前言
前面我们已经学习过了二叉树,二叉搜索树是在二叉树的基础上增添了一些规则,使其能完成快速查找的功能,同时它也帮助我们更好的理解后续将要学习的map和set。
1. 二叉搜索树
1.2 二叉搜索树的概念
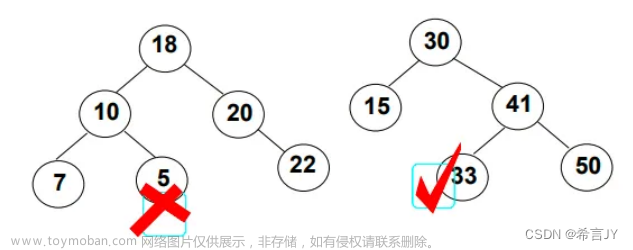
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值。
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值。
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树。
2.2 二叉搜索树操作

- 二叉搜索树的查找
a、从根开始比较,查找,比根大则往右边走查找,比根小则往左边走查找。
b、最多查找高度次,走到到空,还没找到,这个值不存在。 - 二叉搜索树的插入
插入的具体过程如下:
a. 树为空,则直接新增节点,赋值给root指针。
b. 树不空,按二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点。
- 二叉搜索树的删除
首先查找元素是否在二叉搜索树中,如果不存在,则返回, 否则要删除的结点可能分下面四种情况:
a. 要删除的结点无孩子结点
b. 要删除的结点只有左孩子结点
c. 要删除的结点只有右孩子结点
d. 要删除的结点有左、右孩子结点
看起来有待删除节点有4中情况,实际情况a可以与情况b或者c合并起来,因此真正的删除过程如下:
情况b:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除节点的左孩子结点–直接删除
情况c:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除结点的右孩子结点–直接删除
情况d:在它的右子树中寻找中序下的第一个结点(关键码最小),用它的值填补到被删除节点中,再来处理该结点的删除问题–替换法删除。 此部分会在实现小节进行详细讲解。
此部分会在实现小节进行详细讲解。
2. 二叉搜索树的实现
2.1 插入
2.1.1 迭代插入
插入十分简单,新插入值比当前节点的值小就进入它的左子树,比它大就进入它的右子树,相等就返回false,说明这个值已经存在,无需插入,(注意:二叉搜索树一般是不会存储重复值的) 遇到空节点就该进行插入了。但是在进行链接时需要注意,我们的结构并不是三叉链结构,因此对于一个节点是无法找到它的父亲节点的,因此在比较时还需要保存父亲节点,方便进行链接操作。
bool insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
}
//保存父亲节点
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
//确保每一次循环结束parent就是cur的父亲节点
parent = cur;
if (key > cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (key > parent->_key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
2.1.2 递归插入
递归需要传入根节点,但是在类外面我们无法传入根节点,因为它的类的私有成员变量,因此我们可以套一层,在类里面我们是可以访问根节点的。递归插入更加简单,只需要在递归到空的时候直接开一个新结点给root就可以了,因为我们是引用传值,不需要保存父亲节点,直接就可以链接上了。
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
_InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
_InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
return false;
}
2.2 查找
2.2.1 迭代查找
查找也比较简单,被查找节点的值比当前节点的值小就进入它的左子树,比它大就进入它的右子树,相等就返回true或者返回该节点的指针。
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if(key > cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
2.2.2 递归查找
依次遍历左子树右子树进行比较就可以了。如果不太懂的小伙伴可以画画递归展开图,在数据结构篇六:二叉树中有说明怎么画。
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key == key)
return true;
if (_FindR(root->_left, key))
return true;
if (_FindR(root->_right, key))
return true;
return false;
}
2.3 删除
2.3.1 迭代删除
删除的情况有很多,我们分开来看。
2.3.1.1 情况一

这种情况下直接删除就好了,因为没有孩子节点,并不会有什么影响。
2.3.1.2 情况二
 删除该节点,并将它的孩子节点链接到它的父亲节点。如果被删除节点是父亲的右孩子,就将被删除节点的孩子链接到父亲的右子树上;同理,如果被删除节点是父亲的左孩子,就将被删除节点的孩子链接到父亲的左子树上。原因很好理解,父亲节点的右子树都是比它大的,左子树都是比它小的,大的值自然要链接到右边,小的值自然要链接到左边。
删除该节点,并将它的孩子节点链接到它的父亲节点。如果被删除节点是父亲的右孩子,就将被删除节点的孩子链接到父亲的右子树上;同理,如果被删除节点是父亲的左孩子,就将被删除节点的孩子链接到父亲的左子树上。原因很好理解,父亲节点的右子树都是比它大的,左子树都是比它小的,大的值自然要链接到右边,小的值自然要链接到左边。
2.3.1.3 情况三

我们发现如果删除该节点就会打乱它的左右子树,打破二叉搜索树的规则。自然我们可以选择将所有值(除了被删除节点)重新构造一个新的二叉搜索树出来,但是这样太麻烦了。我们可以用替换法来解决这个问题。
替换法:我们可以找出一个节点,在不破坏二叉搜索树规则的前提下来代替被删除节点,我们通常可以找被删除节点的左子树的最右节点(左子树中最大的节点)或者右子树的最左节点(右子树中最大节点)来替换它,我采用的是找右子树的最左节点来解决问题,我们来看:
我们此时就发现继续删除节点3就变成了我们前面所说的情况一,直接删除就可以了。
bool Earse(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
//找到了,准备删除
//左右都为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr && cur->_right == nullptr)
{
cur = nullptr;
}
//左为空或者右为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr || cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = _root->_right;
}
else if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
else
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = _root->_left;
}
else if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
}
//左右都不为空
else
{
//替换法
//找到右子树的最小节点
Node* parent = cur;
Node* subLeft = cur->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
