目录
一、写在前面
二、本文内容
三、开发环境
四、代码实现
4.1引入所需包
4.2 定义一个类并初始化
4.3 定义绘制一界面并实现音量控制的主方法
五、看一看实际效果吧
六、完整代码
七、小结
八、感谢
一、写在前面
本文所用例子为个人学习的小结,如有不足之处请各位多多海涵,欢迎小伙伴一起学习进步,如果想法可在评论区指出,我会尽快回复您,不胜感激!
所公布代码或截图均为运行成功后展示。
嘿嘿,小小免责声明一下!部分代码可能与其他网络例子相似,如原作者看到有不满,请联系我修改,感谢理解与支持!
本次代码基于下方链接的小伙伴的代码,进行学习后并改造了部分代码,十分感谢“四冠王”Faker:是Dream呀
OpenCV实现手势音量控制_opencv 修改响度-CSDN博客
二、本文内容
通过使用OpenCV和Mediapipe提供的库,通过摄像头捕捉并检测手的关键帧,描绘骨骼和手部特征点,并通过改变大拇指与食指间的距离,改变系统音量的大小,实现在线打碟(苏喂~苏喂~)
三、开发环境
1.Python 3.9
2.OpenCV
3.Mediapipe:https://developers.google.com/mediapipe/solutions/vision/hand_landmarker
4.comtypes
5.numpy
IDE:
1.Pycharm
四、代码实现
4.1引入所需包
引入后报红,则说明缺少对应module,可以通过pip install xx解决,如果pip install失败,可以尝试更换镜像源
#更换为豆瓣的镜像源
pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.douban.com/simple
import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
from ctypes import cast, POINTER
from comtypes import CLSCTX_ALL
from mediapipe.python.solutions.drawing_utils import DrawingSpec
from pycaw.pycaw import AudioUtilities, IAudioEndpointVolume
import time
import math
import numpy as np4.2 定义一个类并初始化
初始化mediapipe的一些属性,并获取系统音量控制器及音量范围。
class HandControlVolume:
def __init__(self):
# 初始化medialpipe
self.mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
self.mp_drawing_styles = mp.solutions.drawing_styles
self.mp_hands = mp.solutions.hands
# 获取电脑音量范围
devices = AudioUtilities.GetSpeakers()
interface = devices.Activate(
IAudioEndpointVolume._iid_, CLSCTX_ALL, None)
self.volume = cast(interface, POINTER(IAudioEndpointVolume))
self.volume.SetMute(0, None)
self.volume_range = self.volume.GetVolumeRange()4.3 定义绘制一界面并实现音量控制的主方法
4.3.1 获取摄像头的视频流
# 主函数
def recognize(self):
# 计算刷新率
fpsTime = time.time()
# OpenCV读取视频流
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0,cv2.CAP_DSHOW)
# 视频分辨率
resize_w = 1280
resize_h = 960
# 画面显示初始化参数
rect_height = 0
rect_percent_text = 04.3.2 调用手势识别的模型,并设定最小检测可信度、最小追踪可信度、最大数量的时候等数据
并在界面上绘制一个音量框的基础
# 识别手的模型,可信度标注
with self.mp_hands.Hands(min_detection_confidence=0.7, # 最小检测可信度
min_tracking_confidence=0.5, # 最小追踪可信度
max_num_hands=2) as hands: # 最大数量的手
while cap.isOpened():
# 读取帧
success, image = cap.read()
# 如果读取到空帧,继续循环
if not success:
print("空帧.")
