由于系统原因导致Flink作业无法正常运行的情况非常多,且很多时候都是无法避免的。对于Flink集群来讲,能够快速从异常状态中恢复,同时保证处理数据的正确性和一致性非常重要。Flink主要借助Checkpoint的方式保障整个系统状态数据的一致性,也就是基于ABS算法实现轻量级快照服务。
本节我们详细了解Checkpoint的设计与实现。
1. Checkpoint的整体设计
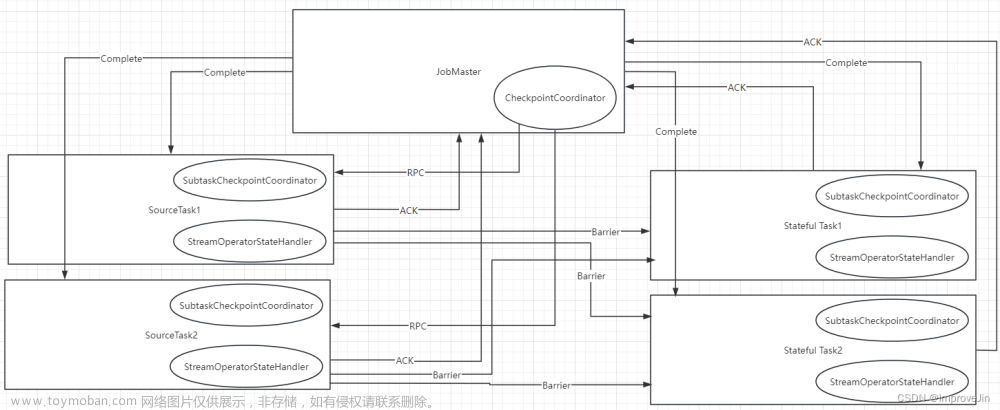
Checkpoint的执行过程分为三个阶段:启动、执行以及确认完成。其中Checkpoint的启动过程由JobManager管理节点中的CheckpointCoordinator组件控制,该组件会周期性地向数据源节点发送执行Checkpoint的请求,执行频率取决于用户配置的CheckpointInterval参数。
执行过程:
- 在JobManager管理节点通过CheckpointCoordinator组件向每个数据源节点发送Checkpoint执行请求,此时数据源节点中的算子会将
消费数据对应的Position发送到JobManager管理节点中。- JobManager节点会存储Checkpoint元数据,用于记录每次执行Checkpoint操作过程中算子的元数据信息,例如在FlinkKafkaConsumer中会记录消费Kafka主题的偏移量,用于确认从Kafka主题中读取数据的位置。
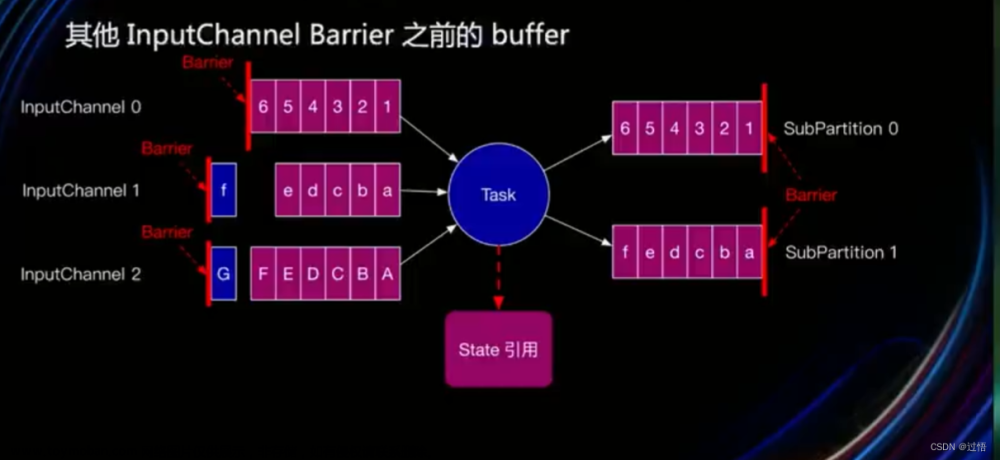
- 在数据源节点执行完Checkpoint操作后,继续向下游节点发送CheckpointBarrier事件,下游算子通过对齐Barrier事件,触发该算子的Checkpoint操作。
当下游的map算子接收到数据源节点的Checkpoint
Barrier事件后,首先对当前算子的数据进行处理,并等待其他上游数据源节点的Barrier事件到达。该过程就是Checkpoint
Barrier对齐,目的是确保属于同一Checkpoint的数据能够全部到达当前节点。

Barrier事件的作用就是切分不同Checkpoint批次的数据。
当map算子接收到所有上游的Barrier事件后,就会触发当前算子的Checkpoint操作,并将状态数据快照到指定的外部持久化介质中,该操作主要借助状态后端存储实现。
当状态数据执行完毕后,继续将Barrier事件发送至下游的算子,进行后续算子的Checkpoint操作。
另外,在map算子中执行完Checkpoint操作后,也会向JobManager管理节点发送Ack消息,确认当前算子的Checkpoint操作正常执行。此时Checkpoint数据会存储该算子对应的状态数据,如果StateBackend为MemoryStateBackend,则主要会将状态数据存储在JobManager的堆内存中。
sink节点的ack
像map算子节点一样,当Barrier事件到达sink类型的节点后,sink节点也会进行Barrier对齐操作,确认上游节点的数据全部接入。然后对接入的数据进行处理,将结果输出到外部系统中。完成以上步骤后,sink节点会向JobManager管理节点发送Ack确认消息,确认当前Checkpoint中的状态数据都正常进行了持久化操作。(之后呢?当任务结束之后,cp会消失还是?)
2. Checkpoint创建源码解析
通过调用StreamExecutionEnvironment.enableCheckpointing(),开启Checkpoint。
此时Checkpoint的配置会被存储在StreamGraph中,然后将StreamGraph中的CheckpointConfig转换为JobCheckpointingSettings数据结构存储在JobGraph对象中,并伴随JobGraph提交到集群运行。启动JobMaster服务后,JobMaster调度和执行Checkpoint操作。
2.1. DefaultExecutionGraphBuilder.buildGraph
如下代码,通过JobGraph构建ExecutionGraph的过程中,获取JobGraph中存储的JobCheckpointingSettings配置,然后创建ExecutionGraph。
1)根据snapshotSettings配置获取triggerVertices、ackVertices以及confirmVertices节点集合,并转换为对应的ExecutionJobVertex集合。
- 其中triggerVertices集合存储了所有SourceOperator节点,这些节点通过CheckpointCoordinator主动触发Checkpoint操作。
- ackVertices和confirmVertices集合存储了StreamGraph中的全部节点,代表所有节点都需要返回Ack确认信息并确认Checkpoint执行成功。
2)创建CompletedCheckpointStore组件,用于存储Checkpoint过程中的元数据。
- 当对作业进行恢复操作时会在CompletedCheckpointStore中检索最新完成的Checkpoint元数据信息,然后基于元数据信息恢复Checkpoint中存储的状态数据。CompletedCheckpointStore有两种实现,分别为StandaloneCompletedCheckpointStore和ZooKeeperCompletedCheckpointStore。
- 在CompletedCheckpointStore中通过maxNumberOfCheckpointsToRetain参数配置以及结合checkpointIdCounter计数器保证只会存储固定数量的CompletedCheckpoint。
3)创建CheckpointStatsTracker实例
