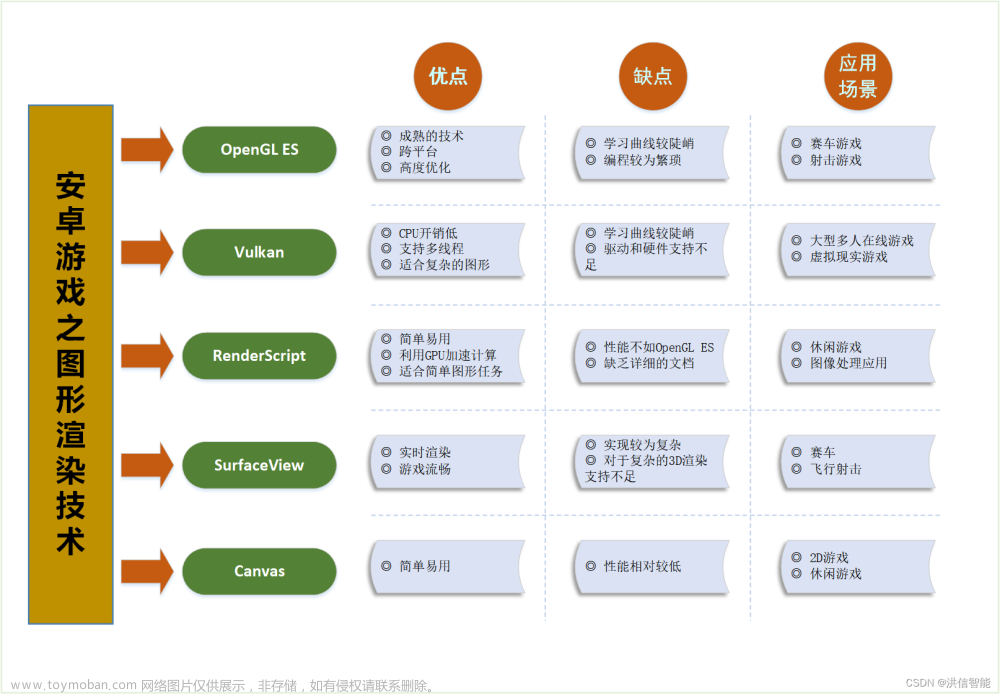
大气散射效果对游戏画质提升来说巨大,本文主要从代码层面讲解下大气散射
单次散射

路径 AB 观察大气,并且求解 B 点的大气颜色,光线在大气中只发生一次散射,散射点为 P
阳光进入大气层CP开始衰减,在P点发生散射,然后PA衰减进入A点相机
T表示衰减系数 表示某段路径上光照的衰减程度
S表示散射系数 表示有多少光散射的角度为θ,λ为波长,h

)
实际上在路径 AB(也可能是斜的一条射线) 上有无数个 P 点,因此最终求解是对 AB 路径上每一个点的光照贡献进行累加 (求积分,不同高度不同密度)

散射类型分2种
Rayleigh Scattering
大小远小于光线波长的粒子,由于粒子比波长还要小很多,所以光的波长也会影响散射程度
Mie Scattering
大小远大于光线波长的粒子,由于光的波长相较于这些粒子大小来说是可以忽略的,所以认为Mie Scattering和光线波长无关,Mie Scattering是太阳周围光晕的主要成因
散射方程
λ光的波长(R680 G550 B440nm),θ散射角度,h高度,n空气的折射率,N一个常数表示大气厚度,大气密度ρ(h)密度比,在海平面为1,随高度呈指数下降

散射方程主要分为,1散射系数,2相位函数,3大气密度比
1 散射系数
在海平面上,是一个常数
Rayleigh 0.005802f, 0.013558f, 0.033100f
Mie 来说 0.003996f, 0.003996f, 0.003996f
2 相位函数