continue
# 重置该图片的大小
image = cv2.resize(image, (resize_w, resize_h))
# 摄像头拍摄为镜像画面,再翻转过来
image = cv2.flip(image, 1)
# mediapipe模型处理
results = hands.process(image)
# 音量框左上角和右下角坐标
vol_box_point1_x = 30
vol_box_point1_y = 100
vol_box_point2_x = 70
vol_box_point2_y = 300
image = cv2.rectangle(image, (vol_box_point1_x, vol_box_point1_y), (vol_box_point2_x, vol_box_point2_y),
(191, 255, 0), 1)4.3.3 通过mediapipe的 results.multi_hand_landmarks值来判断画面中是否有手掌,如果有手掌循环获取每个手掌。
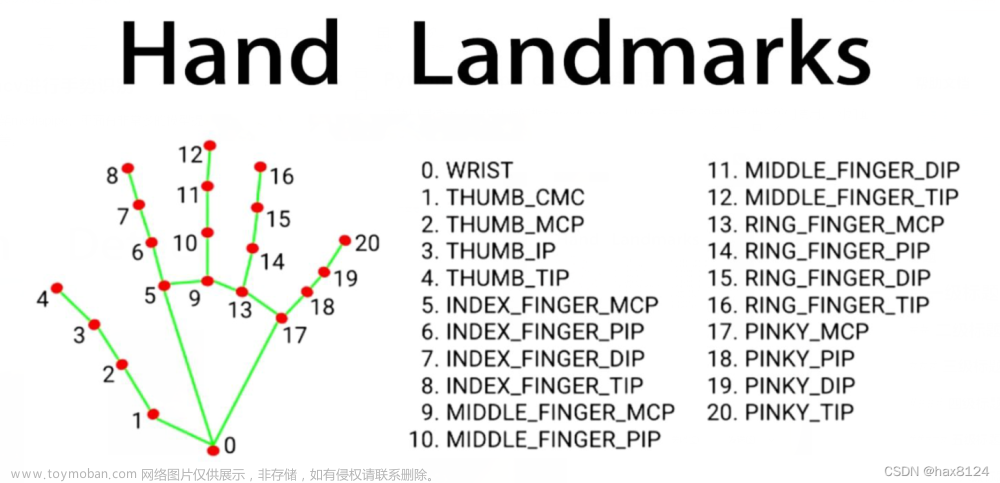
hand_connections_style = self.mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_connections_style()为获取mediapipe的手部连线的默认样式,此处我们可以进行自定义,改变各处连线的不同样式
此处先引入一张图:
![[ Python+OpenCV+Mediapipe ] 实现手势控制音量,小紧张的Python学习之路,python,opencv,开发语言,计算机视觉,机器学习,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/836149-1.png)
这是Mediapipe官方给出的手掌模型图,代码中if判断key的部分就是和上面这些值进行比较,从而改变对应样式。
官方API中手掌连线和手指关键点的样式均由Tuple[int ,int] 和DrawingSpec组成传参。
Tuple[int ,int]:在手掌连线中为 (0,1)等连线的值,在手掌关键点中为HandLandmark.WRIST等枚举值
![[ Python+OpenCV+Mediapipe ] 实现手势控制音量,小紧张的Python学习之路,python,opencv,开发语言,计算机视觉,机器学习,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/836149-2.png)
DrawingSpec(self.color, self.thickness, self.circle_radius):在API中为样式设定,
color为颜色,thickness为厚度,radius为半径
![[ Python+OpenCV+Mediapipe ] 实现手势控制音量,小紧张的Python学习之路,python,opencv,开发语言,计算机视觉,机器学习,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/836149-3.png)
好了,回到代码,此处是手掌连线的样式设定,我把每一部分连线分成了不同的颜色,并设定了thickness为2官方默认值就是2
# 判断是否有手掌
if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 遍历每个手掌
for hand_landmarks in results.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 首先,获取默认的手部连线样式
hand_connections_style = self.mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_connections_style()
hand_connections_style_m = {}
'''
connection_style未使用,
可以使用默认值:
connection_style.color,颜色
connection_style.thickness,厚度
connection_style.circle_radius
'''
for key, connection_style in hand_connections_style.items():
self.color = (255, 255, 255)
self.thickness = 2
self.circle_radius = 0
print(key)
# key值请查看手掌标示图
if key == (0, 1) or key == (0, 5) or key == (0, 17) or key == (5, 9) or key == (
9, 13) or key == (13, 17):
self.color = (0, 255, 255)
elif key == (1, 2) or key == (2, 3) or key == (3, 4):
self.color = (255, 0, 255)
elif key == (5, 6) or key == (6, 7) or key == (7, 8):
self.color = (255, 255, 0)
elif key == (9, 10) or key == (10, 11) or key == (11, 12):
self.color = (125, 125, 125)
elif key == (13, 14) or key == (14, 15) or key == (15, 16):
self.color = (0, 125, 125)
elif key == (17, 18) or key == (18, 19) or key == (19, 20):
self.color = (125, 0, 125)
hand_connections_style_m[key] = DrawingSpec(self.color, self.thickness, self.circle_radius)手掌关键点检测也是同理,获取默认值,传入新值以改变原有样式,此处{0, 1, 5, 9, 13, 17}为手掌关键点的枚举值,我不想拷贝那么多值就用了数字代替,严谨一点可以用HandLandmark.WRIST等
