灰狼优化算法(MOGWO)
摘要
- 固定大小的外部档案用来保存帕累托优化解
- 在多目标搜索空间中,这个档案被用来定义狼群社会等级和捕猎行为
- 这个算法在10个多目标测试集进行测试,并与MOEA/D和MOPSO进行对比
引言
- 将多个目标集成一个单一的目标
两个缺点:一个均匀分布的权重不能保证生成一组均匀分布的帕累托优化解集;由于不能使用负权重,且所有权重之和必须为常数,该方法无法找帕累托最优前沿的非凸区域。
- MOPSO的收敛速度非常快,在多目标优化中容易出现假帕累托最优前沿过早终止的问题
GWO
该算法是模拟灰狼的社会领导关系和捕猎技术,为了模拟灰狼在狩猎过程中的包围行为,除了社会领导外,提出了一下方程:

t表示当前代数,A和C是向量系数,Xp表示猎物位置,X表示一只灰狼的位置,A和C的计算公式:

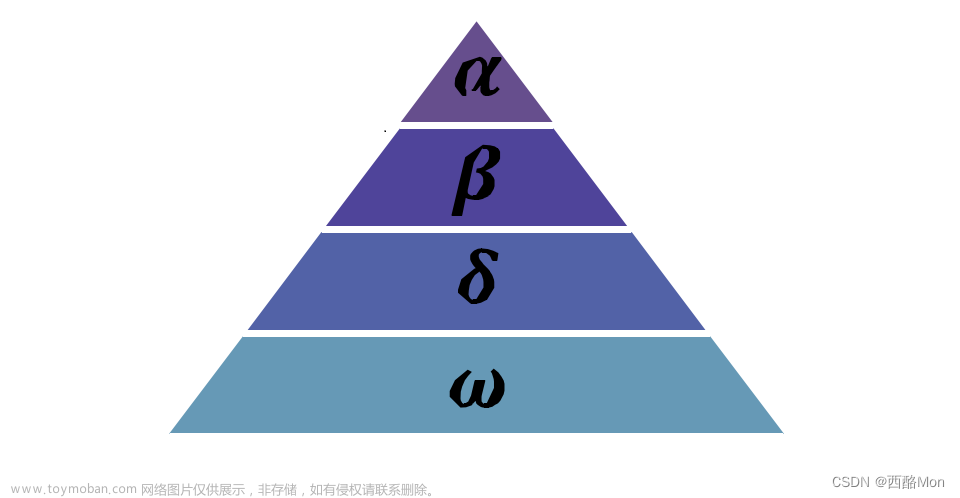
a是在迭代过程中从2线性减到0,r1和r2是[0,1]中的随机数,alpha、beta、gamma是前三个最优解。

