List of devices attached
SJQ4C19325004095 device
- 常见 ADB 命令:
./adb shell ls
3rdmodem
3rdmodemnvm
3rdmodemnvmbkp
acct
bugreports
cache
charger
config
cust
cust_comm
cust_spec
cust_spec_cfg
d
data
default.prop
dev
dload
etc
hw_odm
hw_oem
hw_preload
log
mnt
odm
oem
patch
patch_hw
preload
proc
product
res
root
sbin
sdcard
splash2
storage
sys
system
vendor
version
ls: ./mnvm2:0: Permission denied
ls: ./modem_fw: Permission denied
ls: ./modem_log: Permission denied
ls: ./modem_secure: Permission denied
ls: ./hisee_fs: Permission denied
ls: ./sec_storage: Permission denied
ls: ./version.prop: Permission denied
ls: ./verity_key: Permission denied
ls: ./ueventd.rc: Permission denied
ls: ./resetFactory.cfg: Permission denied
ls: ./init.zygote64_32.rc: Permission denied
ls: ./init.zygote32.rc: Permission denied
ls: ./init.usb.rc: Permission denied
ls: ./init.usb.configfs.rc: Permission denied
ls: ./init.rc: Permission denied
ls: ./init.environ.rc: Permission denied
ls: ./init: Permission denied
ls: ./fstab.zram768m: Permission denied
ls: ./fstab.zram512m: Permission denied
ls: ./fstab.zram256m: Permission denied
ls: ./fstab.zram2240m: Permission denied
ls: ./fstab.zram1536m: Permission denied
ls: ./fstab.zram1280m: Permission denied
ls: ./fstab.zram1024m: Permission denied
CG
-
安装APK时显示“已安装了签名冲突的应用”,但是手机上又没有该软件的解决办法
-
首先必须明确一个条件,那就是如果手机系统没有Root过的话,是绝对不可以对磁盘进行扇区级操作的。所以,第一步,请先Root了你的手机或者模拟器吧
-
ddrescue 电脑恢复数据软件不用付费ddrescue,抢救损坏的硬盘数据,Linux下的软件国产操作系
-
https://www.gnu.org/software/ddrescue/
-
https://www.gnu.org/software/ddrescue/manual/ddrescue_manual.html
-
sudo apt install gddrescue
-
OPTIONAL : sudo apt-get install ddrescueview
-
ddrescue的一个最大的好处是 mapFile 他可以记录进度,即使中断,下次在执行这个命令,他会检测已恢复的进度,并继续恢复,可以通过 ddrescueview 来通过GUI 的方式来查看 mapfile
-
:C/C++
-
https://github.com/lich4/DataRecovery
-
TestDisk 是一款功能强大的免费数据恢复软件!
-
Undark - a SQLite recovery tool for deleted data or corrupt database
-
Data recovery for IPFS protocol.
-
:PYTHON
-
Data recovery tools for FATX drives (XBOX and XBOX 360).
-
SQBrite is a data recovery tool for SQLite databases
-
:Rust
-
Simple read only zfs implementation with some simple tools for data recovery.
-
这是一个用于恢复最终处于不可恢复状态的丢失钱包的工具。如果你把你的种子输入到这个 工具,它会导致您的频道在您下次打开钱包时强制关闭。这将使您能够收回资金 从渠道。
-
用 Rust 编写的 BTRFS 数据恢复工具
-
ANDROID
-
https://github.com/android-rooting-tools/android_run_root_shell
-
Android-External-Root-Memory-库
-
嘿,我是格兰特。我是一名安全工程师,专注于逆向工程和漏洞研究。最近,我发现自己花了很多时间在与Android安全相关的主题上。 了解我的学术研究,阅读我一些关于杂项主题的不常发表的博客文章,查看我的项目索引,或查看我的简历以了解有关我的工作经历的更多信息。我的一些爱好包括玩 CTF(目前没有团队)、系统管理、游戏黑客、计算机图形学和网页设计。
-
Rooting with root cause: finding a variant of a Project Zero bug
-
Android Root Exploits Abuse Dirty COW Vulnerability文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-828641.html
-
Exploiting CVE-2020-0041 - Part 2: Escalating to root文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-828641.html
到了这里,关于磁盘database数据恢复: ddrescue,dd和Android 设备的数据拷贝的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!





![[12 种安卓数据恢复方案] 最佳免费 Android 照片恢复工具榜单](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/01/824853-1.jpeg)