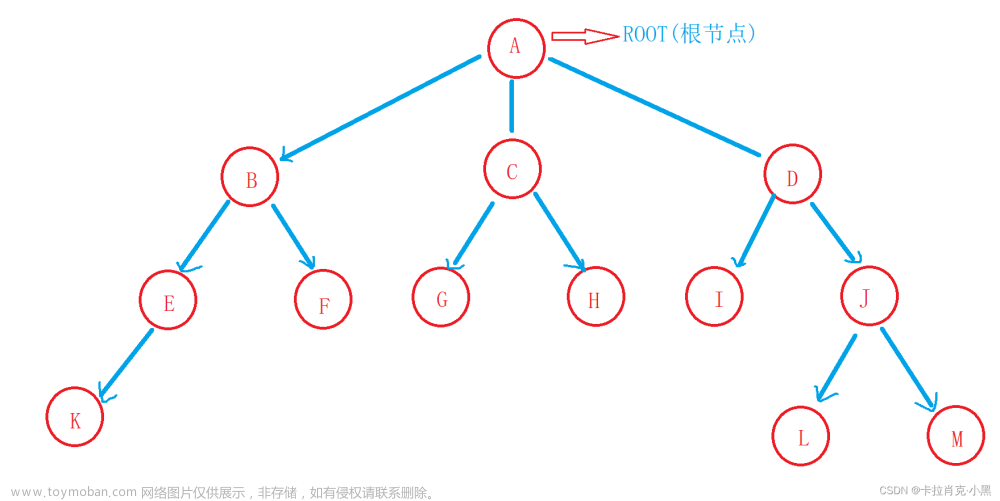
判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
思路:层次遍历,如果之前某个节点叶子节点为空,队列后续的所有节点的左右节点都不能非空,并且如果节点左节点为null但是右节点不为null该二叉树一定不是满二叉树
public static boolean isCBT1(Node head) {
// PC
if(head == null)
return true;
LinkedList<Node > queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean isLeaf = false;
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
Node cur = queue.poll();
Node left = cur.left;
Node right = cur.right;
if(
(isLeaf && (left != null || right != null)) || (left == null && right != null)
)
return false;
if(left != null ){
queue.add(left);
}
if(right != null){
queue.add(right);
}
if(left == null || right == null)
isLeaf = true;
}
return true;
}
思路2:使用递归方式,返回以当前节点为头结点的二叉树是否是满二叉树|完全二叉树以及返回当前树高度,调用方根据左右子树返回的信息判断当前树是否为完全二叉树
// 使用递归方式
public static boolean isCBT2(class13.Code01_IsCBT.Node head) {
if(head == null)
return true;
Info process = process(head);
return process.isc;
}
public static Info process(Node head){
if (head == null){
return new Info(true,true,0);
}
Info l = process(head.left);
Info r = process(head.right);
boolean isFull = l.isf && r.isf && l.height == r.height;
int height = Math.max(l.height,r.height)+1;
boolean isComplate = false;
if(l.height == r.height){
if((l.isf && r.isf)||(l.isf && r.isc)){
isComplate = true;
}
}else {
if(l.height == r.height+1){
if((r.isf && l.isf)||(r.isf && l.isc)){
isComplate = true;
}
}
}
return new Info(isComplate,isFull,height);
}
static class Info{
// 也包括满二叉树场景
private boolean isc;
private boolean isf;
private int height;
public Info(boolean isc,boolean isf,int height){
this.isc = isc;
this.isf = isf;
this.height = height;
}
}
题目:给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,和另外两个节点a和b。返回a和b的最低公共祖先
思路:先序遍历二叉树,过程中记录子节点的父节点,维护在Map类型参数中,然后求第一个相同的祖先
方法2:递归,返回当前节点左右子树是否包含指定节点,如果是直接返回否则根据返回内容处理
static class Info{
boolean finda;
boolean findb;
Node ans ;
public Info(boolean finda, boolean findb, Node ans) {
this.finda = finda;
this.findb = findb;
this.ans = ans;
}
}
public static Node lowestAncestor1(Node head, Node o1, Node o2) {
// PC
Info ans = process(head, o1, o2);
return ans.ans;
}
public static Info process(Node head, Node o1, Node o2){
if(head == null)
return new Info(false,false,null);
Info l = process(head.left,o1,o2);
Info r = process(head.right,o1,o2);
boolean finda = head == o1?true:l.finda||r.finda;
boolean findb = head == o2?true:r.findb||l.findb;
Node ans = null;
if(l.ans != null){
ans = l.ans;
}else if (r.ans != null){
ans = r.ans;
}else {
if(finda && findb){
ans = head;
}
}
return new Info(finda,findb,ans);
}
题目:派对的最大快乐值 公司的每个员工都符合 Employee 类的描述。整个公司的人员结构可以看作是一棵标准的、 没有环的多叉树。树的头节点是公司唯一的老板。除老板之外的每个员工都有唯一的直接上级。 叶节点是没有任何下属的基层员工(subordinates列表为空),除基层员工外,每个员工都有一个或多个直接下级。派对的最大快乐值这个公司现在要办party,你可以决定哪些员工来,哪些员工不来,规则:1.如果某个员工来了,那么这个员工的所有直接下级都不能来2.派对的整体快乐值是所有到场员工快乐值的累加3.你的目标是让派对的整体快乐值尽量大给定一棵多叉树的头节点boss,请返回派对的最大快乐值。
思路:递归实现
public static int maxHappy1(Employee boss) {
// PC
if(boss == null)
return 0;
return Math.max(process(boss,true),process(boss,false));
}
// cur 来到当前人员
// exist 直接领导是否来
// 返回最大快乐值
public static int process(Employee cur,boolean exist){
if(cur == null)
return 0;
// 当前人员选择不来 这种情况和上级领导来或者不来都不影响
