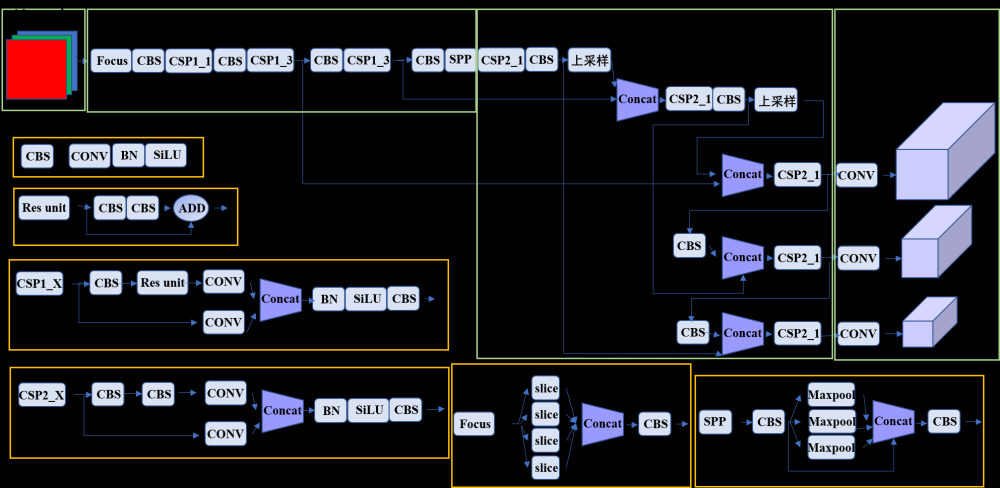
介绍一下yolov5怎么生成热力图,并且修改模型后如何生成热力图。
1、在原始yolov5中生成热力图
首先我们在原始版本的yolov5中进行一个热力图代码的搭建,后续修改模型后的热力图代码只需要在此基础上修改就可以了。
v5生成热力图的博客非常多,但是还是介绍一下吧。
1、代码版本
v5的版本是6.0
2、热力图代码
1、在项目根目录下创建一个main_gradcam.py
import os
import random
import time
import argparse
import numpy as np
from models.gradcam import YOLOV5GradCAM, YOLOV5GradCAMPP
from models.yolov5_object_detector import YOLOV5TorchObjectDetector
import cv2
# 数据集类别名
names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush'] # class names
# yolov5s网络中的三个detect层
target_layers = ['model_17_cv3_act', 'model_20_cv3_act', 'model_23_cv3_act']
# Arguments
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--model-path', type=str, default="yolov5s.pt", help='Path to the model')
parser.add_argument('--img-path', type=str, default='data/images/bus.jpg', help='input image path')
parser.add_argument('--output-dir', type=str, default='runs/result17', help='output dir')
parser.add_argument('--img-size', type=int, default=640, help="input image size")
parser.add_argument('--target-layer', type=str, default='model_17_cv3_act',
help='The layer hierarchical address to which gradcam will applied,'
' the names should be separated by underline')
parser.add_argument('--method', type=str, default='gradcam', help='gradcam method')
parser.add_argument('--device', type=str, default='cuda', help='cuda or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--no_text_box', action='store_true',
help='do not show label and box on the heatmap')
args = parser.parse_args()
def get_res_img(bbox, mask, res_img):
mask = mask.squeeze(0).mul(255).add_(0.5).clamp_(0, 255).permute(1, 2, 0).detach().cpu().numpy().astype(
np.uint8)
heatmap = cv2.applyColorMap(mask, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
# n_heatmat = (Box.fill_outer_box(heatmap, bbox) / 255).astype(np.float32)
n_heatmat = (heatmap / 255).astype(np.float32)
res_img = res_img / 255
res_img = cv2.add(res_img, n_heatmat)
res_img = (res_img / res_img.max())
return res_img, n_heatmat
def plot_one_box(x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=3):