# 手指手掌关键点的绘制
hand_landmarks_style = self.mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_landmarks_style()
hand_landmarks_style_m = {}
for key, landmarks_style in hand_landmarks_style.items():
self.color = (255, 255, 255)
self.thickness = 2
self.circle_radius = 2
print(key, ':', int(key))
# key值请查看手掌标示图
if key in {0, 1, 5, 9, 13, 17}:
self.color = (0, 255, 255)
elif key in {2, 3, 4}:
self.color = (255, 0, 255)
elif key in {6, 7, 8}:
self.color = (255, 255, 0)
elif key in {10, 11, 12}:
self.color = (125, 125, 125)
elif key in {14, 15, 16}:
self.color = (0, 125, 125)
elif key in {18, 19, 20}:
self.color = (125, 0, 125)
hand_landmarks_style_m[key] = DrawingSpec(self.color, self.thickness, self.circle_radius)
# 在画面标注手指
self.mp_drawing.draw_landmarks(
image,
hand_landmarks,
self.mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS,
hand_landmarks_style_m,
hand_connections_style_m)4.3.4 将自定义的值传入绘制的方法
# 在画面标注手指
self.mp_drawing.draw_landmarks(
image,
hand_landmarks,
self.mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS,
hand_landmarks_style_m,
hand_connections_style_m)4.3.5 解析大拇指和食指,获取手指间的距离
根据两指的画面中坐标,先将两指间用线连起来,再计算中间点的坐标并绘制圆点
# 解析手指,存入各个手指坐标
landmark_list = []
for landmark_id, finger_axis in enumerate(hand_landmarks.landmark):
landmark_list.append([
landmark_id, finger_axis.x, finger_axis.y,
finger_axis.z
])
if landmark_list:
# 获取大拇指指尖坐标
thumb_finger_tip = landmark_list[4]
thumb_finger_tip_x = math.ceil(thumb_finger_tip[1] * resize_w)
thumb_finger_tip_y = math.ceil(thumb_finger_tip[2] * resize_h)
# 获取食指指尖坐标
index_finger_tip = landmark_list[8]
index_finger_tip_x = math.ceil(index_finger_tip[1] * resize_w)
index_finger_tip_y = math.ceil(index_finger_tip[2] * resize_h)
# 两指中间点, 画线坐标只能取整数
finger_middle_point = (thumb_finger_tip_x + index_finger_tip_x) // 2, (
thumb_finger_tip_y + index_finger_tip_y) // 2
# 大拇指坐标
thumb_finger_point = (thumb_finger_tip_x, thumb_finger_tip_y)
# 食指坐标
index_finger_point = (index_finger_tip_x, index_finger_tip_y)
# 画2点连线
image = cv2.line(image, thumb_finger_point, index_finger_point, (255, 0, 255), 2)
# args: 图片资源,手指中间点,半径,颜色,厚度
image = cv2.circle(image, finger_middle_point, 2, (255, 255, 0), 2)
4.3.6 根据勾股定理计算出两指间绘制线的长度,并设定当线小于50时认为是最小音量,当线大于300时设定为最大音量。
根据绘制线的长度,调用np.interp方法(numpy真的强大~),得出类比值。
# 勾股定理计算长度
line_len = math.hypot((index_finger_tip_x - thumb_finger_tip_x),
(index_finger_tip_y - thumb_finger_tip_y))
# 获取电脑最大最小音量
min_volume = self.volume_range[0]
max_volume = self.volume_range[1]
line_min = 50
line_max = 300
# 将指尖长度映射到音量上
# 50 - 300,可以根据需要设定的长度更改,为设定的线段最大和最小值,少于50则认为是最小值,大于300认为是最大值
'''
np.interp(x,xp,fp) 将x在xp中计算百分比,再在fp中求相应的值
先在xp中求百分比 xp_p, xp_p = (x-xp_min)/(xp_max-xp_min)
再用xp在fp中求值 f_value = xp_p * (fp_max - fp_min) + fp_min
'''
vol = np.interp(line_len, [line_min, line_max], [min_volume, max_volume])