用于监控和追踪Checkpoint执行和更新的情况,包括Checkpoint执行的统计信息以及执行状况,WebUI中显示的Checkpoint监控数据主要来自CheckpointStatsTracker。4)创建StateBackend,从UserClassLoader中反序列化出应用指定的StateBackend并设定为applicationConfiguredBackend。
5)初始化用户自定义的Checkpoint Hook函数
6)最终调用executionGraph.enableCheckpointing()方法,在作业的执行和调度过程中开启Checkpoint。
// 配置状态数据checkpointing
// 从jobGraph中获取JobCheckpointingSettings
JobCheckpointingSettings snapshotSettings = jobGraph.getCheckpointingSettings();
//如果snapshotSettings不为空,则开启checkpoint功能
if (snapshotSettings != null) {
List<ExecutionJobVertex> triggerVertices =
idToVertex(snapshotSettings.getVerticesToTrigger(), executionGraph);
List<ExecutionJobVertex> ackVertices =
idToVertex(snapshotSettings.getVerticesToAcknowledge(), executionGraph);
List<ExecutionJobVertex> confirmVertices =
idToVertex(snapshotSettings.getVerticesToConfirm(), executionGraph);
//创建CompletedCheckpointStore
CompletedCheckpointStore completedCheckpoints;
CheckpointIDCounter checkpointIdCounter;
try {
int maxNumberOfCheckpointsToRetain = jobManagerConfig.getInteger(
CheckpointingOptions.MAX_RETAINED_CHECKPOINTS);
if (maxNumberOfCheckpointsToRetain <= 0) {
maxNumberOfCheckpointsToRetain = CheckpointingOptions.MAX_RETAINED_
CHECKPOINTS.defaultValue();
}
// 通过recoveryFactory创建CheckpointStore
completedCheckpoints = recoveryFactory.createCheckpointStore(jobId,
maxNumberOfCheckpointsToRetain, classLoader);
// 通过recoveryFactory创建CheckpointIDCounter
checkpointIdCounter = recoveryFactory.createCheckpointIDCounter(jobId);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(jobId, "Failed to initialize high-
availability checkpoint handler", e);
}
// 获取checkpoints最长的记录次数
int historySize = jobManagerConfig.getInteger(WebOptions.CHECKPOINTS_HISTORY_SIZE);
// 创建CheckpointStatsTracker实例
CheckpointStatsTracker checkpointStatsTracker = new CheckpointStatsTracker(
historySize,
ackVertices,
snapshotSettings.getCheckpointCoordinatorConfiguration(),
metrics);
// 从application中获取StateBackend
final StateBackend applicationConfiguredBackend;
final SerializedValue<StateBackend> serializedAppConfigured =
snapshotSettings.getDefaultStateBackend();
if (serializedAppConfigured == null) {
applicationConfiguredBackend = null;
}
else {
try {
applicationConfiguredBackend = serializedAppConfigured.
deserializeValue(classLoader);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(jobId,
"Could not deserialize application-defined state backend.", e);
}
}
// 获取最终的rootBackend
final StateBackend rootBackend;
try {
rootBackend = StateBackendLoader.fromApplicationOrConfigOrDefault(
applicationConfiguredBackend, jobManagerConfig, classLoader, log);
}
catch (IllegalConfigurationException | IOException |
DynamicCodeLoadingException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(jobId,