3 大气密度比
Rayleigh 来说,H= 8500米
Mie 来说,H = 1200米
颜色来表示Rayleigh的散射

Absorption
除了发生散射,大气中还有臭氧和甲烷吸收
臭氧(O3)臭氧主要吸收短波紫外线
甲烷(CH4)甲烷是一种吸收红外光而反射蓝光的气体

Ragleigh没有吸收
用颜色来表示下Absorption

公式表

伪代码
Function Transmittance(float3 A, float3 B)
{
float SAMPLE=64//采样次数
float distance=length(A,B)
float3 dir=B-A
float ds=distance/SAMPLE
float3 p = A + (dir * ds) * 0.5;
float3 result=0
//算积分
for(int i=0; i<SAMPLE; i++)
{
float h = length(p)
float3 extinctionMie = MieExtinction(h);
float3 extinctionRay = RayleighCoefficient(h)
float3 extinctionOzo = OzoneAbsorption(h)
result += (extinctionMie + extinctionRay + extinctionOzo)*ds
}
return exp(-result)
}
float3 eyePos
float3 viewDir
float3 lightDir
float3 P = eyePos + (viewDir * ds) * 0.5
float cos𝜃 = dot(lightDir, viewDir)
float3 RayleighScattering = RayleighCoefficient(h) * RayleiPhase(cos𝜃)
float3 MieScattering = MieCoefficient(h) * MiePhase(cos𝜃)
Single Scattering = Transmittance(P,lightDir) *(RayleighScattering+MieScattering) * Transmittance(eyePos,P)Multi Scattering
微分立体角
在讲解多次散射,需要对微分立体角有一个了解,好理解能量守恒


整个球体的立体角就是4π
微分立体角就是A/(r*r) 面积除以半径的平方
辐射度量学

辐射强度(Radiant Intensity) 是从光源出发,每单位立体角上的功率(亮度)
辐照度(Irradiance) 是入射投影到单位面积上的功率(光照、辐射通量)
辐射(Radiance) 是描述光在环境中分布的基本场量,辐射描述 每单位立体角、每单位垂直面积的功率
总结:假设从光源总的辐射强度Radiant Intensity为1,半径为2的立体角的辐照度Irradiance就是1/(4π2^2),
辐射Radiance就是1/(4π2^2)dw,每个微分立体角可以接受到的能量
比如我们要算一个半球面能接受多少光照,直接做一个积分,就可以直接算出来,这样计算的光照能量守恒

