> 作者简介:დ旧言~,目前大二,现在学习Java,c,c++,Python等
> 座右铭:松树千年终是朽,槿花一日自为荣。> 目标:熟练掌握二叉搜索树,能自己模拟实现二叉搜索树
> 毒鸡汤:不断的努力,不断的去接近梦想,越挫越勇,吃尽酸甜苦辣,能够抵御寒冬,也能够拥抱春天,这样的才叫生活。
> 望小伙伴们点赞👍收藏✨加关注哟💕💕

🌟前言
前期呢我们学习了简单二叉树,这个简单真的是一点都不简单呀,如果大家对二叉树的知识点忘记的小伙伴们可以看看这篇博客二叉树的实现-CSDN博客,这篇博客不单单是二叉树的进阶,这次的知识是为了后面的map和set以及红黑树...打下基础,c++的学习也是上了一个层次,进入今天的主题----二叉树进阶之二叉搜索树。

⭐主体
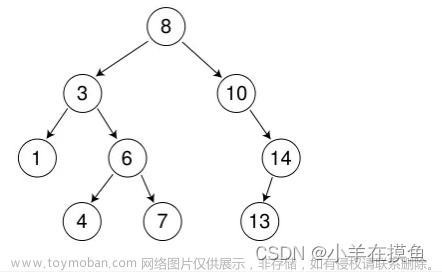
学习二叉树进阶之二叉搜索树咱们按照下面的图解:

🌙二叉搜索树基本概念

💫基本概念
二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree),(又:二叉排序树)它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根节点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值; 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树。二叉搜索树作为一种经典的数据结构,它既有链表的快速插入与删除操作的特点,又有数组快速查找的优势;所以应用十分广泛,例如在文件系统和数据库系统一般会采用这种数据结构进行高效率的排序与检索操作。
💫基本结构
二叉搜索树是能够高效地进行如下操作的数据结构。
- 插入一个数值
- 查询是否包含某个数值
- 删除某个数值
💫基本性质
设x是二叉搜索树中的一个结点。如果y是x左子树中的一个结点,那么y.key≤x.key。如果y是x右子树中的一个结点,那么y.key≥x.key。
在二叉搜索树中:
- 若任意结点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均不大于它的根结点的值。
- 若任意结点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均不小于它的根结点的值。
- 任意结点的左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
1.这也就说明二叉搜索树的中序遍历(左 根 右)是升序的。
2.如果共有n个元素,那么平均每次操作需要O(logn)的时间。

🌙二叉搜索树模拟实现
基本框架:
template <class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
public:
//默认成员函数
BSTree ();
BSTree (const K& key);
BSTree& operator=(BSTree Tree);
~BSTree();
bool Insert(const K& key);
void Inorder();
bool find(const K& key);
bool Erase(const K& key);
//递归实现
bool FindR(const K& key);
bool InsertR(const K& key);
bool EraseR(const K& key);
}💫二叉搜索树节点创建
创建树之前要先定义好节点,跟之前普通链式二叉树没有什么区别。
代码实现:
// 对每个结点初始化
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; // 重命名
Node* _left; // 左子树
Node* _right; // 右子树
K _key; // 二叉搜索树节点元素的值
BSTreeNode(const K& key) // 初始化列表,成员变量初始化
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};拓展分析:
- 我们会不断的通过 key 创建树节点, new 出的对象会调用带参的构造函数。所以,我们定义好节点中的成员变量后还要书写好构造函数。
- 因为树节点会频繁访问成员变量,所以我们要将其置为公有成员(public),如果觉得麻烦,可以直接使用 struct 定义节点。
💫二叉搜索树构造函数
二叉搜索树这个类只要存入二叉树的根节点就可以了
代码实现:
// 强制生成默认构造函数
BSTree() = default;拓展分析:
这里加入default关键字是让编译器强制生成默认构造函数,因为等会我们要写拷贝构造,根据C++的类和对象的知识,我们只要显式的写一个构造函数,编译器就不会生成默认构造函数
💫二叉搜索树查找函数
二叉搜索树,左树比根小,右树比根大我们可以根据这个特性去寻找,走到空的位置还没有找到,证明该树中没有该元素。
1)非递归
代码实现:
// 查找函数
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}拓展分析:
这里采用左树比根小,右树比根大的特性来实现代码。
2)递归
步骤拆分:
- 如果 root 指向为 nullptr ,说明未找到 key 值
- 如果 key 大于 root->key,说明 key 在 root 的右边,使用root->right继续递归。
- 如果 key 小于 root->key,说明 key 在 root 的左边,使用root->left继续递归。
- 最后就是 key==root->key 的情况,返回 true 。
代码实现:
// 递归版本
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}拓展分析:
递归这里有一点小问题,因为在C++类中,实现递归是有一些问题的,因为我们把根直接封在类中了,函数根本就不需要参数就可以访问根节点,但是我们的递归函数需要参数来控制向哪棵树递归

