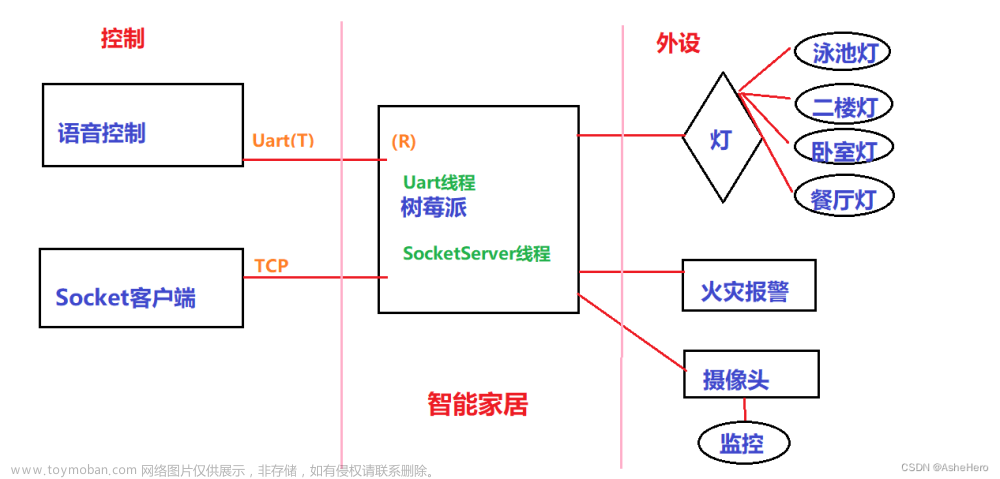
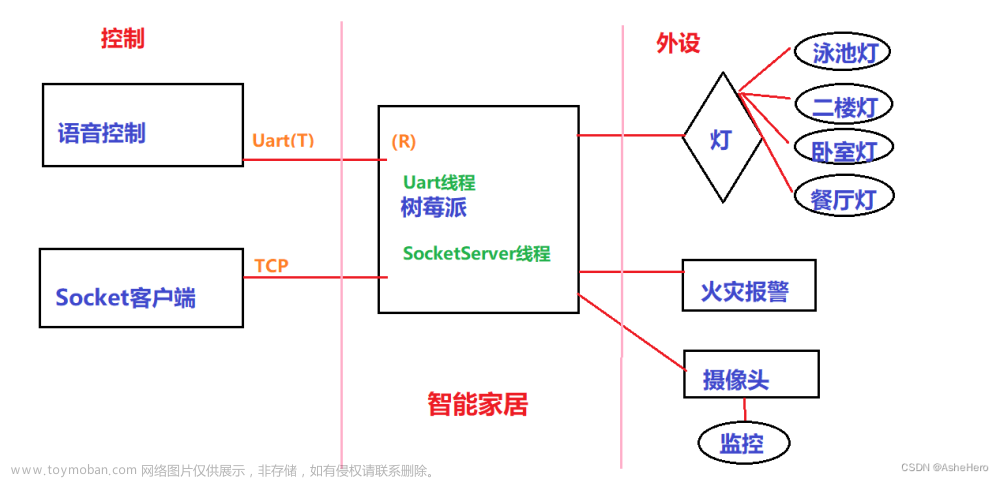
前期准备:

Orange Pi Zero 2、AI智能语音识别模块、USB转TTL串口模块、USB-typeCx2、杜邦线若干



1、SU03T语音模块的配置
使用USB串口转TTL模块,将配置固件烧写到SU03T语音模块中
步骤:1、进入智能公元/AI产品零代码平台 (smartpi.cn)官网进行语音模块的配置
2、尤其是对这两个管脚的配置

3 、设置好对应的指令

4、生成对应的SDK,然后下载固件(此过程需要等到30分钟左右)

5、将串口与语音模块进行接入,将配置好的SDK固件烧入语音模块里(注意接线)

6、用烧录工具进行烧录

7、可以打开串口助手工具查看是否烧录成功
2、编程实现语音指令的识别
此处编程涉及到wiringPi库的一些使用
将语音模块插入开发板并编程实现基础逻辑代码,添加串口读取一个字符的接口 myserialGetchar()
myserialGetchar()函数的使用,这里对指令进行测试
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "uartTool.h"
int fd;
char myserialGetchar (const int fd)
{
char x ;
if (read (fd, &x, 1) != 1)
return -1 ;
return x ;
}
void* readSerial()
{
char cmd;
while(1){
cmd = myserialGetchar(fd);
//printf("GET->0x%c\n",cmd);
switch (cmd){
case 'N':
printf("next\n");
break;
case 'P':
printf("pre\n");
break;
case 'Z':
printf("dianzan\n");
break;
case 'Q':
printf("guanbi\n");
break;
}
}
}
/*
void* sendSerial()
{
char buffer[32];
while(1){
memset(buffer,'\0',sizeof(buffer));
scanf("%s",buffer);
serialSendString(fd, buffer);
}
}
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char deviceName[32] = {'\0'};
pthread_t readt;
// pthread_t sendt;
if(argc < 2){
printf("uage:%s /dev/ttyS?\n",argv[0]);
return -1;
}
strcpy(deviceName, argv[1]);
if( (fd = myserialOpen(deviceName, 115200)) == -1){
printf("open %s error\n",deviceName);
return -1;
}
pthread_create(&readt, NULL, readSerial,NULL);
// pthread_create(&sendt, NULL, sendSerial,NULL);
while(1){sleep(10);}
return 0;
}