parent = subLeft;
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, subLeft->_key);
if (parent->_right == subLeft)
parent->_right = subLeft->_right;
else
parent->_left = subLeft->_right;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
2.3.2 递归删除
递归删除采用了最开始说的删除方法,分为左为空、右为空、左右都不为空。前两个看代码就可以看懂,对于左右都不为空,我们在找到替换节点后:
问题就变成了不是删除root节点了,而是删除subRoot,此时我们可以直接换成子问题解决,就变成了删除root节点右子树的中的subRoot节点,只需要再次调用递归删除函数就可以了。
bool EarseR(const K& key)
{
return _EarseR(_root,key);
}
bool _EarseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EarseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EarseR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_right;
delete del;
return true;
}
else if(root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_left;
delete del;
return true;
}
else
{
Node* subRoot = root->_right;
while (subRoot->_left)
{
subRoot = subRoot->_left;
}
swap(subRoot->_key, root->_key);
return _EarseR(root->_right, key);
}
}
return false;
}
2.4 析构
使用递归用后序的顺便依次删除就可以了。
~BSTree()
{
_BSTree(_root);
}
void _BSTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_BSTree(root->_left);
_BSTree(root->_right);
delete root;
}
2.5 拷贝构造和赋值运算符重载
与前面问题一样,需要套一层来实现。
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& bt)
{
_root = Copy(bt._root);
}
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> bt)
{
swap(_root, bt._root);
return *this;
}
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* newroot = new Node(root->_key);
newroot->_left = Copy(root->_left);
newroot->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return newroot;
}
而对于赋值运算符重载,我们是进行传值传参,会发生拷贝构造,因此本身就是一块新空间,我们只需要交换一下地址就可以了。(在STL篇二:vector中的赋值运算符中有详细讲解。)
3. 二叉搜索树的两种结构
- K模型:K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到
的值。
比如:给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下:
以词库中所有单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树
在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
- KV模型:每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即<Key, Value>的键值对。该种方
式在现实生活中非常常见:
比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英文单词与其对应的中文<word,chinese>就构成一种键值对;
再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出现次数就是<word,count>就构成一种键值对。
一个对应后面需要学的set,一个对应map。
template<class K>
struct BinarySearchSTree
{
BinarySearchSTree<K>* _left;
BinarySearchSTree<K>* _right;
K _key;
BinarySearchSTree(const K& key = K())
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
struct BinarySearchSTree
{
BinarySearchSTree<K, V>* _left;
BinarySearchSTree<K, V>* _right;
K _key;
V _val;
BinarySearchSTree(const K& key = K(), const V& val = V())
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
, _val(val)
{}
};
(K,V)的结构与上面讲的内容一样,需要修改的地方也只有在开辟空间时多传入一个值。
4. 二叉搜索树的性能分析
插入和删除操作都必须先查找,查找效率代表了二叉搜索树中各个操作的性能。
对有n个结点的二叉搜索树,若每个元素查找的概率相等,则二叉搜索树平均查找长度是结点在二叉搜索树的深度的函数,即结点越深,则比较次数越多。
但对于同一个关键码集合,如果各关键码插入的次序不同,可能得到不同结构的二叉搜索树:
最优情况下,二叉搜索树为完全二叉树(或者接近完全二叉树),其平均比较次数为:
l
o
g
2
N
log_2 N
log2N
最差情况下,二叉搜索树退化为单支树(或者类似单支),其平均比较次数为:
N
2
\frac{N}{2}
2N
问题:如果退化成单支树,二叉搜索树的性能就失去了。那能否进行改进,不论按照什么次序插入关键码,二叉搜索树的性能都能达到最优?那么我们后续章节学习的AVL树和红黑树就可以上场了。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-839112.html
5. 全部代码
5.1 BinarySreachTree.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
template<class K>
struct BinarySearchSTree
{
BinarySearchSTree<K>* _left;
BinarySearchSTree<K>* _right;
K _key;
BinarySearchSTree(const K& key = K())
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
public:
typedef BinarySearchSTree<K> Node;
BSTree()
{}
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& bt)