int no = 0;
for (Employee next : cur.nexts) {
no += process(next,false);
}
int yes = 0;
// 上级领未来并且当前人员参加
if(!exist){
for (Employee next : cur.nexts) {
yes += process(next,true);
}
yes += cur.happy;
}
return Math.max(yes,no);
}
上面递归方式传递参数包含了上级是否参加信息,另外一种递归方式,返回当前人员参加或者不参加两种情况的最大值,由上级决定自己是否参加
static class Info {
private int no;
private int yes;
public Info(int no, int yes) {
this.no = no;
this.yes = yes;
}
}
public static int maxHappy2(Employee boss) {
if (boss == null)
return 0;
Info info = process2(boss);
return Math.max(info.yes, info.no);
}
// 返回当前人员参加或者不参加最大happy值
// 具体如何使用由上层决定
public static Info process2(Employee cur) {
if (cur == null)
return new Info(0, 0);
int yes = cur.happy;
int no = 0;
for (Employee next : cur.nexts) {
Info info = process2(next);
no += Math.max(info.no, info.yes);
yes += info.no;
}
return new Info(no, yes);
}
题目:判断二叉树是否是搜索二叉树
方法1:递归,左右子树返回是否递归相关信息,调用方法根据返回信息判断
public static boolean isBST1(Node head) {
if(head == null)
return true;
Info info = process(head);
return info.isSearch;
}
// 以当前节点为根节的二叉树,返回是否搜索二叉树信息
public static Info process(Node head){
Info left = null;
if(head.left != null){
left = process(head.left);
}
Info right = null;
if(head.right != null){
right = process(head.right);
}
int max = head.value;
int min = head.value;
if(left != null){
max = Math.max(max, left.max);
min = Math.min(min, left.min);
}
if(right != null){
max = Math.max(right.max,max);
min = Math.min(min, right.min);
}
boolean flag = true;
if(left != null && !left.isSearch)
flag = false;
if(right != null && !right.isSearch)
flag = false;
if(left != null && left.max >= head.value)
flag = false;
if(right!=null && right.min<= head.value){
flag = false;
}
return new Info(max,min,flag);
}
static class Info{
private int max;
private int min;
private boolean isSearch;
public Info(int max, int min, boolean isSearch) {
this.max = max;
this.min = min;
this.isSearch = isSearch;
}
}
方法2:利用二叉搜索树性质,先序遍历一定是递增序列
题目:给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,返回这颗二叉树是不是平衡二叉树
思路:递归方法
public static boolean isBalanced1(Node head) {
if(head == null)
return true;
Info ans = process(head);
return ans.isblance;
}
// 以当前节点为根节点的二叉树,返回该二叉树是否为平衡二叉树
public static Info process(Node head){
if(head == null)
return new Info(true,0);
Info l = process(head.left);
Info r = process(head.right);
boolean is = false;
// 不管左右子树是否为平衡二叉树 直接计算,调用方最终需要的不是高度而是 是否平衡
int height = Math.max(l.height,r.height)+1;
// process方法返回对象一定不为null
if(l.isblance && r.isblance && Math.abs(l.height-r.height)<=1){
is = true;
}
return new Info(is,height);
}
static class Info {
private boolean isblance;
private Integer height ;
public Info(boolean isblance, Integer height) {
this.isblance = isblance;
this.height = height;
}
}
题目:给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,返回这颗二叉树是不是满二叉树
思路:层次遍历上一层和当前层数量二倍关系,特殊情况最后一层遍历时候需要特殊处理
public static boolean isFull1(Node head) {
if(head == null)
return true;
// 层次遍历 判断上一层和当前层数量是否二倍关系
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
// 用于判断是否为最后一行
boolean allNull = true;
int pre = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < pre; i++) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
if(cur.left != null){