💫二叉搜索树插入函数
对于链式结构来说,我们直接向这个空节点赋值,表面上是链接了,实际上根本没有链接上,因为我们遍历所使用的节点是一个临时变量,出了作用域就会自动销毁,所以根本没有链接上,所以我们还要记住最后走到的空节点的父节点,用父节点来链接新插入的节点。
1)非递归
步骤拆分:
- 传入空树直接 new 一个节点,将其置为 root 。
- 找到 key 值该在的位置,如果 key 大于 当前节点的 _key,则往右走,小于则往左走。
- 如果 key 等于当前节点的 _key,直接返回 false。
- 直到 cur 走到空,此时 cur 指向的便是 key 应当存放的地方。
- 创建一个节点并链接到树中(链接到 parent 节点的左或右)
代码实现:
// 插入结点
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr) // 如果没有结点
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur) // 开始插入
{
if (cur->_key < key) // 比它小走左子树
{
parent = cur;
cut = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key > key) // 比它大走右子树
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key); // 开始链接
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}2)递归
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key)
}
// 递归版本
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}拓展分析:

💫二叉搜索树节点删除
问题剖析:
Erase 删除分为以下三种情况:
- 删除节点为叶子节点
- 删除节点有一个子节点
- 删除节点有两个子节点
第一点和第二点可以归纳为一点,而第二点是这个三点最为复杂的。
问题分析:
①:删除节点为叶子节点 && 删除节点有一个子节点
分析:其本质都属于左或右节点为空,当该节点只有一个孩子或无孩子时,直接让 parent 指向该节点子节点,然后将此节点移除出树。
1.删除的是根节点
如果parent指向的是nullptr,则直接让_root后移动即可。
2. 链接时,应该链接到父亲的左还是右。
如果parent的左边是待删节点,即parent->left==cur,则将cur的右边链接到parent的左边
如果parent的右边是待删节点,即parent->right==cur,将cur的右边链接到parent的右边
①:删除节点有两个子节点
分析:采用的是替换法删除,我们要删除3,我们知道cur的右子树中最左边的节点的值是与cur节点的值是最接近的,所以我们交换3和4,这样就转换为删除叶子节点了,这样就会把问题的难度降低。
1.此时 6 节点的_left 仍然指向原来的 4 节点,出现野指针的问题。并且如果 4 节点还有右子树呢?如图:
解决方案:我们的方法是仍要记录下min的父节点,让父节点指向 min->right,此时无论min->right有子树还是min->right==nullptr,都可以很好的解决该问题,
2. 无法删除根节点(8)
解决方案:删除8节点,此时 min 指向了cur->right,min ->left 为空,没有进入循环,导致minparent 为空指针,指向 minparent->_left = min->right;出现非法访问。
1)非递归
代码实现:
// 删除节点
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key) // 先去找值
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key) // 先去找值
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else // 找到了
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr) // 第一种情况
{
if (cur == _root)
_root = cur->_right;
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr) // 第二种情况
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else // 第三种情况
{
// 替换法
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}2)递归
代码实现:
// 递归版本
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else
{
Node* rightMin = root->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, rightMin->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}💫二叉搜索树拷贝构造
拷贝构造,我们可以参考前面的二叉树重建,直接递归解决,所以我们让二叉搜索树的拷贝构造调用我们的_Copy函数。
// 拷贝构造
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t.root); // 调用拷贝构造
}
// 拷贝构造
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_key); // 创建一个节点
newRoot->_left = Copy(root->left); // 拷贝左子树
newRoot->_right = Copy(root->_right); // 拷贝右子树
return newRoot; // 返回根
}💫二叉搜索树operator=
operator=我们采用现代写法,传参时会调用拷贝构造,我们直接将形参与我们当前对象交换。
// 赋值运算重载
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}💫二叉搜索树析构函数
析构函数也要递归实现,采用后序遍历,一个一个节点的删除
// 析构函数
~BSTree()
{
Destroy(_root); // 调用析构函数
}
// 析构函数
void Destroy(Node* root) // 采用递归的形式
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->right);
delete root;
}🌙二叉搜索树应用场景
1.K模型:K模型即只有 key 作为关键码,结构中只需要存储 key 即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值。
比如: 给一个单词 word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方法如下:
- 以词库中所有单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构造一棵二叉搜索树
- 在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
2.KV模型:每一个关键码 key ,都有与之对应的值 value,即<key,value>的键值对。该种方法式在现实生活中非常常见:
- 比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英文单词与其对应的中文<word,chinese>就构成一种键值对;
- 再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出现的次数就是<world,count>,就够成一种键值对。
代码实现:
