1. Phantom Rows的定义(现象)
The so-called phantom problem occurs within a transaction when the same query produces different sets of rows at different times. For example, if a SELECT is executed twice, but returns a row the second time that was not returned the first time, the row is a “phantom” row.
2.举例说明
Suppose that there is an index on the id column of the child table and that you want to read and lock all rows from the table having an identifier value larger than 100, with the intention of updating some column in the selected rows later:
SELECT * FROM child WHERE id > 100 FOR UPDATE;
The query scans the index starting from the first record where id is bigger than 100. Let the table contain rows having id values of 90 and 102. If the locks set on the index records in the scanned range do not lock out inserts made in the gaps (in this case, the gap between 90 and 102), another session can insert a new row into the table with an id of 101. If you were to execute the same SELECT within the same transaction, you would see a new row with an id of 101 (a “phantom”) in the result set returned by the query.
If we regard a set of rows as a data item, the new phantom child would violate the isolation principle of transactions that a transaction should be able to run so that the data it has read does not change during the transaction.---违法了事务ACID原则中的Isolation【隔离;孤立;隔绝,绝缘;脱离】。
【Isolation,可以理解为把你选中的数据 隔离出来,保护起来,防止被其它事务污染了】
3.机制设计上采取的预防措施
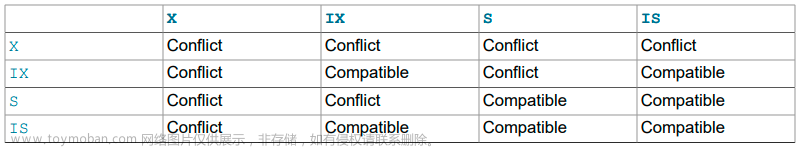
To prevent phantoms, InnoDB uses an algorithm called next-key locking that combines index-row locking with gap locking. InnoDB performs row-level locking in such a way that when it searches or scans a table index, it sets shared or exclusive locks on the index records it encounters. Thus, the row-level locks are actually index-record locks. In addition【此外】, a next-key lock on an index record also affects the “gap” before the index record. That is, a next-key lock is an index-record lock plus a gap lock on the gap preceding the index record. If one session has a shared or exclusive lock on record R in an index, another session cannot insert a new index record in the gap immediately before R in the index order.【行锁+间隙锁,且加的gap 是 瞻前不顾后】
4.补充说明
【既要瞻前又要顾后怎么办呢?】
When InnoDB scans an index, it can also lock the gap after the last record in the index. Just that happens in the preceding example: To prevent any insert into the table where id would be bigger than 100, the locks set by InnoDB include a lock on the gap following id value 102.--【加锁呗,就要例子中的语句,加个 FOR UPDATE】
【唯一性+next-key lock 条件下的insert】
You can use next-key locking to implement【实施】 a uniqueness 【唯一性、单值性】check in your application: If you read your data in share mode and do not see a duplicate for a row you are going to insert, then you can safely insert your row and know that the next-key lock set on the successor【继任者;后继的事物】 of your row during the read prevents anyone meanwhile inserting a duplicate for your row. Thus, the next-key locking enables you to “lock” the nonexistence【不存在】 of something in your table.
5.回顾
很有必要再次回顾下什么是Next-Key Locks。
定义:
A next-key lock is a combination of a record lock on the index record and a gap lock on the gap before the index record.
具体的解释
InnoDB performs row-level locking in such a way that when it searches or scans a table index, it sets shared or exclusive locks on the index records it encounters. Thus, the row-level locks are actually indexrecord locks. A next-key lock on an index record also affects the “gap” before that index record. That is, a next-key lock is an index-record lock plus a gap lock on the gap preceding the index record. If one session has a shared or exclusive lock on record R in an index, another session cannot insert a new index record in the gap immediately before R in the index order.
作用:
Next-Key Locks 在RR的隔离级别下出现,主要是解决phantom的情况。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842607.html
By default, InnoDB operates in REPEATABLE READ transaction isolation level. In this case, InnoDB uses next-key locks for searches and index scans, which prevents phantom rows。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842607.html
到了这里,关于MySQL 8.0 Reference Manual(读书笔记67节--Phantom Rows)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!