queue.add(cur.left);
allNull = false;
}
if(cur.right != null){
queue.add(cur.right);
allNull = false;
}
}
int nextlen = queue.size();
// 不是最后一行,name上一层和当前层节点数量一定是二倍关系
if(!allNull && nextlen != 2*pre){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
思路2:递归方法,返回左右子树是否为满二叉树
static class Info{
private boolean isFull;
private int height ;
public Info(boolean isFull, int height) {
this.isFull = isFull;
this.height = height;
}
}
public static boolean isFull2(Node head) {
if(head == null)
return true;
Info process = process(head);
return process.isFull;
}
public static Info process(Node head){
if(head == null){
return new Info(true,0);
}
Info l = process(head.left);
Info r = process(head.right);
boolean isFull = false;
int height = Math.max(l.height,r.height)+1;
if(l.isFull && r.isFull && l.height == r.height){
isFull = true;
}
return new Info(isFull,height);
}
题目:给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,返回这颗二叉树中最大的二叉搜索子树的大小
思路:递归返回子树作为根节点二叉搜索树信息、
public static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int value) {
val = value;
}
}
// 提交如下的代码,可以直接通过
public static int largestBSTSubtree(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
return process(head).maxBSTSubtreeSize;
}
public static class Info {
public int maxBSTSubtreeSize;
public int allSize;
public int max;
public int min;
public Info(int m, int a, int ma, int mi) {
maxBSTSubtreeSize = m;
allSize = a;
max = ma;
min = mi;
}
}
public static Info process(TreeNode x) {
if (x == null) {
return null;
}
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
int max = x.val;
int min = x.val;
int allSize = 1;
if (leftInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(leftInfo.max, max);
min = Math.min(leftInfo.min, min);
allSize += leftInfo.allSize;
}
if (rightInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(rightInfo.max, max);
min = Math.min(rightInfo.min, min);
allSize += rightInfo.allSize;
}
int p1 = -1;
if (leftInfo != null) {
p1 = leftInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize;
}
int p2 = -1;
if (rightInfo != null) {
p2 = rightInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize;
}
int p3 = -1;
boolean leftBST = leftInfo == null ? true : (leftInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize == leftInfo.allSize);
boolean rightBST = rightInfo == null ? true : (rightInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize == rightInfo.allSize);
if (leftBST && rightBST) {
boolean leftMaxLessX = leftInfo == null ? true : (leftInfo.max < x.val);
boolean rightMinMoreX = rightInfo == null ? true : (x.val < rightInfo.min);
if (leftMaxLessX && rightMinMoreX) {
int leftSize = leftInfo == null ? 0 : leftInfo.allSize;
int rightSize = rightInfo == null ? 0 : rightInfo.allSize;
p3 = leftSize + rightSize + 1;
}
}
return new Info(Math.max(p1, Math.max(p2, p3)), allSize, max, min);
}
题目:给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,任何两个节点之间都存在距离,
返回整棵二叉树的最大距离
思路:递归方法,最大宽度,要么经过当前节点,要么是左右子树任意一个最长路径
public static Info process(Node head){
if(head == null){
return null;
}
Info left = process(head.left);
Info right = process(head.right);
// 最大宽度经过当前head节点
int has = 1;
int maxwide = 0;
int depth = 0;
if(left != null){