rect_height = np.interp(line_len, [line_min, line_max],
[0, vol_box_point2_y - vol_box_point1_y])
# [0,100]是百分比
rect_percent_text = np.interp(line_len, [line_min, line_max], [0, 100])
print('vol: ', vol, 'rect_height', rect_height, 'rect_percent_text', rect_percent_text)
# 设置电脑音量
self.volume.SetMasterVolumeLevel(vol, None)4.3.7 绘制实际音量的矩形填充框,并计算FPS显示在界面上,调用cv2.imshow显示窗体
# 显示矩形
cv2.putText(image, str(math.ceil(rect_percent_text)) + "%", (10, 350),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (191, 255, 0), 3)
image = cv2.rectangle(image, (vol_box_point1_x, math.ceil(vol_box_point2_y - rect_height)),
(vol_box_point2_x, vol_box_point2_y), (191, 255, 0), -1)
# 显示刷新率FPS
cTime = time.time()
fps_text = 1 / (cTime - fpsTime)
fpsTime = cTime
cv2.putText(image, "FPS: " + str(int(fps_text)), (10, 70),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (191, 255, 0), 3)
# 显示画面
cv2.imshow('mediapipe', image)4.3.8 按下‘q’退出循环
# 按下'q'键退出循环
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break全部代码会在最后奉上哦~
五、看一看实际效果吧
通过捏合打开拇指和食指,控制音量的变化,不过100%音量请小心!!!耳朵差点聋了!
另外,如果开了一首很嗨的歌曲可以实现快乐DJ,在线打碟的乐趣!
![[ Python+OpenCV+Mediapipe ] 实现手势控制音量,小紧张的Python学习之路,python,opencv,开发语言,计算机视觉,机器学习,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/836149-4.jpeg)
![[ Python+OpenCV+Mediapipe ] 实现手势控制音量,小紧张的Python学习之路,python,opencv,开发语言,计算机视觉,机器学习,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/836149-5.jpeg)
![[ Python+OpenCV+Mediapipe ] 实现手势控制音量,小紧张的Python学习之路,python,opencv,开发语言,计算机视觉,机器学习,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/836149-6.jpeg)
六、完整代码
import cv2
import mediapipe as mp
from ctypes import cast, POINTER
from comtypes import CLSCTX_ALL
from mediapipe.python.solutions.drawing_utils import DrawingSpec
from pycaw.pycaw import AudioUtilities, IAudioEndpointVolume
import time
import math
import numpy as np
class HandControlVolume:
def __init__(self):
# 初始化medialpipe
self.mp_drawing = mp.solutions.drawing_utils
self.mp_drawing_styles = mp.solutions.drawing_styles
self.mp_hands = mp.solutions.hands
# 获取电脑音量范围
devices = AudioUtilities.GetSpeakers()
interface = devices.Activate(
IAudioEndpointVolume._iid_, CLSCTX_ALL, None)
self.volume = cast(interface, POINTER(IAudioEndpointVolume))
self.volume.SetMute(0, None)
self.volume_range = self.volume.GetVolumeRange()
# 主函数
def recognize(self):
# 计算刷新率
fpsTime = time.time()
# OpenCV读取视频流
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0,cv2.CAP_DSHOW)
# 视频分辨率
resize_w = 1280
resize_h = 960
# 画面显示初始化参数
rect_height = 0
rect_percent_text = 0
# 识别手的模型,可信度标注
with self.mp_hands.Hands(min_detection_confidence=0.7, # 最小检测可信度
min_tracking_confidence=0.5, # 最小追踪可信度
max_num_hands=2) as hands: # 最大数量的手
while cap.isOpened():
# 读取帧
success, image = cap.read()
# 如果读取到空帧,继续循环
if not success:
print("空帧.")
