DFS
排列数字

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int a[N], b[N];
int n;
void dfs(int u){
if(u > n){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(!b[i]){
b[i] = 1;
a[u] = i;
dfs(u + 1);
b[i] = 0;
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
dfs(1);
return 0;
}
n-皇后问题

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20;
char g[N][N];
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
int n;
void dfs(int u){
if(u > n){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
cout<<g[i][j];
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(!a[i] && !b[u + i] && !c[-u + i + n]){
a[i] = b[u + i] = c[-u + i + n] = 1;
g[u][i] = 'Q';
dfs(u + 1);
g[u][i] = '.';
a[i] = b[u + i] = c[-u + i + n] = 0;
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
g[i][j] = '.';
dfs(1);
return 0;
}
BFS
走迷宫

#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int g[N][N], d[N][N];
pair<int, int> q[N * N];
int hh, tt = - 1;
int n, m;
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
void bfs(int x, int y){
memset(d, -1, sizeof(d));
q[++tt] = make_pair(x, y);
d[x][y] = 0;
while(hh <= tt){
auto t = q[hh++];
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int a = dx[i] + t.first, b = dy[i] + t.second;
if(a < 1 || a > n || b < 1 || b > m) continue;
if(d[a][b] != -1) continue;
if(g[a][b] != 0) continue;
d[a][b] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;
q[++tt] = make_pair(a, b);
}
}
cout<<d[n][m];
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin>>g[i][j];
bfs(1, 1);
return 0;
}
八数码


#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6; //一共有9!种情况
unordered_map<string, int> d;
string q[N];
int hh, tt = -1;
int n = 9;
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int bfs(string s){
q[++tt] = s;
d[s] = 0;
//记录终点
string end = "12345678x";
while(hh <= tt){
string t = q[hh++];
//存储当前位置到起点的距离
int dis = d[t];
//如果到终点了,那就返回距起点距离
if(t == end) return dis;
//查找x的下标
int k = t.find('x');
//x在矩阵中的位置
int x = k / 3, y = k % 3;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if(a < 0 || a > 2 || b < 0 || b > 2) continue;
//转移x
swap(t[k], t[3 * a + b]);
//如果没有遍历过,那就存储到队列中
if(!d.count(t)){
d[t] = dis + 1;
q[++tt] = t;
}
//还原
swap(t[k], t[3 * a + b]);
}
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
char c;
string s = "";
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin>>c;
s += c;
}
cout<<bfs(s);
return 0;
}
树和图的存储
树是一种特殊的图
存储可以用链式向前星或者vector
//链式向前星
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = 2 * N;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int st[N];
void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx;
idx++;
}
void dfs(int u){
st[u] = 1;
for(int i = u; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(!st[j]) dfs(j);
}
}
int main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));
return 0;
}
//vector存储
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
vector<int> v[N];
int st[N];
void add(int a, int b){
v[a].push_back(b);
v[b].push_back(a);
}
void dfs(int u){
st[u] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < v[u].size(); i++){
int j = v[u][i];
if(!st[j]) dfs(j);
}
}
int main(){
return 0;
}
树与图的深度优先遍历
树的重心


#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = 2 * N;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx;
int st[N];
int n, ans = 1e9;
void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx;
idx++;
}
int dfs(int u){
st[u] = 1;
//cnt存储以u为根的节点数(包括u),res是删除掉某个节点后的最大连通子图节点数
int cnt = 1, res = 0;
for(int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(!st[j]){
//以u为节点的单棵子树的节点数
int t = dfs(j);
//计算以j为根的树的节点数
cnt += t;
//记录最大连通子图节点数
res = max(res, t);
}
}
//以u为重心,最大的连通子图节点数
res = max(res, n - cnt);
ans = min(ans, res);
return cnt;
}
int main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));
cin>>n;
int a, b;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){
cin>>a>>b;
add(a, b);
add(b, a);
}
dfs(1);
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
树与图的宽度优先遍历
图中点的层次

#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = 2 * N;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx;
int q[N], d[N], hh, tt = -1;
int n, m;
void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx;
idx++;
}
void bfs(int u){
memset(d, -1, sizeof(d));
q[++tt] = u;
d[u] = 0;
while(hh <= tt){
//使用队头,弹出队头
int t = q[hh++];
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(d[j] == -1){
//更新距离
d[j] = d[t] + 1;
//入队
q[++tt] = j;
}
}
}
cout<<d[n];
}
int main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));
cin>>n>>m;
int x, y;
while(m--){
cin>>x>>y;
add(x, y);
}
bfs(1);
return 0;
}
拓扑排序
有向无环图也是拓扑图
入度:有多少条边指向自己
出度:有多少条边出去
有向图的拓扑序列