has += left.maxdepth;
maxwide = Math.max(left.maxwide,maxwide);
depth = Math.max(depth,left.maxdepth);
}
if(right != null){
has += right.maxdepth;
maxwide = Math.max(right.maxwide,maxwide);
depth = Math.max(depth,right.maxdepth);
}
// 最大宽度要么经过当前节点,要么在左右任意子树
maxwide = Math.max(has,maxwide);
return new Info(depth+1,maxwide);
}
static class Info{
// 最大深度
private int maxdepth;
// 最大宽度
private int maxwide;
public Info(int maxdepth, int maxwide) {
this.maxdepth = maxdepth;
this.maxwide = maxwide;
}
}
问题:给定字符串数组,返回所有组合中字典排序最小的组合对应的字符串
思路:1 暴力方法,获取所有排列组合,然后取字典排序最小的
// process 拿到所有的排列租户,然后找到最小的一个并返回
public static String lowestString1(String[] strs) {
// PC
if (strs == null || strs.length <= 0) return "";
TreeSet<String> process = process(strs);
return process.size() == 0 ? "" : process.first();
}
// 返回当前数组 arrs 的所有组合
public static TreeSet<String> process(String[] arrs) {
TreeSet<String> ans = new TreeSet<>();
if (arrs == null || arrs.length <= 0) {
ans.add("");
return ans;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arrs.length; i++) {
String[] strings = removeIndex(arrs, i);
TreeSet<String> process = process(strings);
for (String string : process) {
ans.add(arrs[i] + string);
}
}
return ans;
}
public static String[] removeIndex(String[] arrs, int index) {
int N = arrs.length;
String[] ans = new String[N-1];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arrs.length; i++) {
if (i == index) continue;
ans[j++] = arrs[i];
}
return ans;
}
方法2 :贪心算法,维护优先队列,将目标字符串元素加入队列,最终的队列即使字典排序最小的组合。优先队列指定比较器文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-831472.html
public static String lowestString2(String[] strs) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) return "";
// 1 优先队列 将元素依次放入
Arrays.sort(strs,new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return (o1 + o2).compareTo(o2 + o1);
}
});
// 2 最终的队列就是结果
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String str : strs) {
sb.append(str);
}
return sb.toString();
}
需要注意的是:往队列塞入元素时候,如果在比较i位置元素时候就确定大小顺序,i之前的所有元素是不会进行比较的,所以这里存在一个问题,咋判断当前插入元素和i之前的元素组合就不是最小的。论证如下文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-831472.html
递推法
队列初始有两个字符串 a b 并且 ab 字典序小于 ba ,所以a排在b前面
当前字符串c需要进入队列,和b进行比较,字典序大于b所以排在b后面,
比较a 和 c的字典序
字符串ac可以转换为 N(a)*M(c)+N(c) K进制的数字, 其中M(c): Math.sqrt(K,c.length) N(a) 为字符串a对应的K进制数字
字符串ca可以转换为 N(c)*M(a)+N(a)
现在需要求 N(c)*M(a)+N(a) < N(a)*M(c)+N(c)
已知:
ab<ba
N(a)*M(b)+N(b) < N(b)*M(a)+N(a) 公式1
bc<cb
N(b)*M(c)+N(c) < N(c)*M(b)+N(b) 公式2
公式1 两边同时减去 N(b) 后同时乘 N(c) 因为数字不为负数所以不改变比较符号
N(a)*M(b)*N(c) < N(c)*N(b)*M(a) + N(a)*N(c) - N(b)*N(c) 公式3
公式2 两边同时减去 N(b) 后同时乘 N(a) 因为数字不为负数所以不改变比较符号
N(b)*M(c)*N(a) +N(c)*N(a)-N(b)*N(a) < N(c)*M(b)*N(a) 公式4
公式3 左边等于公式4右边 整理得
N(b)*M(c)*N(a) +N(c)*N(a)-N(b)*N(a) < N(c)*N(b)*M(a) + N(a)*N(c) - N(b)*N(c)
N(b)*M(c)*N(a)-N(b)*N(a) < N(c)*N(b)*M(a)- N(b)*N(c)
M(c)*N(a) -N(a) < N(c)*M(a) -N(c)
M(c)*N(a) +N(c) < N(c)*M(a) +N(a)
最终得
ac<ca
所以得到结论,ab<ba 并且 bc<cb 那么 ac 一定小于 ca
如果队列前面有n个已排序字符串 现在往里面塞 字符串 s,并且 arr[n-1]+s < s+arr[n-1]
那么可以得到 [0,n-1) 和字符串 s 存在这样的关系 Str(0,n-2)+s < s+ Str(0,n-2)
其中Str(0,n-2) 为[0,n-2] 范围任意长度字符串组合
最终得到结论,按照代码Comparator方式插入队列后,最终的队列就是字典序最小的组合
到了这里,关于算法-二叉树相关的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!