template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key, value);
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
// 替换法
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};🌙全部代码
namespace lyk
{
// 对每个结点初始化
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; // 重命名
Node* _left; // 左子树
Node* _right; // 右子树
K _key; // 二叉搜索树节点元素的值
BSTreeNode(const K& key) // 初始化列表,成员变量初始化
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
};
/
// 二叉搜索树功能基本实现
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; // 重命名
public:
// 强制生成默认构造函数
BSTree() = default;
// 拷贝构造
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t.root); // 调用拷贝构造
}
// 赋值运算重载
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
// 析构函数
~BSTree()
{
Destroy(_root); // 调用析构函数
}
// 插入结点
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr) // 如果没有结点
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur) // 开始插入
{
if (cur->_key < key) // 比它小走左子树
{
parent = cur;
cut = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key > key) // 比它大走右子树
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key); // 开始链接
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
// 查找函数
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 删除节点
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key) // 先去找值
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key) // 先去找值
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else // 找到了
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr) // 第一种情况
{
if (cur == _root)
_root = cur->_right;
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr) // 第二种情况
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else // 第三种情况
{
// 替换法
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
// 这样方便调用
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
// 析构函数
void Destroy(Node* root) // 采用递归的形式
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->right);
delete root;
}
// 拷贝构造
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_key); // 创建一个节点
newRoot->_left = Copy(root->left); // 拷贝左子树
newRoot->_right = Copy(root->_right); // 拷贝右子树
return newRoot; // 返回根
}
// 递归版本
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else
{
Node* rightMin = root->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, rightMin->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
// 递归版本
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// 递归版本
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
// 中序遍历
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr
};
}
namespace key_value
{
template<class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
Node* _left;
Node* _right;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
, _value(value)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key, value);
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else
{
// 替换法
Node* rightMinParent = cur;
Node* rightMin = cur->_right;
while (rightMin->_left)
{
rightMinParent = rightMin;
rightMin = rightMin->_left;
}
cur->_key = rightMin->_key;
if (rightMin == rightMinParent->_left)
rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right;
else
rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right;
delete rightMin;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
}🌟结束语
今天内容就到这里啦,时间过得很快,大家沉下心来好好学习,会有一定的收获的,大家多多坚持,嘻嘻,成功路上注定孤独,因为坚持的人不多。那请大家举起自己的小手给博主一键三连,有你们的支持是我最大的动力💞💞💞,回见。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-840482.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-840482.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-840482.html
到了这里,关于【C++】二叉树进阶之二叉搜索树的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!