{
_root = Copy(bt._root);
}
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> bt)
{
swap(_root, bt._root);
return *this;
}
bool insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
parent = cur;
if (key > cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (key > parent->_key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if(key > cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//bool Earse(const K& key)
//{
// Node* parent = nullptr;
// Node* cur = _root;
// while (cur)
// {
// if (key < cur->_key)
// {
// parent = cur;
// cur = cur->_left;
// }
// else if (key > cur->_key)
// {
// parent = cur;
// cur = cur->_right;
// }
// else
// {
// //找到了,准备删除
// //左为空
// if (cur->_left == nullptr)
// {
// if (cur == _root)
// {
// _root = cur->_right;
// }
// else
// {
// if (cur == parent->_left)
// {
// parent->_left = cur->_right;
// }
// else
// {
// parent->_right = cur->_right;
// }
// }
// }
// //右为空
// else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
// {
// if (cur == _root)
// {
// _root = cur->_left;
// }
// else
// {
// if (cur == parent->_left)
// {
// parent->_left = cur->_left;
// }
// else
// {
// parent->_right = cur->_left;
// }
// }
// }
// //左右都不为空
// else
// {
// //替换法
// //找到右子树的最小节点
//
// Node* parent = cur;
// Node* subLeft = cur->_right;
// while (subLeft->_left)
// {
// parent = subLeft;
// subLeft = subLeft->_left;
// }
// swap(cur->_key, subLeft->_key);
// if (parent->_right == subLeft)
// parent->_right = subLeft->_right;
// else
// parent->_left = subLeft->_right;
// }
// return true;
// }
// }
// return false;
//}
bool Earse(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
//找到了,准备删除
//左右都为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr && cur->_right == nullptr)
{
cur = nullptr;
}
//左为空或者右为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr || cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = _root->_right;
}
else if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
else
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = _root->_left;
}
else if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
}
//左右都不为空
else
{
//替换法
//找到右子树的最小节点
Node* parent = cur;
Node* subLeft = cur->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
parent = subLeft;
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, subLeft->_key);
if (parent->_right == subLeft)
parent->_right = subLeft->_right;
else
parent->_left = subLeft->_right;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool EarseR(const K& key)
{
return _EarseR(_root,key);
}
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
~BSTree()
{
_BSTree(_root);
}
private:
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* newroot = new Node(root->_key);
newroot->_left = Copy(root->_left);
newroot->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return newroot;
}
void _BSTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_BSTree(root->_left);
_BSTree(root->_right);
delete root;
}
void _InOrder(Node* _root)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(_root->_left);
cout << _root -> _key << " ";
_InOrder(_root->_right);
}
bool _EarseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EarseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EarseR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_right;
delete del;
return true;
}
else if(root->_right == nullptr)
{
Node* del = root;
root = root->_left;
delete del;
return true;
}
else
{
Node* subRoot = root->_right;
while (subRoot->_left)
{
subRoot = subRoot->_left;
}