continue
# 重置该图片的大小
image = cv2.resize(image, (resize_w, resize_h))
# 摄像头拍摄为镜像画面,再翻转过来
image = cv2.flip(image, 1)
# mediapipe模型处理
results = hands.process(image)
# 音量框左上角和右下角坐标
vol_box_point1_x = 30
vol_box_point1_y = 100
vol_box_point2_x = 70
vol_box_point2_y = 300
image = cv2.rectangle(image, (vol_box_point1_x, vol_box_point1_y), (vol_box_point2_x, vol_box_point2_y),
(191, 255, 0), 1)
# 判断是否有手掌
if results.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 遍历每个手掌
for hand_landmarks in results.multi_hand_landmarks:
# 首先,获取默认的手部连线样式
hand_connections_style = self.mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_connections_style()
hand_connections_style_m = {}
'''
connection_style未使用,
可以使用默认值:
connection_style.color,颜色
connection_style.thickness,厚度
connection_style.circle_radius
'''
for key, connection_style in hand_connections_style.items():
self.color = (255, 255, 255)
self.thickness = 2
self.circle_radius = 0
print(key)
# key值请查看手掌标示图
if key == (0, 1) or key == (0, 5) or key == (0, 17) or key == (5, 9) or key == (
9, 13) or key == (13, 17):
self.color = (0, 255, 255)
elif key == (1, 2) or key == (2, 3) or key == (3, 4):
self.color = (255, 0, 255)
elif key == (5, 6) or key == (6, 7) or key == (7, 8):
self.color = (255, 255, 0)
elif key == (9, 10) or key == (10, 11) or key == (11, 12):
self.color = (125, 125, 125)
elif key == (13, 14) or key == (14, 15) or key == (15, 16):
self.color = (0, 125, 125)
elif key == (17, 18) or key == (18, 19) or key == (19, 20):
self.color = (125, 0, 125)
hand_connections_style_m[key] = DrawingSpec(self.color, self.thickness, self.circle_radius)
# 手指手掌关键点的绘制
hand_landmarks_style = self.mp_drawing_styles.get_default_hand_landmarks_style()
hand_landmarks_style_m = {}
for key, landmarks_style in hand_landmarks_style.items():
self.color = (255, 255, 255)
self.thickness = 2
self.circle_radius = 2
print(key, ':', int(key))
# key值请查看手掌标示图
if key in {0, 1, 5, 9, 13, 17}:
self.color = (0, 255, 255)
elif key in {2, 3, 4}:
self.color = (255, 0, 255)
elif key in {6, 7, 8}:
self.color = (255, 255, 0)
elif key in {10, 11, 12}:
self.color = (125, 125, 125)
elif key in {14, 15, 16}:
self.color = (0, 125, 125)
elif key in {18, 19, 20}:
self.color = (125, 0, 125)
hand_landmarks_style_m[key] = DrawingSpec(self.color, self.thickness, self.circle_radius)
# 在画面标注手指
self.mp_drawing.draw_landmarks(
image,
hand_landmarks,
self.mp_hands.HAND_CONNECTIONS,
hand_landmarks_style_m,
hand_connections_style_m)
# 解析手指,存入各个手指坐标
landmark_list = []
for landmark_id, finger_axis in enumerate(hand_landmarks.landmark):
landmark_list.append([
landmark_id, finger_axis.x, finger_axis.y,
finger_axis.z
])
if landmark_list:
# 获取大拇指指尖坐标
thumb_finger_tip = landmark_list[4]
thumb_finger_tip_x = math.ceil(thumb_finger_tip[1] * resize_w)