多散次射的经过

总的来说,a算出单次散射,b加上地面的反射,c做一个球面的积分,d把整个视线路径做一个积分,求出有多少光可以到眼睛里
Bruneton2017
https://github.com/ebruneton/precomputed_atmospheric_scattering
参考了Bruneton的代码,功能很全,仅需自己修改采样shadow
伪代码
ComputeTransmittanceLUT()
ComputeDirectIrradianceLUT()
ComputeSingleScatteringLUT()
for (uint order = 2; order <= numScatteringOrders; order++) {
ComputeScatteringDensity()// order>=2计算间接光照, order>2地球表面反射光
ComputeIndirectIrradiance()//地球表面反射光
ComputeMultipleScattering()//PA积分
}优点就是一次计算完各个方向r(高度), mu(视角天顶角), mu_s(太阳天顶角), nu(视线和太阳的夹角)
并且把mu_s和nu压缩到一个变量里面
Number frag_coord_nu = floor(frag_coord.x / Number(SCATTERING_TEXTURE_MU_S_SIZE));
Number frag_coord_mu_s = fmod(frag_coord.x, Number(SCATTERING_TEXTURE_MU_S_SIZE))保存结果到一个3DTexture,直接采样就行了
缺点就是如果需要修改默认参数,就要重新渲染一次,消耗巨大,PC都卡,移动端更受不了
UnrealEngineSkyAtmosphere的LUT预处理
GitHub - sebh/UnrealEngineSkyAtmosphere: Unreal Engine Sky Atmosphere Rendering Technique
主要需要计算4个LUT
TransmittanceLUT MultipleScatteringLUT Sky-ViewLUT AerialPerspectiveLUT
TransmittanceLUT
uv 分别表示 高度(r)和视角天顶角(mu)
[numthreads(8, 8, 1)]
void IntergalTransmittanceLUT(uint3 id: SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 pixPos = id.xy + 0.5f;
AtmosphereParameters Atmosphere = GetAtmosphereParameters();
// Compute camera position from LUT coords
float2 uv = (pixPos) / float2(TRANSMITTANCE_TEXTURE_WIDTH, TRANSMITTANCE_TEXTURE_HEIGHT);
float viewHeight;
float viewZenithCosAngle;
UvToLutTransmittanceParams(Atmosphere, viewHeight, viewZenithCosAngle, uv);
// A few extra needed constants
float3 WorldPos = float3(0.0f, viewHeight, 0.0f);
float3 WorldDir = float3(sqrt(1.0 - viewZenithCosAngle * viewZenithCosAngle), viewZenithCosAngle, 0.0f);
const bool ground = false;
const float SampleCountIni = 40.0f; // Can go a low as 10 sample but energy lost starts to be visible.
const float DepthBufferValue = -1.0;
const bool VariableSampleCount = false;
const bool MieRayPhase = false;
float3 transmittance = exp(-IntegrateScatteredLuminance(uv, WorldPos, WorldDir, sun_direction, Atmosphere,
ground, SampleCountIni, DepthBufferValue,
VariableSampleCount, MieRayPhase).OpticalDepth);
_TransmittanceLUT[id.xy] = float4(transmittance, 1.0f);
}代码很简单,就是遍历 高度和视角天顶角,太阳朝向已知,其他都可以算出来,把透射记录到Texture里面就行
void UvToLutTransmittanceParams(AtmosphereParameters Atmosphere, out float viewHeight, out float viewZenithCosAngle, in float2 uv)
{
//uv = float2(fromSubUvsToUnit(uv.x, TRANSMITTANCE_TEXTURE_WIDTH), fromSubUvsToUnit(uv.y, TRANSMITTANCE_TEXTURE_HEIGHT)); // No real impact so off
float x_mu = uv.x;
float x_r = uv.y;
float H = sqrt(Atmosphere.TopRadius * Atmosphere.TopRadius - Atmosphere.BottomRadius * Atmosphere.BottomRadius);
float rho = H * x_r;
viewHeight = sqrt(rho * rho + Atmosphere.BottomRadius * Atmosphere.BottomRadius);
float d_min = Atmosphere.TopRadius - viewHeight;
float d_max = rho + H;
float d = d_min + x_mu * (d_max - d_min);
viewZenithCosAngle = d == 0.0 ? 1.0f : (H * H - rho * rho - d * d) / (2.0 * viewHeight * d);
viewZenithCosAngle = clamp(viewZenithCosAngle, -1.0, 1.0);
}
UvToLutTransmittanceParams把r和mu压缩到一个最大范围里面用来提高精度
mu视线角度长度范围就是d_min 和 d_max