swap(subRoot->_key, root->_key);
return _EarseR(root->_right, key);
}
}
return false;
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key == key)
return true;
if (_FindR(root->_left, key))
return true;
if (_FindR(root->_right, key))
return true;
return false;
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
_InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
_InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
return false;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
namespace kv
{
template<class K, class V>
struct BinarySearchSTree
{
BinarySearchSTree<K, V>* _left;
BinarySearchSTree<K, V>* _right;
K _key;
V _val;
BinarySearchSTree(const K& key = K(), const V& val = V())
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
, _val(val)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
public:
typedef BinarySearchSTree<K, V> Node;
bool insert(const K& key, const V& val)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key, val);
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
parent = cur;
if (key > cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key, val);
if (key > parent->_key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (key > cur->_key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Earse(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
//找到了,准备删除
//左为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
}
//右为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
}
//左右都不为空
else
{
//替换法
//找到右子树的最小节点
Node* parent = cur;
Node* subLeft = cur->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
parent = subLeft;
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, subLeft->_key);
if (parent->_right == subLeft)
parent->_right = subLeft->_right;
else
parent->_left = subLeft->_right;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* _root)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(_root->_left);
cout << _root->_key << " " << _root->_val << endl;;
_InOrder(_root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}
5.2 Test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"BinarySearchTree.h"
void Test1()
{
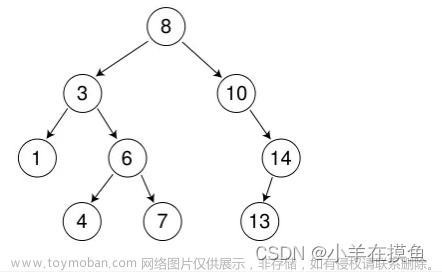
BSTree<int> bt;
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
for (auto e : a)
{
bt.insert(e);
}
cout << bt.Find(8) << endl;
bt.InOrder();
bt.Earse(14);
bt.InOrder();
bt.Earse(3);
bt.InOrder();
bt.Earse(8);
bt.InOrder();
for (auto e : a)
{
bt.Earse(e);
bt.InOrder();
}
}
void TestR()
{
BSTree<int> bt;
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
for (auto e : a)
{
bt.InsertR(e);
}
//cout << bt.FindR(8) << endl;
//bt.InOrder();
for (auto e : a)
{
bt.EarseR(e);
bt.InOrder();
}
}
void Test2()
{
BSTree<int> bt;
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
for (auto e : a)
{
bt.InsertR(e);
}
BSTree<int> copy(bt);
copy.InOrder();
}
void Test3()
{
kv::BSTree<string, string> dic;
dic.insert("left", "左边");
dic.insert("right", "右边");
dic.InOrder();
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
kv::BinarySearchSTree<string, string>* ret = dic.Find(str);
if (ret)
{
cout << ret->_val << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "无此单词" << endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
Test1();
//TestR();
//Test2();
//Test3();
return 0;
}
6. 总结
此部分的学习主要是为了后续的AVL树和红黑树打基础,因此需要熟练理解,希望能与大家共同进步。
如果大家发现有什么错误的地方,可以私信或者评论区指出喔。我会继续深入学习C++,希望能与大家共同进步,那么本期就到此结束,让我们下期再见!!觉得不错可以点个赞以示鼓励!!文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-839112.html
到了这里,关于数据结构篇八:二叉搜索树的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!