入度为0就是起点,出度为0就是终点
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int q[N], hh, tt = -1;
int n, m;
int r[N]; //存储入度
void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx;
idx++;
}
void bfs(){
//判断哪些点入度为0
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if(!r[i]) q[++tt] = i;
while(hh <= tt){
int t = q[hh++];
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
r[j]--;
if(!r[j]) q[++tt] = j;
}
}
if(tt == n - 1){
for(int i = 0; i <= tt; i++) cout<<q[i]<<" ";
}else cout<<-1;
}
int main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));
cin>>n>>m;
int x, y;
while(m--){
cin>>x>>y;
add(x, y);
r[y]++;
}
bfs();
return 0;
}
最短路
帮助理解
Dijkstra
Dijkstra求最短路 I

#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510;
int g[N][N], d[N], b[N];
int n, m;
void dijkstra(int u){
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d));
d[u] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int t = -1;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if(!b[j] && (t == -1 || d[t] > d[j])) t = j;
b[t] = 1;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
d[j] = min(d[j], d[t] + g[t][j]);
}
cout<<((d[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) ? -1 : d[n]);
}
int main(){
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof(g));
cin>>n>>m;
int x, y, z;
while(m--){
cin>>x>>y>>z;
g[x][y] = min(g[x][y], z);
}
dijkstra(1);
return 0;
}
Dijkstra求最短路 II
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], w[N], idx; //w[i]存储上个点到i的距离
int d[N], b[N];
int n, m;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> q; //小根堆,第一个元素存储距离,第二个元素存储下标
void add(int x, int y, int z){
e[idx] = y;
w[idx] = z;
ne[idx] = h[x];
h[x] = idx;
idx++;
}
void dijkstra(int u){
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d));
d[u] = 0;
q.push(make_pair(0, 1));
while(q.size()){
auto t = q.top();
q.pop();
int x = t.first, y = t.second;
if(b[y]) continue; //如果遍历过就退出
b[y] = 1;
for(int i = h[y]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(d[j] > x + w[i]){
d[j] = x + w[i];
q.push(make_pair(d[j], j));
}
}
}
cout<<(d[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : d[n]);
}
int main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));
cin>>n>>m;
int x, y, z;
while(m--){
cin>>x>>y>>z;
add(x, y, z);
}
dijkstra(1);
return 0;
}
增加点权,求有多少条最短路
题目链接
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int g[505][505], dis[505], st[505];
int a[505], paths[505], teams[505];
int n, m, c1, c2;
void dj(int u){
teams[u] = a[u];
paths[u] = 1;
dis[u] = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
int t = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(!st[i] && (t == -1 || dis[t] > dis[i])){
t = i;
}
}
st[t] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(dis[i] > dis[t] + g[t][i]){
dis[i] = dis[t] + g[t][i];
paths[i] = paths[t]; //继承路径条数
teams[i] = teams[t] + a[i]; //更新救援队人数
}else if(dis[i] == dis[t] + g[t][i]){
if(teams[i] < teams[t] + a[i]){
teams[i] = teams[t] + a[i]; //选救援队人数更多的
}
paths[i] += paths[t]; //累加路径条数
}
}
}
}
int main(){
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof(g));
cin>>n>>m>>c1>>c2;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin>>a[i];
while(m--){
int x, y, z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
g[x][y] = g[y][x] = min(g[x][y], z);
}
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
dj(c1);
cout<<paths[c2]<<" "<<teams[c2];
return 0;
}
增加边权,求花费最少
题目链接
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int g[505][505], dis[505], st[505];
int cost[505][505], c[505], pre[505];
vector<int> path;
int n, m, s, d;
void dj(int u){
dis[u] = 0;
c[u] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int t = -1;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(!st[j] && (t == -1 || dis[t] > dis[j])){
t = j;
}
}
st[t] = 1;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(dis[j] > dis[t] + g[t][j]){
pre[j] = t;
dis[j] = dis[t] + g[t][j];
c[j] = c[t] + cost[t][j];
}else if(dis[j] == dis[t] + g[t][j] && c[j] > c[t] + cost[t][j]){
pre[j] = t;
c[j] = c[t] + cost[t][j];
}
}
}
}
int main(){
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof(g));
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
memset(c, 0x3f, sizeof(c));
memset(cost, 0x3f, sizeof(cost));
cin>>n>>m>>s>>d;
while(m--){
int x, y, z, h;
cin>>x>>y>>z>>h;
g[x][y] = g[y][x] = min(g[x][y], z);
cost[x][y] = cost[y][x] = min(cost[x][y], h);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) pre[i] = i;
dj(s);
int q = d;
while(q != s){
path.push_back(q);
q = pre[q];
}
path.push_back(s);
int p = path.size();
for(int i = p - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout<<path[i]<<" ";
cout<<dis[d]<<" "<<c[d];
return 0;
}
bellman-ford
有边数限制的最短路
如果负环在1到n的路径上,那就不存在最短路
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510, M = 1e4 + 10;
int d[N], b[N]; //b数组备份
int n, m, k;
struct E{
int x, y, z;
}e[M];
void bellman_ford(int u){
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d));
d[u] = 0;
//最多k条边
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
//每次只更新一条串联路径,防止更新了多条串联路径
memcpy(b, d, sizeof(d));
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
int x = e[j].x, y = e[j].y, z = e[j].z;
d[y] = min(d[y], b[x] + z);
}
}
if(d[n] > 0x3f3f3f3f / 2) cout<<"impossible";
else cout<<d[n];
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m>>k;
int x, y, z;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin>>x>>y>>z;
e[i] = {x, y, z};
}
bellman_ford(1);
return 0;
}
spfa
spfa求最短路


