🎉个人名片:
🐼作者简介:一名乐于分享在学习道路上收获的大二在校生
🙈个人主页🎉:GOTXX
🐼个人WeChat:ILXOXVJE
🐼本文由GOTXX原创,首发CSDN🎉🎉🎉
🐵系列专栏:零基础学习C语言----- 数据结构的学习之路----C++的学习之路
🐓每日一句:如果没有特别幸运,那就请特别努力!🎉🎉🎉
——————————————————————————————————————————————
🎉文章简介:
🎉本篇文章对 用C语言实现单链表 学习的相关知识进行分享!🎉💕
如果您觉得文章不错,期待你的一键三连哦,你的鼓励是我创作动力的源泉,让我们一起加油,一起奔跑,让我们顶峰相见!!!🎉🎉🎉
————————————————
一.链表的概念及结构
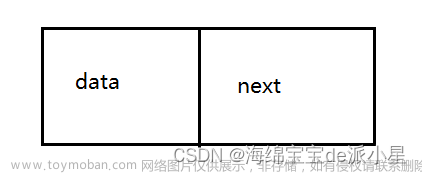
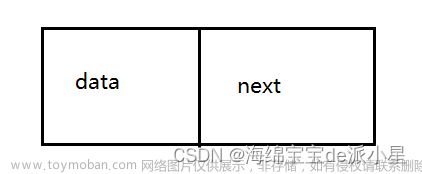
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的
 从图片中可以看出,链表的每个节点都是一个结构体,该结构体中有一个存储数据的变量和一个指向下一节点的结构体指针;
从图片中可以看出,链表的每个节点都是一个结构体,该结构体中有一个存储数据的变量和一个指向下一节点的结构体指针;
在逻辑上是连续的,但是在物理空间上不一定连续,因为链表节点都是每次插入数据时在堆上申请出来的;每次申请出来的空间不一定是连续的;
二.无头单向非循环链表的结构
 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结
无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结
构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等;
二.无头单向非循环链表的结构及实现
一.结构:

二.功能函数的实现(含性能分析与图解)
- 打印链表
- 创建节点函数
- 头插节点函数
- 头删节点函数
- 尾插节点函数
- 尾删节点函数
- 查找函数
- 在一节点位置之前插入一个节点
- 在一节点位置之后插入一个节点
- 在一节点位置之前删除一个节点
- 在一节点位置之后删除一个节点
打印链表
图解:遍历访问 先定义一个结点指针指向头节点,往后依次遍历,与数组不同的是,不是cur++,而是让cur指向下一个节点,即cur=cur->next;
先定义一个结点指针指向头节点,往后依次遍历,与数组不同的是,不是cur++,而是让cur指向下一个节点,即cur=cur->next;
代码实现:
void SLPrint(SLNode* pphead)
{
assert(pphead); //断言
SLNode* cur = pphead; //让cur指向头节点进行遍历
while (cur) //注意:条件不是cur->next,因为如果是cur->next为空就不进入循环的话,则最后一个节点就访问不到
{
printf("%d ", cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL"); //最后打印一个NULL、方便观察
printf("\n");
}
性能分析:
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
创建节点函数
代码实现:
SLNode* BuySLnewnode(SLDateType x)
{
SLNode* newnode = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode)); //注意:创建的是节点,一个结构体,而不是一个数据类型
if (newnode == NULL) //判断
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1); //开辟失败,以异常退出程序
}
newnode->next = NULL; //下一个节点置NULL
newnode->val = x; //赋值
return newnode; //返回该该结点指针
}
头插节函数
图解:
代码实现:
void SLPushFront(SLNode** pphead, SLDateType x)
//注意:这里需要节点的二级指针,因为外面调用的时候,如果传的是头指针的话,是传值,
//函数里面改变不影响头指针的指向,所以这里需要二级指针,函数调用的时候需要传二级指针
{
SLNode* newnode = BuySLnewnode(x); //创建新节点
if (*pphead == NULL) //检查,如果为空链表
{
*pphead = newnode; //直接将*pphead指向新节点
}
else
{
newnode->next = *pphead; //第二种情况
(*pphead) = newnode;
}
}
性能分析:
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1)
头删节点函数
图解:
代码实现:
void SLPopFront(SLNode** pphead)
{
assert(*pphead); //头指针不能为空
if((*pphead)->next==NULL) //第一种情况
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
SLNode* tmp = (*pphead)->next; //保存下一个节点
free(*pphead);
*pphead = tmp;
}
性能分析:
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1)
尾插节点函数
图解:
代码实现:
void SLPushBack(SLNode** pphead, SLDateType x)
{
SLNode* newnode = BuySLnewnode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL) //空链表
{
*pphead = newnode;
return;
}
SLNode* tail = *pphead; //定义一个尾指针
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
} //退出循环后tail->next为NULL;
tail->next = newnode; //链接
}
性能分析:
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
尾删节点函数
图解:
代码实现:
在这里插入代码片void SLPopBack(SLNode** pphead)
{
assert(*pphead);
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL) //第一种情况
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
SLNode* Prevtail = *pphead; //记录尾指针前面的一个节点
SLNode* tail = *pphead; //尾指针
while (tail->next)
{
Prevtail = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail); //释放掉尾节点
Prevtail->next = NULL;
}
性能分析:
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
查找函数
代码实现:
SLNode* SLFind(SLNode* pphead, SLDateType x)
{
assert(pphead);
SLNode* cur = pphead; //遍历查找
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val == x)
{
return cur; //返回节点指针
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL; //没找到,返回NULL
}
性能分析:
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
在pos位置之前插入一个节点
图解:
代码实现:
//在pos之前插入
void SLInsert(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos, SLDateType x)
{
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
if (pos == *pphead) //第一种情况:头插
{
SLPushFront(pphead, x);
return;
}
SLNode* newnode = BuySLnewnode(x);
SLNode* cur = *pphead; //遍历,找到pos的前一个节点
while (cur->next)
{
if (cur->next == pos) //找到了
{
newnode->next = cur->next; //链接
cur->next = newnode;
return;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
}
性能分析:
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
在pos位置之后插入一个节点
图解:
代码实现:
//在pos之后插入
void SLInsertBack(SLNode* pos, SLDateType x)
{
assert(pos);
SLNode * newnode = BuySLnewnode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next; //链接
pos->next = newnode;