float H = sqrt(Atmosphere.TopRadius * Atmosphere.TopRadius - Atmosphere.BottomRadius * Atmosphere.BottomRadius);该H和图中H不是一个点,表示把精度压缩到以(0,0)为原点的H坐标系中
IntegrateScatteredLuminance中,主要获取medium.extinction * dt
viewZenithCosAngle = d == 0.0 ? 1.0f : (H * H - rho * rho - d * d) / (2.0 * viewHeight * d);
...
MediumSampleRGB sampleMediumRGB(in float3 WorldPos, in AtmosphereParameters Atmosphere)
{
const float viewHeight = length(WorldPos) - Atmosphere.BottomRadius;
const float densityMie = exp(Atmosphere.MieDensityExpScale * viewHeight);
const float densityRay = exp(Atmosphere.RayleighDensityExpScale * viewHeight);
const float densityOzo = saturate(viewHeight < Atmosphere.AbsorptionDensity0LayerWidth ?
Atmosphere.AbsorptionDensity0LinearTerm * viewHeight + Atmosphere.AbsorptionDensity0ConstantTerm :
Atmosphere.AbsorptionDensity1LinearTerm * viewHeight + Atmosphere.AbsorptionDensity1ConstantTerm);
MediumSampleRGB s;
s.scatteringMie = densityMie * Atmosphere.MieScattering;
s.absorptionMie = densityMie * Atmosphere.MieAbsorption;
s.extinctionMie = densityMie * Atmosphere.MieExtinction;
s.scatteringRay = densityRay * Atmosphere.RayleighScattering;
s.absorptionRay = 0.0f;
s.extinctionRay = s.scatteringRay + s.absorptionRay;
s.scatteringOzo = 0.0;
s.absorptionOzo = densityOzo * Atmosphere.AbsorptionExtinction;
s.extinctionOzo = s.scatteringOzo + s.absorptionOzo;
s.scattering = s.scatteringMie + s.scatteringRay + s.scatteringOzo;
s.absorption = s.absorptionMie + s.absorptionRay + s.absorptionOzo;
s.extinction = s.extinctionMie + s.extinctionRay + s.extinctionOzo;
s.albedo = getAlbedo(s.scattering, s.extinction);
return s;
}
...
MediumSampleRGB medium = sampleMediumRGB(P, Atmosphere);
const float3 SampleOpticalDepth = medium.extinction * dt;
const float3 SampleTransmittance = exp(-SampleOpticalDepth);
OpticalDepth += SampleOpticalDepth;最后得到一张LUT