#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], w[N], idx;
int dis[N], st[N];
int q[N], hh, tt = -1;
int n, m;
void add(int x, int y, int z){
e[idx] = y;
w[idx] = z;
ne[idx] = h[x];
h[x] = idx;
idx++;
}
void spfa(int u){
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
dis[u] = 0;
q[++tt] = u;
st[u] = 1;
while(hh <= tt){
int t = q[hh++];
//有环,所以可能一个点会遍历两次
st[t] = 0;
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(dis[j] > dis[t] + w[i]){
dis[j] = dis[t] + w[i];
if(!st[j]){
q[++tt] = j;
st[j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
if(dis[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) cout<<"impossible";
else cout<<dis[n];
}
int main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));
cin>>n>>m;
int x, y, z;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin>>x>>y>>z;
add(x, y, z);
}
spfa(1);
return 0;
}
spfa判断负环
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e3 + 10, M = 1e4 + 10;;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], w[M], idx;
int dis[N], st[N], cnt[N];
int q[N * N], hh, tt = -1; //有环的时候,一个元素可能会一直插入队列,所以要开N * N
int n, m;
void add(int x, int y, int z){
e[idx] = y;
w[idx] = z;
ne[idx] = h[x];
h[x] = idx;
idx++;
}
void spfa(){
//存在的负权回路,不一定从1开始
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
q[++tt] = i;
st[i] = 1;
}
while(hh <= tt){
int t = q[hh++];
//有环,所以可能一个点会遍历两次
st[t] = 0;
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(dis[j] > dis[t] + w[i]){
dis[j] = dis[t] + w[i];
cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1;
if(cnt[j] >= n){
cout<<"Yes";
return;
}
if(!st[j]){
q[++tt] = j;
st[j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
cout<<"No";
}
int main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));
cin>>n>>m;
int x, y, z;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin>>x>>y>>z;
add(x, y, z);
}
spfa();
return 0;
}
Floyd
Floyd求最短路
f(k, i, j) = f(k - 1, i, k) + f(k - 1, k, j);
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 210;
int f[N][N];
int n, m, k;
void floyd(){
for(int k = 1; k <= n; k++)
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[i][k] + f[k][j]);
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if(i == j) f[i][j] = 0;
else f[i][j] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int x, y, z;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
cin>>x>>y>>z;
f[x][y] = min(f[x][y], z);
}
floyd();
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++){
cin>>x>>y;
//可能存在负权边
if(f[x][y] > 0x3f3f3f3f / 2) cout<<"impossible"<<endl;
else cout<<f[x][y]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
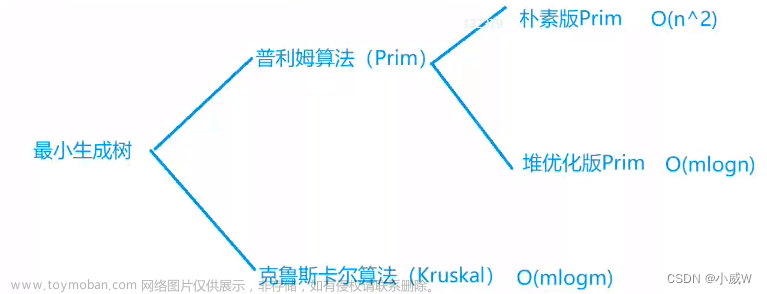
最小生成树
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-830367.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-830367.html
Prim
Kruskal
二分图
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-830367.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-830367.html
染色法判定二分图
匈牙利算法
到了这里,关于三、搜索与图论的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!