"Could not instantiate configured state backend", e);
}
// 初始化用户自定义的checkpoint Hooks函数
final SerializedValue<MasterTriggerRestoreHook.Factory[]> serializedHooks =
snapshotSettings.getMasterHooks();
final List<MasterTriggerRestoreHook<?>> hooks;
// 如果serializedHooks为空,则hooks为空
if (serializedHooks == null) {
hooks = Collections.emptyList();
}
else {
// 加载MasterTriggerRestoreHook
final MasterTriggerRestoreHook.Factory[] hookFactories;
try {
hookFactories = serializedHooks.deserializeValue(classLoader);
}
catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(jobId,
"Could not instantiate user-defined checkpoint hooks", e);
}
// 设定ClassLoader为UserClassLoader
final Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
final ClassLoader originalClassLoader = thread.getContextClassLoader();
thread.setContextClassLoader(classLoader);
// 创建hooks函数
try {
hooks = new ArrayList<>(hookFactories.length);
for (MasterTriggerRestoreHook.Factory factory : hookFactories) {
hooks.add(MasterHooks.wrapHook(factory.create(), classLoader));
}
}
// 将thread的ContextClassLoader设定为originalClassLoader
finally {
thread.setContextClassLoader(originalClassLoader);
}
}
// 获取CheckpointCoordinatorConfiguration
final CheckpointCoordinatorConfiguration chkConfig =
snapshotSettings.getCheckpointCoordinatorConfiguration();
// 开启executionGraph中的Checkpoint功能
executionGraph.enableCheckpointing(
chkConfig,
triggerVertices,
ackVertices,
confirmVertices,
hooks,
checkpointIdCounter,
completedCheckpoints,
rootBackend,
checkpointStatsTracker);
}
2.2. ExecutionGraph.enableCheckpointing
继续看ExecutionGraph.enableCheckpointing()方法的实现,包含如下逻辑。
- 将tasksToTrigger、tasksToWaitFor以及tasksToCommitTo三个ExecutionJobVertex集合转换为ExecutionVertex[]数组,每个ExecutionVertex代表ExecutionJobVertex中的一个SubTask节点。
- 容错管理:创建CheckpointFailureManager,用于Checkpoint执行过程中的
容错管理,包含failJob和failJobDueToTaskFailure两个处理方法。- 定时调度和执行:创建checkpointCoordinatorTimer,用于Checkpoint异步线程的定时调度和执行。
- 协调和管理作业中的Checkpoint:创建CheckpointCoordinator组件,通过CheckpointCoordinator协调和管理作业中的Checkpoint,同时收集各Task节点中Checkpoint的执行状况等信息。
- Hook:将Master Hook注册到CheckpointCoordinator中,实现用户自定义Hook代码的调用。
- 控制CheckpointCoordinator的启停:将JobStatusListener的实现类CheckpointCoordinatorDeActivator注册到JobManager中,此时系统会根据作业的运行状态控制CheckpointCoordinator的启停,当作业的状态为Running时会触发启动CheckpointCoordinator组件。
public void enableCheckpointing(
CheckpointCoordinatorConfiguration chkConfig,
List<ExecutionJobVertex> verticesToTrigger,
List<ExecutionJobVertex> verticesToWaitFor,
List<ExecutionJobVertex> verticesToCommitTo,
List<MasterTriggerRestoreHook<?>> masterHooks,
CheckpointIDCounter checkpointIDCounter,