长:透射率,宽:高度
MultipleScatteringLUT
numthreads(1, 1, 64)]
void NewMultiScattCS(uint3 ThreadId : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 pixPos = float2(ThreadId.xy) + 0.5f;
float2 uv = pixPos / MultiScatteringLUTRes;
uv = float2(fromSubUvsToUnit(uv.x, MultiScatteringLUTRes), fromSubUvsToUnit(uv.y, MultiScatteringLUTRes));
AtmosphereParameters Atmosphere = GetAtmosphereParameters();
float cosSunZenithAngle = uv.x * 2.0 - 1.0;
float3 sunDir = float3(sqrt(saturate(1.0 - cosSunZenithAngle * cosSunZenithAngle)), cosSunZenithAngle, 0.0);
// We adjust again viewHeight according to PLANET_RADIUS_OFFSET to be in a valid range.
float viewHeight = Atmosphere.BottomRadius + saturate(uv.y + PLANET_RADIUS_OFFSET) * (Atmosphere.TopRadius -
Atmosphere.BottomRadius - PLANET_RADIUS_OFFSET);
float3 WorldPos = float3(0.0f, viewHeight, 0.0f);
float3 WorldDir = float3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
const bool ground = true;
const float SampleCountIni = 20; // a minimum set of step is required for accuracy unfortunately
const float DepthBufferValue = -1.0;
const bool VariableSampleCount = false;
const bool MieRayPhase = false;
const float SphereSolidAngle = 4.0 * PI;
const float IsotropicPhase = 1.0 / SphereSolidAngle;
// Reference. Since there are many sample, it requires MULTI_SCATTERING_POWER_SERIE to be true for accuracy and to avoid divergences (see declaration for explanations)
#define SQRTSAMPLECOUNT 8
const float sqrtSample = float(SQRTSAMPLECOUNT);
float i = 0.5f + float(ThreadId.z / SQRTSAMPLECOUNT);
float j = 0.5f + float(ThreadId.z - float((ThreadId.z / SQRTSAMPLECOUNT) * SQRTSAMPLECOUNT));
{
float randA = i / sqrtSample;
float randB = j / sqrtSample;
float theta = 2.0f * PI * randA;
float phi = acos(1.0f - 2.0f * randB);
// uniform distribution https://mathworld.wolfram.com/SpherePointPicking.html
//phi = PI * randB; // bad non uniform
float cosPhi = cos(phi);
float sinPhi = sin(phi);
float cosTheta = cos(theta);
float sinTheta = sin(theta);
WorldDir.x = cosTheta * sinPhi;
WorldDir.y = sinTheta * sinPhi;
WorldDir.z = cosPhi;
SingleScatteringResult result = IntegrateScatteredLuminance(uv, WorldPos, WorldDir, sunDir, Atmosphere,
ground, SampleCountIni, DepthBufferValue,
VariableSampleCount, MieRayPhase);
MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z] = result.MultiScatAs1 * SphereSolidAngle / (sqrtSample * sqrtSample);
LSharedMem[ThreadId.z] = result.L * SphereSolidAngle / (sqrtSample * sqrtSample);
}
#undef SQRTSAMPLECOUNT
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
// 64 to 32
if (ThreadId.z < 32)
{
MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z] += MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z + 32];
LSharedMem[ThreadId.z] += LSharedMem[ThreadId.z + 32];
}
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
// 32 to 16
if (ThreadId.z < 16)
{
MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z] += MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z + 16];
LSharedMem[ThreadId.z] += LSharedMem[ThreadId.z + 16];
}
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
// 16 to 8 (16 is thread group min hardware size with intel, no sync required from there)
if (ThreadId.z < 8)
{
MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z] += MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z + 8];
LSharedMem[ThreadId.z] += LSharedMem[ThreadId.z + 8];
}
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
if (ThreadId.z < 4)
{
MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z] += MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z + 4];
LSharedMem[ThreadId.z] += LSharedMem[ThreadId.z + 4];
}
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
if (ThreadId.z < 2)
{
MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z] += MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z + 2];
LSharedMem[ThreadId.z] += LSharedMem[ThreadId.z + 2];
}
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
if (ThreadId.z < 1)
{
MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z] += MultiScatAs1SharedMem[ThreadId.z + 1];
LSharedMem[ThreadId.z] += LSharedMem[ThreadId.z + 1];
}
GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync();
if (ThreadId.z > 0)
return;
float3 MultiScatAs1 = MultiScatAs1SharedMem[0] * IsotropicPhase; // Equation 7 f_ms
float3 InScatteredLuminance = LSharedMem[0] * IsotropicPhase; // Equation 5 L_2ndOrder
// MultiScatAs1 represents the amount of luminance scattered as if the integral of scattered luminance over the sphere would be 1.
// - 1st order of scattering: one can ray-march a straight path as usual over the sphere. That is InScatteredLuminance.
// - 2nd order of scattering: the inscattered luminance is InScatteredLuminance at each of samples of fist order integration. Assuming a uniform phase function that is represented by MultiScatAs1,
// - 3nd order of scattering: the inscattered luminance is (InScatteredLuminance * MultiScatAs1 * MultiScatAs1)
// - etc.
#if MULTI_SCATTERING_POWER_SERIE==0
float3 MultiScatAs1SQR = MultiScatAs1 * MultiScatAs1;
float3 L = InScatteredLuminance * (1.0 + MultiScatAs1 + MultiScatAs1SQR + MultiScatAs1 * MultiScatAs1SQR + MultiScatAs1SQR * MultiScatAs1SQR);
#else
// For a serie, sum_{n=0}^{n=+inf} = 1 + r + r^2 + r^3 + ... + r^n = 1 / (1.0 - r), see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geometric_series
const float3 r = MultiScatAs1;
const float3 SumOfAllMultiScatteringEventsContribution = 1.0f / (1.0 - r);
float3 L = InScatteredLuminance * SumOfAllMultiScatteringEventsContribution; // Equation 10 Psi_ms
#endif
OutputTexture[ThreadId.xy] = float4(MultipleScatteringFactor * L, 1.0f);
}uv 分别表示 高度(r)和太阳天顶角(mu_s)
根据r算出WorldPos,根据mu_s算出sunDir,均匀采样球面64个点,算球面积分
WorldDir.x = cosTheta * sinPhi;
WorldDir.y = sinTheta * sinPhi;
WorldDir.z = cosPhi;如何球面均匀采样,参考https://mathworld.wolfram.com/SpherePointPicking.html
MultipleScattering和Bruneton2017对比,做了优化
const float SphereSolidAngle = 4.0 * PI;
const float IsotropicPhase = 1.0 / SphereSolidAngle;1.各项同性
2.采样周围点的光能量相同
相当于一个系数衰减
float3 MultiScatAs1 = MultiScatAs1SharedMem[0] * IsotropicPhase; // Equation 7 f_ms
float3 InScatteredLuminance = LSharedMem[0] * IsotropicPhase; // Equation 5 L_2ndOrder把结果加一起,GroupMemoryBarrierWithGroupSync是做什么的,可以参考
Compute Shader中的Parallel Reduction和Parallel Scan - 知乎

