语言:Java/C++
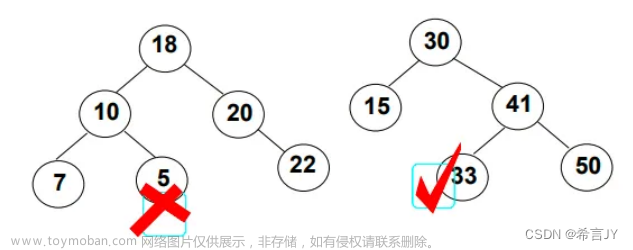
513.找树左下角的值
给定一个二叉树的 根节点
root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
输入: root = [2,1,3] 输出: 1示例 2:
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7] 输出: 7
递归法
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数必须有要遍历的树的根节点,额外使用一个变量来记录深度,不需要有返回值。设置一个全局变量result记录结果。
- 确定终止条件:当遇到叶子节点时,判断一下是否为最大深度,用叶子节点来更新最大深度。
- 确定单层递归逻辑:在找到最大深度时,递归过程依然需要回溯,因为若当前已经没有节点,需要返回到上一个节点继续找另一条路径进行遍历。
class Solution {
int maxDepth=-1;
int result;
void traversal(TreeNode node, int depth){
if(node.left==null && node.right==null){ //叶子节点
if(depth>maxDepth) {
maxDepth=depth;
result=node.val;
}
}
if(node.left!=null){
depth++;
traversal(node.left,depth);
depth--; //回溯
}
if(node.right!=null){
depth++;
traversal(node.right,depth);
depth--; //回溯
}
return;
}
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
traversal(root,0);
return result;
}
}112. 路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点root和一个表示目标和的整数targetSum。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和targetSum。如果存在,返回true;否则,返回false示例 1:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 输出:true 解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
- 递归函数的参数和返回值:本题需要进行判断是否存在满足条件的路径,所以函数类型为bool,参数有根节点和计数器count。主函数里count传入的是目标值减去根节点的值即target-root.val,因此搜索的过程是一个做减法的过程,如果到某一个叶子节点减去以后刚好count=0,则说明存在满足条件的路径。
- 终止条件:如果为叶子节点且count==0,则返回true,否则返回false
- 单层递归逻辑:即然前中后都可,用前序遍历,先用count减去当前节点的值,判断如果当前回溯的返回值为true,则继续返回true,回溯再把减去的当前值加回去。
class Solution {
boolean traversal(TreeNode node, int count){
if(node.left==null && node.right==null && count==0) return true;
if(node.left==null && node.right==null && count!=0) return false;
//左
if(node.left!=null){
count-=node.left.val;
if(traversal(node.left, count)) return true; //若之前判断有满足条件的,直接true
count+=node.left.val;
}
if(node.right!=null){
count-=node.right.val;
if(traversal(node.right, count)) return true; //若之前判断有满足条件的,直接true
count+=node.right.val;
}
return false;
}
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root==null) return false;
return traversal(root, targetSum-root.val);
}
}113.路径总和ii
和路径总和1不同的是这里让给出所有符合条件的路径,因此返回值发生了变化,不需要有返回值因为要遍历整个树,设置全局变量记录路径和结果。
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path =new LinkedList<>();
void traversal(TreeNode node, int count){
if(node.left==null && node.right == null && count==0){
//res.add(path);
res.add(new LinkedList<>(path));
return;
}
if(node.left==null && node.right == null && count!=0) return;
if(node.left!=null){
path.add(node.left.val);
count-=node.left.val;
traversal(node.left, count);
count+=node.left.val;
path.removeLast();
}
if(node.right!=null){
path.add(node.right.val);
count-=node.right.val;
traversal(node.right, count);
count+=node.right.val;
path.removeLast();
}
return;
}
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
res.clear();
path.clear();
if(root==null) return res;
path.add(root.val);
traversal(root, targetSum-root.val);
return res;
}
}path的引用,而不是新的路径。当修改
path时,之前添加到
res中的路径也会被修改,导致最终结果中出现重复的路径。因此需要在将
path添加到
res中时创建一个新的
path对象,而不是使用现有的
path对象。
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树。
注意: 你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
- 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
- 后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 返回如下的二叉树:
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-832349.html
- 递归函数的参数和返回值:不需要有返回值,参数则是后序和中序序列
- 终止条件:当前序列为空
- 单层递归逻辑:后序数组的最后一个元素,根据这个元素的值找到在中序数组的位置root_idx,将中序数组分为,左中序数组和右中序数组。计算左中序数组的个数,以此来确定后序数组中左后序数组的个数。将后序数组分为左后序和右后序。将后序数组中的最后一个元素去掉。
class Solution {
Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
return traversal(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder, 0, postorder.length);
}
public TreeNode traversal(int[] inorder, int inB, int inE, int[] postorder, int postB, int postE){
if(inB >= inE || postB >= postE) return null; //返回空树
map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i=0; i<inorder.length;i++){
map.put(inorder[i], i); //用map来存放中序数组的值和位置,以实现快速查找
}
int rootIdx=map.get(postorder[postE-1]); //在中序数组中查找后序的最后一个元素
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIdx]);
int lenofLeft=rootIdx-inB; //左中数组的个数
root.left=traversal(inorder, inB, rootIdx, postorder, postB, postB+lenofLeft); //保持左闭右开
root.right=traversal(inorder, rootIdx+1, inE, postorder, postB+lenofLeft, postE-1);
return root;
}
}前序和中序的思路和上面的基本一样,就是把取后序数组的最后一个元素换成取前序数组的第一个元素即可。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-832349.html
class Solution {
Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode traversal(int[] preorder,int preB, int preE, int[] inorder, int inB, int inE){
if(preE<=preB||inE<=inB) return null;
map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0; i<inorder.length;i++){
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
int rootIdx=map.get(preorder[preB]);
TreeNode root =new TreeNode(inorder[rootIdx]);
int lengthOfLeft=rootIdx-inB;
root.left=traversal(preorder, preB+1, lengthOfLeft+preB+1, inorder,inB, rootIdx);
root.right=traversal(preorder, lengthOfLeft+preB+1, preE, inorder, rootIdx+1, inE);
return root;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return traversal(preorder, 0, preorder.length, inorder, 0, inorder.length);
}
}到了这里,关于Leetcoder Day16| 二叉树 part05的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!