thumb_finger_tip_y = math.ceil(thumb_finger_tip[2] * resize_h)
# 获取食指指尖坐标
index_finger_tip = landmark_list[8]
index_finger_tip_x = math.ceil(index_finger_tip[1] * resize_w)
index_finger_tip_y = math.ceil(index_finger_tip[2] * resize_h)
# 两指中间点, 画线坐标只能取整数
finger_middle_point = (thumb_finger_tip_x + index_finger_tip_x) // 2, (
thumb_finger_tip_y + index_finger_tip_y) // 2
# 大拇指坐标
thumb_finger_point = (thumb_finger_tip_x, thumb_finger_tip_y)
# 食指坐标
index_finger_point = (index_finger_tip_x, index_finger_tip_y)
# 画2点连线
image = cv2.line(image, thumb_finger_point, index_finger_point, (255, 0, 255), 2)
# args: 图片资源,手指中间点,半径,颜色,厚度
image = cv2.circle(image, finger_middle_point, 2, (255, 255, 0), 2)
# 勾股定理计算长度
line_len = math.hypot((index_finger_tip_x - thumb_finger_tip_x),
(index_finger_tip_y - thumb_finger_tip_y))
# 获取电脑最大最小音量
min_volume = self.volume_range[0]
max_volume = self.volume_range[1]
line_min = 50
line_max = 300
# 将指尖长度映射到音量上
# 50 - 300,可以根据需要设定的长度更改,为设定的线段最大和最小值,少于50则认为是最小值,大于300认为是最大值
'''
np.interp(x,xp,fp) 将x在xp中计算百分比,再在fp中求相应的值
先在xp中求百分比 xp_p, xp_p = (x-xp_min)/(xp_max-xp_min)
再用xp在fp中求值 f_value = xp_p * (fp_max - fp_min) + fp_min
'''
vol = np.interp(line_len, [line_min, line_max], [min_volume, max_volume])
rect_height = np.interp(line_len, [line_min, line_max],
[0, vol_box_point2_y - vol_box_point1_y])
# [0,100]是百分比
rect_percent_text = np.interp(line_len, [line_min, line_max], [0, 100])
print('vol: ', vol, 'rect_height', rect_height, 'rect_percent_text', rect_percent_text)
# 设置电脑音量
self.volume.SetMasterVolumeLevel(vol, None)
# 显示矩形
cv2.putText(image, str(math.ceil(rect_percent_text)) + "%", (10, 350),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (191, 255, 0), 3)
image = cv2.rectangle(image, (vol_box_point1_x, math.ceil(vol_box_point2_y - rect_height)),
(vol_box_point2_x, vol_box_point2_y), (191, 255, 0), -1)
# 显示刷新率FPS
cTime = time.time()
fps_text = 1 / (cTime - fpsTime)
fpsTime = cTime
cv2.putText(image, "FPS: " + str(int(fps_text)), (10, 70),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 3, (191, 255, 0), 3)
# 显示画面
cv2.imshow('mediapipe', image)
# 按下'q'键退出循环
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
control = HandControlVolume()
control.recognize()
七、小结
我原来的想法是看看如何通过手势控制电脑鼠标操作电脑,搜到了这个好玩的例子,就花了点时间把代码学习了一下,吃透了再进行下一步控制,不得不感叹有好多很好玩的库啊,我还得继续努力学习!嘻嘻~!
八、感谢
感谢各位大佬的莅临,学习之路漫漫,吾将上下而求索。有任何想法请在评论区留言哦!
再次感谢!
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-836149.html
![[ Python+OpenCV+Mediapipe ] 实现手势控制音量,小紧张的Python学习之路,python,opencv,开发语言,计算机视觉,机器学习,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/836149-7.jpg) 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-836149.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-836149.html
到了这里,关于[ Python+OpenCV+Mediapipe ] 实现手势控制音量的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!