IntegrateScatteredLuminance里面积分运算用了寒霜引擎的方法
float3 MS = medium.scattering * 1;
float3 MSint = (MS - MS * SampleTransmittance) / medium.extinction;
result.MultiScatAs1 += throughput * MSint;
...
float3 Sint = (S - S * SampleTransmittance) / medium.extinction; // integrate along the current step segment
L += throughput * Sint; // accumulate and also take into account the transmittance from previous steps
throughput *= SampleTransmittance;
Sky-ViewLUT
[numthreads(8, 8, 1)]
void IntergalSkyViewLutPS(uint3 id: SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 pixPos = id.xy + 0.5f;
AtmosphereParameters Atmosphere = GetAtmosphereParameters();
float3 WorldPos = camera + float3(0, Atmosphere.BottomRadius, 0);
float2 uv = pixPos / float2(192.0, 108.0);
float viewHeight = length(WorldPos);
float viewZenithCosAngle;
float lightViewCosAngle;
UvToSkyViewLutParams(Atmosphere, viewZenithCosAngle, lightViewCosAngle, viewHeight, uv);
float3 SunDir;
{
float3 UpVector = WorldPos / viewHeight;
float sunZenithCosAngle = dot(UpVector, sun_direction);
SunDir = normalize(float3(sqrt(1.0 - sunZenithCosAngle * sunZenithCosAngle), sunZenithCosAngle, 0.0));
}
WorldPos = float3(0.0f, viewHeight, 0.0f);
float viewZenithSinAngle = sqrt(1 - viewZenithCosAngle * viewZenithCosAngle);
float3 WorldDir = float3(viewZenithSinAngle * lightViewCosAngle,
viewZenithCosAngle,
viewZenithSinAngle * sqrt(1.0 - lightViewCosAngle * lightViewCosAngle));
// Move to top atmospehre
if (!MoveToTopAtmosphere(WorldPos, WorldDir, Atmosphere.TopRadius))
{
// Ray is not intersecting the atmosphere
_SkyViewLUT[id.xy] = float3(0, 0, 0);
return;
}
const bool ground = false;
const float SampleCountIni = 30;
const float DepthBufferValue = -1.0;
const bool VariableSampleCount = true;
const bool MieRayPhase = true;
SingleScatteringResult ss = IntegrateScatteredLuminance(uv, WorldPos, WorldDir, SunDir, Atmosphere, ground,
SampleCountIni, DepthBufferValue, VariableSampleCount,
MieRayPhase);
_SkyViewLUT[id.xy] = ss.L;
}viewZenithCosAngle和lightViewCosAngle取值范围[1,-1]角度0-90度
UvToSkyViewLutParams(Atmosphere, viewZenithCosAngle, lightViewCosAngle, viewHeight, uv);WorldPos UpVector WorldDir 跟UE的区别改了up朝向,UE是z朝上,unity是y朝上