CompletedCheckpointStore checkpointStore,
StateBackend checkpointStateBackend,
CheckpointStatsTracker statsTracker) {
checkState(state == JobStatus.CREATED, "Job must be in CREATED state");
checkState(checkpointCoordinator == null, "checkpointing already enabled");
ExecutionVertex[] tasksToTrigger = collectExecutionVertices(verticesToTrigger);
ExecutionVertex[] tasksToWaitFor = collectExecutionVertices(verticesToWaitFor);
ExecutionVertex[] tasksToCommitTo = collectExecutionVertices(verticesToCommitTo);
checkpointStatsTracker = checkNotNull(statsTracker, "CheckpointStatsTracker");
// 创建CheckpointFailureManager
CheckpointFailureManager failureManager = new CheckpointFailureManager(
chkConfig.getTolerableCheckpointFailureNumber(),
new CheckpointFailureManager.FailJobCallback() {
@Override
public void failJob(Throwable cause) {
getJobMasterMainThreadExecutor().execute(() -> failGlobal(cause));
}
@Override
public void failJobDueToTaskFailure(Throwable cause,
ExecutionAttemptID failingTask) {
getJobMasterMainThreadExecutor()
.execute(() -> failGlobalIfExecutionIsStillRunning(cause,
failingTask));
}
}
);
// 创建checkpointCoordinatorTimer
checkState(checkpointCoordinatorTimer == null);
checkpointCoordinatorTimer = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(
new DispatcherThreadFactory(
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(), "Checkpoint Timer"));
// 创建checkpointCoordinator
checkpointCoordinator = new CheckpointCoordinator(
jobInformation.getJobId(),
chkConfig,
tasksToTrigger,
tasksToWaitFor,
tasksToCommitTo,
checkpointIDCounter,
checkpointStore,
checkpointStateBackend,
ioExecutor,
new ScheduledExecutorServiceAdapter(checkpointCoordinatorTimer),
SharedStateRegistry.DEFAULT_FACTORY,
failureManager);
// 向checkpoint Coordinator中注册master Hooks
for (MasterTriggerRestoreHook<?> hook : masterHooks) {
if (!checkpointCoordinator.addMasterHook(hook)) {
LOG.warn("Trying to register multiple checkpoint hooks with the name: {}",
hook.getIdentifier());
}
}
//向checkpointCoordinator中设定checkpointStatsTracker
checkpointCoordinator.setCheckpointStatsTracker(checkpointStatsTracker);
// 注册JobStatusListener,用于自动启动CheckpointCoordinator
if (chkConfig.getCheckpointInterval() != Long.MAX_VALUE) {
registerJobStatusListener(checkpointCoordinator.
createActivatorDeactivator());
}
this.stateBackendName = checkpointStateBackend.getClass().getSimpleName();
}
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-833463.html
参考:《Flink设计与实现:核心原理与源码解析》–张利兵文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-833463.html
到了这里,关于【Flink状态管理五】Checkpoint的设计与实现的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!