A的随机值大于1或小于-1,保证了狼群和猎物的偏离,C有助于GWO在优化过程中表现出更随机的行为,有利于规避局部最优。当A的绝对值大于1时,狼群偏离猎物,当A的绝对值小于1时,狼群向猎物收敛。
MOGWO
MOGWO比起GWO多了两个新增部分:
- 一个档案用于存储所得帕累托最优解集和进行非支配排序
- 选择策略,用于选择alpha、beta、gamma作为领导。
MOGWO的伪代码如下:
MOGWO算法的收敛性是有保证的,因为它利用了相同的数学模型来搜索最优解。事实证明,GWO要求搜索智能体在优化的初期突然改变位置,在优化的后期逐渐改变位置。MOGWO算法继承了GWO的所有特征,这意味着搜索智能体以相同的方式探索和开发搜索空间。主要的区别是,MOGWO围绕一组存档个体进行搜索(即使存档没有变化,也可能不同),而GWO只保存和改进三个最好的解。
MOGWO部分源代码如下,需要完整代码请联系我(免费)。
%% 清理空间
clear all
clc
close all
%% MOGWO算法参数
drawing_flag = 1;
% 测试函数及其细节确定
TestProblem='UF1';
nVar=10;
fobj = cec09(TestProblem);
xrange = xboundary(TestProblem, nVar);
lb=xrange(:,1)';
ub=xrange(:,2)';
VarSize=[1 nVar];
% 迭代次数、种群数量、存档数量
GreyWolves_num=100;
MaxIt=200; % Maximum Number of Iterations
Archive_size=100; % Repository Size
% 网格机制的参数
alpha=0.1; % Grid Inflation Parameter
nGrid=10; % Number of Grids per each Dimension
beta=4; % Leader Selection Pressure Parameter
gamma=2;
%% 种群初始化
GreyWolves=CreateEmptyParticle(GreyWolves_num);
for i=1:GreyWolves_num
GreyWolves(i).Velocity=0;%灰狼的初始速度为0
GreyWolves(i).Position=zeros(1,nVar);%灰狼的初始位置也为0
for j=1:nVar
GreyWolves(i).Position(1,j)=unifrnd(lb(j),ub(j),1);%灰狼的位置
end
GreyWolves(i).Cost=fobj(GreyWolves(i).Position')';
GreyWolves(i).Best.Position=GreyWolves(i).Position;
GreyWolves(i).Best.Cost=GreyWolves(i).Cost;
end文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842055.html
% 确定支配关系
GreyWolves=DetermineDomination(GreyWolves);
% 非支配解存档
Archive=GetNonDominatedParticles(GreyWolves);
% 网格机制
Archive_costs=GetCosts(Archive); % 存档种群的适应度
G=CreateHypercubes(Archive_costs,nGrid,alpha);
for i=1:numel(Archive)
[Archive(i).GridIndex Archive(i).GridSubIndex]=GetGridIndex(Archive(i),G);
end
%% 迭代
for it=1:MaxIt
a=2-it*((2)/MaxIt);
for i=1:GreyWolves_num
clear rep2
clear rep3
% 选头狼
% Choose the alpha, beta, and delta grey wolves
Delta=SelectLeader(Archive,beta);
Beta=SelectLeader(Archive,beta);
Alpha=SelectLeader(Archive,beta);
% If there are less than three solutions in the least crowded
% hypercube, the second least crowded hypercube is also found
% to choose other leaders from.
if size(Archive,1)>1
counter=0;
for newi=1:size(Archive,1)
if sum(Delta.Position=Archive(newi).Position)=0
counter=counter+1;
rep2(counter,1)=Archive(newi);
end
end
Beta=SelectLeader(rep2,beta);
end
% This scenario is the same if the second least crowded hypercube
% has one solution, so the delta leader should be chosen from the
% third least crowded hypercube.
if size(Archive,1)>2
counter=0;
for newi=1:size(rep2,1)
if sum(Beta.Position=rep2(newi).Position)=0
counter=counter+1;
rep3(counter,1)=rep2(newi);
end
end
Alpha=SelectLeader(rep3,beta);
end
% 同GWO一样
% Eq.(3.4) in the paper
c=2.*rand(1, nVar);
% Eq.(3.1) in the paper
D=abs(c.*Delta.Position-GreyWolves(i).Position);
% Eq.(3.3) in the paper
A=2.a.rand(1, nVar)-a;
% Eq.(3.8) in the paper
X1=Delta.Position-A.*abs(D);
% Eq.(3.4) in the paper
c=2.*rand(1, nVar);
% Eq.(3.1) in the paper
D=abs(c.*Beta.Position-GreyWolves(i).Position);
% Eq.(3.3) in the paper
A=2.a.rand()-a;
% Eq.(3.9) in the paper
X2=Beta.Position-A.*abs(D);
% Eq.(3.4) in the paper
c=2.*rand(1, nVar);
% Eq.(3.1) in the paper
D=abs(c.*Alpha.Position-GreyWolves(i).Position);
% Eq.(3.3) in the paper
A=2.a.rand()-a;
% Eq.(3.10) in the paper
X3=Alpha.Position-A.*abs(D);
% Eq.(3.11) in the paper
GreyWolves(i).Position=(X1+X2+X3)./3;
% Boundary checking
GreyWolves(i).Position=min(max(GreyWolves(i).Position,lb),ub);
GreyWolves(i).Cost=fobj(GreyWolves(i).Position')';
end
% 支配关系、存档、网格更新
GreyWolves=DetermineDomination(GreyWolves);
non_dominated_wolves=GetNonDominatedParticles(GreyWolves);
Archive=[Archive
non_dominated_wolves];
Archive=DetermineDomination(Archive);
Archive=GetNonDominatedParticles(Archive);
for i=1:numel(Archive)
[Archive(i).GridIndex Archive(i).GridSubIndex]=GetGridIndex(Archive(i),G);
end
if numel(Archive)>Archive_size
EXTRA=numel(Archive)-Archive_size;
Archive=DeleteFromRep(Archive,EXTRA,gamma);
Archive_costs=GetCosts(Archive);
G=CreateHypercubes(Archive_costs,nGrid,alpha);
end
disp(['In iteration ' num2str(it) ': Number of solutions in the archive = ' num2str(numel(Archive))]);
save results
% Results
costs=GetCosts(GreyWolves);
Archive_costs=GetCosts(Archive);
hold off
plot(costs(1,:),costs(2,:),'k.');
hold on
plot(Archive_costs(1,:),Archive_costs(2,:),'rd');
legend('Grey wolves','Non-dominated solutions');
drawnow文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842055.html
end
到了这里,关于灰狼优化算法(MOGWO)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!