AerialPerspectiveLUT
[numthreads(8, 8, 1)]
void IntergalCameraVolumeLUT(uint3 id: SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
float2 pixPos = id.xy + 0.5f;
float w, h, d;
_CameraVolumeLUT.GetDimensions(w, h, d);
AtmosphereParameters Atmosphere = GetAtmosphereParameters();
float2 uv = pixPos / float2(w, h);
float3 ClipSpace = float3(uv * float2(2.0, -2.0) - float2(1.0, -1.0), 0.5);
float4 HViewPos = mul(gSkyInvProjMat, float4(ClipSpace, 1.0));
float3 WorldDir = normalize(mul((float3x3)gSkyInvViewMat, HViewPos.xyz / HViewPos.w));
float earthR = Atmosphere.BottomRadius;
float3 camPos = camera + float3(0, earthR, 0);
float3 SunDir = sun_direction;
float Slice = ((id.z + 0.5f) / AP_SLICE_COUNT);
Slice *= Slice; // squared distribution
Slice *= AP_SLICE_COUNT;
float3 WorldPos = camPos;
// Compute position from froxel information
float tMax = AerialPerspectiveSliceToDepth(Slice);
float3 newWorldPos = WorldPos + tMax * WorldDir;
// If the voxel is under the ground, make sure to offset it out on the ground.
float viewHeight = length(newWorldPos);
if (viewHeight <= (Atmosphere.BottomRadius + PLANET_RADIUS_OFFSET))
{
// Apply a position offset to make sure no artefact are visible close to the earth boundaries for large voxel.
newWorldPos = normalize(newWorldPos) * (Atmosphere.BottomRadius + PLANET_RADIUS_OFFSET + 0.001f);
WorldDir = normalize(newWorldPos - camPos);
tMax = length(newWorldPos - camPos);
}
float tMaxMax = tMax;
const bool ground = false;
const float SampleCountIni = max(1.0, float(id.z + 1.0) * 2.0f);
const float DepthBufferValue = -1.0;
const bool VariableSampleCount = false;
const bool MieRayPhase = true;
SingleScatteringResult ss = IntegrateScatteredLuminance(uv, WorldPos, WorldDir, SunDir, Atmosphere, ground,
SampleCountIni, DepthBufferValue, VariableSampleCount,
MieRayPhase, tMaxMax);
const float Transmittance = dot(ss.Transmittance, float3(1.0f / 3.0f, 1.0f / 3.0f, 1.0f / 3.0f));
_CameraVolumeLUT[id] = float4(ss.L, 1.0 - Transmittance);
}
#define AP_SLICE_COUNT 32.0f 切片数
#define AP_KM_PER_SLICE 3.0f 一切片包含多少公里
...
float tMax = AerialPerspectiveSliceToDepth(Slice); 根据切片还原射线最远可到达距离
号称1ms可以在6s上渲染完成4个lut

最后在后处理加上AerialPerspective和shadow的处理即可
结尾:
SlightlyMad,Sebh,Bruneton 的大气散射效果实现各不相同,需要根据实际项目需求修改效果
在移动端性能需要做一个取舍,比如原神的天空不是完全基于物理大气渲染,效果也是很棒的
本人能力有限,可能有一些错误,请多多指教
项目源码
https://github.com/wujuju/UnitySkyAtmosphere
参考资料:
01.游戏引擎导论 | GAMES104-现代游戏引擎:从入门到实践_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
GAMES101-现代计算机图形学入门-闫令琪_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
GitHub - sebh/UnrealEngineSkyAtmosphere: Unreal Engine Sky Atmosphere Rendering Technique
GitHub - SlightlyMad/AtmosphericScattering: Atmospheric Scattering for Unity
https://github.com/ebruneton/precomputed_atmospheric_scattering
Volumetric Atmospheric Scattering - Alan Zucconi文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842233.html
https://sebh.github.io/publications/egsr2020.pdf文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842233.html
到了这里,关于unity大气散射的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!