此处有个小插曲(热拔插机制)
手机接入Linux热拔插相关
a. 把手机接入开发板
b. 安装adb工具,在终端输入adb安装指令:
sudo apt-get install adb
c. dmeg能查看到手机接入的信息,但是输入adb devices会出现提醒
dinsufficient permissions for device: user in plugdev group; are your udev rules wrong?
d. 配置文件,以支持USB设备的热拔插,支持UDEV的机制
在/etc/udev/rules.d 文件夹下创建规则文件 cd /etc/udev/rules.d/ sudo vim 51-android.rules
在文件中添加内容
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ENV{DEVTYPE}=="usb_device", MODE="0666"
e. 在手机开发者选项中,打开USB调试,重新拔插手机
f. 手机弹出调试提醒,点确认手机调试模式这里的热拔插就相当于给手机添加一个管理的文件,正是有了这个文件,手机才能够于Linux系统进行交互
3、adb指令的控制
用shell指令来操作手机屏幕,模拟手动滑屏幕
向下滑动540是水平的,1300是竖直方向,下是500,下滑的操作时间为100ms
adb shell input swipe 540 1300 540 500 100
向上滑动
adb shell input swipe 540 500 540 1300 100
点赞(点击屏幕两次,用到了循环的脚本)
adb shell "seq 3 | while read i;do input tap 350 1050 & input tap 350 1050 &
sleep 0.01;done;"
锁屏
adb shell input keyevent 26
4.代码功能的整合
uartTool.h
int myserialOpen (const char *device, const int baud);
void serialSendString (const int fd, const char *s);
char myserialGetchar (const int fd);
int serialGetString (const int fd, char *buffer);
uartTool.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include "wiringSerial.h"
int myserialOpen (const char *device, const int baud)
{
struct termios options ;
speed_t myBaud ;
int status, fd ;
switch (baud)
{
case 9600: myBaud = B9600 ; break ;
case 115200: myBaud = B115200 ; break ;
}
if ((fd = open (device, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY | O_NONBLOCK)) == -1)
return -1 ;
fcntl (fd, F_SETFL, O_RDWR) ;
// Get and modify current options:
tcgetattr (fd, &options) ;
cfmakeraw (&options) ;
cfsetispeed (&options, myBaud) ;
cfsetospeed (&options, myBaud) ;
options.c_cflag |= (CLOCAL | CREAD) ;
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB ;
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB ;
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE ;
options.c_cflag |= CS8 ;
options.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG) ;
options.c_oflag &= ~OPOST ;
options.c_cc [VMIN] = 0 ;
options.c_cc [VTIME] = 100 ; // Ten seconds (100 deciseconds)
tcsetattr (fd, TCSANOW, &options) ;
ioctl (fd, TIOCMGET, &status);
status |= TIOCM_DTR ;
status |= TIOCM_RTS ;
ioctl (fd, TIOCMSET, &status);
usleep (10000) ; // 10mS
return fd ;
}
void serialSendString (const int fd, const char *s)
{
int ret;
ret = write (fd, s, strlen (s));
if (ret < 0)
printf("Serial Puts Error\n");
}
int serialGetString (const int fd, char *buffer)
{
int n_read;
n_read = read(fd,buffer,32);
return n_read;
}
uartTest.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "uartTool.h"
int fd;
char myserialGetchar (const int fd)
{
char x ;
if (read (fd, &x, 1) != 1)
return -1 ;
return x ;
}
void* readSerial()
{
char cmd;
while(1){
cmd = myserialGetchar(fd);
//printf("GET->0x%c\n",cmd);
switch (cmd){
case 'N':
printf("next\n");
system("adb shell input swipe 540 1300 540 500 100");
break;
case 'P':
printf("pre\n");
system("adb shell input swipe 540 500 540 1300 100");
break;
case 'Z':
printf("dianzan\n");
system("adb shell \"seq 3 | while read i;do input tap 350 1050 &
input tap 350 1050 & sleep 0.01;done;\"");
break;
case 'Q':
printf("guanbi\n");
system("adb shell input keyevent 26");
break;
}
}
}
/*
void* sendSerial()
{
char buffer[32];
while(1){
memset(buffer,'\0',sizeof(buffer));
scanf("%s",buffer);
serialSendString(fd, buffer);
}
}
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char deviceName[32] = {'\0'};
pthread_t readt;
// pthread_t sendt;
if(argc < 2){
printf("uage:%s /dev/ttyS?\n",argv[0]);
return -1;
}
strcpy(deviceName, argv[1]);
if( (fd = myserialOpen(deviceName, 115200)) == -1){
printf("open %s error\n",deviceName);
return -1;
}
pthread_create(&readt, NULL, readSerial,NULL);
// pthread_create(&sendt, NULL, sendSerial,NULL);
while(1){sleep(10);}
return 0;
}
关键语句

运行结果文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-838320.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-838320.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-838320.html
到了这里,关于基于OrangePi的语音控制刷抖音项目的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!