}
性能分析:
删除pos位置之前一个节点
图解:
代码实现:
//删除pos之前的节点
void SLErase(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pos != *pphead);
if (pos== (*pphead)->next) //头删,第一种情况
{
free(*pphead);
(*pphead) = pos;
return;
}
SLNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->next->next == pos) //找到pos前面的第二个节点
{
free(cur->next);
cur->next = pos; //链接
return;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
}
性能分析:
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
删除pos位置之后一个节点
图解:
代码实现:
//删除pos之后的节点
void SLEraseAfter(SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pos->next); //当pos后无节点,无意义
if (pos->next->next == NULL) //尾删
{
pos->next = NULL;
return;
}
SLNode* cur = pos->next->next;
free(pos->next);
pos->next = cur; //链接
cur = NULL;
}
性能分析:
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1)
二.总代码
```cpp
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLDateType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLDateType val;
struct SListNode* next;
}SLNode;
SLNode* BuySLnewnode(SLDateType x);
void SLPrint(SLNode* pphead);
void SLPushBack(SLNode** pphead, SLDateType x);
void SLPushFront(SLNode** pphead, SLDateType x);
void SLPopFront(SLNode** pphead);
void SLPopBack(SLNode** pphead);
SLNode* SLFind(SLNode* pphead,SLDateType x);
//在pos之前插入
void SLInsert(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos,SLDateType x);
//在pos之后插入
void SLInsertBack(SLNode* pos, SLDateType x);
//删除pos之后的节点
void SLEraseBack(SLNode* pos);
//删除pos之前的节点
void SLErase(SLNode** pphead,SLNode* pos);
```cpp
#include"SList.h"
SLNode* BuySLnewnode(SLDateType x)
{
SLNode* newnode = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->val = x;
return newnode;
}
void SLPrint(SLNode* pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
SLNode* cur = pphead;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d ", cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL");
printf("\n");
}
void SLPushFront(SLNode** pphead, SLDateType x)
{
SLNode* newnode = BuySLnewnode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
(*pphead) = newnode;
}
}
void SLPushBack(SLNode** pphead, SLDateType x)
{
SLNode* newnode = BuySLnewnode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
return;
}
SLNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
void SLPopFront(SLNode** pphead)
{
assert(*pphead);
if((*pphead)->next==NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
SLNode* tmp = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = tmp;
}
void SLPopBack(SLNode** pphead)
{
assert(*pphead);
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
SLNode* Prevtail = *pphead;
SLNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next)
{
Prevtail = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
Prevtail->next = NULL;
}
SLNode* SLFind(SLNode* pphead, SLDateType x)
{
assert(pphead);
SLNode* cur = pphead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//在pos之前插入
void SLInsert(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos, SLDateType x)
{
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
if (pos == *pphead)
{
SLPushFront(pphead, x);
return;
}
SLNode* newnode = BuySLnewnode(x);
SLNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur->next)
{
if (cur->next == pos)
{
newnode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newnode;
return;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
}
//在pos之后插入
void SLInsertBack(SLNode* pos, SLDateType x)
{
assert(pos);
SLNode * newnode = BuySLnewnode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
//删除pos之后的节点
void SLEraseBack(SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pos->next);
if (pos->next->next == NULL)
{
pos->next = NULL;
return;
}
SLNode* cur = pos->next->next;
free(pos->next);
pos->next = cur;
cur = NULL;
}
//删除pos之前的节点
void SLErase(SLNode** pphead, SLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pos != *pphead);
if (pos== (*pphead)->next)
{
free(*pphead);
(*pphead) = pos;
return;
}
SLNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->next->next == pos)
{
free(cur->next);
cur->next = pos;
return;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
}
三.性能分析
与顺序表相比:
优点:
1.按需申请,没有空间浪费;
2.头插头删效率高
缺点:
1.不支持下标随机访问
2.尾插尾删效率低文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-838016.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-838016.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-838016.html
到了这里,关于数据结构之单链表详解(C语言手撕)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!