# this is a bug in cv2. It does not put box on a converted image from torch unless it's buffered and read again!
cv2.imwrite('temp.jpg', (img * 255).astype(np.uint8))
img = cv2.imread('temp.jpg')
# Plots one bounding box on image img
tl = line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
outside = c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3 >= 0 # label fits outside box up
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3 if outside else c1[1] + t_size[1] + 3
outsize_right = c2[0] - img.shape[:2][1] > 0 # label fits outside box right
c1 = c1[0] - (c2[0] - img.shape[:2][1]) if outsize_right else c1[0], c1[1]
c2 = c2[0] - (c2[0] - img.shape[:2][1]) if outsize_right else c2[0], c2[1]
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(img, label, (c1[0], c1[1] - 2 if outside else c2[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3, [225, 255, 255], thickness=tf,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
return img
# 检测单个图片
def main(img_path):
colors = [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in names]
device = args.device
input_size = (args.img_size, args.img_size)
# 读入图片
img = cv2.imread(img_path) # 读取图像格式:BGR
print('[INFO] Loading the model')
# 实例化YOLOv5模型,得到检测结果
model = YOLOV5TorchObjectDetector(args.model_path, device, img_size=input_size, names=names)
# img[..., ::-1]: BGR --> RGB
# (480, 640, 3) --> (1, 3, 480, 640)
torch_img = model.preprocessing(img[..., ::-1])
tic = time.time()
# 遍历三层检测层
for target_layer in target_layers:
# 获取grad-cam方法
if args.method == 'gradcam':
saliency_method = YOLOV5GradCAM(model=model, layer_name=target_layer, img_size=input_size)
elif args.method == 'gradcampp':
saliency_method = YOLOV5GradCAMPP(model=model, layer_name=target_layer, img_size=input_size)
masks, logits, [boxes, _, class_names, conf] = saliency_method(torch_img) # 得到预测结果
result = torch_img.squeeze(0).mul(255).add_(0.5).clamp_(0, 255).permute(1, 2, 0).detach().cpu().numpy()
result = result[..., ::-1] # convert to bgr
# 保存设置
imgae_name = os.path.basename(img_path) # 获取图片名
save_path = f'{args.output_dir}{imgae_name[:-4]}/{args.method}'
if not os.path.exists(save_path):
os.makedirs(save_path)
print(f'[INFO] Saving the final image at {save_path}')
# 遍历每张图片中的每个目标
for i, mask in enumerate(masks):
# 遍历图片中的每个目标
res_img = result.copy()
# 获取目标的位置和类别信息
bbox, cls_name = boxes[0][i], class_names[0][i]
label = f'{cls_name} {conf[0][i]}' # 类别+置信分数
# 获取目标的热力图
res_img, heat_map = get_res_img(bbox, mask, res_img)
res_img = plot_one_box(bbox, res_img, label=label, color=colors[int(names.index(cls_name))],
line_thickness=3)
# 缩放到原图片大小
res_img = cv2.resize(res_img, dsize=(img.shape[:-1][::-1]))
output_path = f'{save_path}/{target_layer[6:8]}_{i}.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(output_path, res_img)
print(f'{target_layer[6:8]}_{i}.jpg done!!')
print(f'Total time : {round(time.time() - tic, 4)} s')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 图片路径为文件夹
if os.path.isdir(args.img_path):
img_list = os.listdir(args.img_path)
print(img_list)
for item in img_list:
# 依次获取文件夹中的图片名,组合成图片的路径
main(os.path.join(args.img_path, item))
# 单个图片
else:
main(args.img_path)
2、在model文件夹下添加如下两个py文件,分别是gradcam.py和yolov5_object_detector.py

gradcam.py代码如下:
import numpy as np
import torch
from models.experimental import attempt_load
from utils.general import xywh2xyxy
from utils.dataloaders import letterbox
import cv2
import time
import torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
from utils.metrics import box_iou
class YOLOV5TorchObjectDetector(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
model_weight,
device,
img_size,
names=None,
mode='eval',
confidence=0.45,
iou_thresh=0.45,
agnostic_nms=False):
super(YOLOV5TorchObjectDetector, self).__init__()
self.device = device
self.model = None
self.img_size = img_size
self.mode = mode
self.confidence = confidence
self.iou_thresh = iou_thresh
self.agnostic = agnostic_nms
self.model = attempt_load(model_weight, inplace=False, fuse=False)
self.model.requires_grad_(True)
self.model.to(device)
if self.mode == 'train':
self.model.train()
else:
self.model.eval()
# fetch the names
if names is None:
self.names = ['your dataset classname']
else:
self.names = names
# preventing cold start
img = torch.zeros((1, 3, *self.img_size), device=device)
self.model(img)
@staticmethod
def non_max_suppression(prediction, logits, conf_thres=0.3, iou_thres=0.45, classes=None, agnostic=False,
multi_label=False, labels=(), max_det=300):
"""Runs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference and logits results
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls] and pruned input logits (n, number-classes)
"""
nc = prediction.shape[2] - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
# Settings
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
time_limit = 10.0 # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
t = time.time()
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6), device=prediction.device)] * prediction.shape[0]
logits_output = [torch.zeros((0, nc), device=logits.device)] * logits.shape[0]
# logits_output = [torch.zeros((0, 80), device=logits.device)] * logits.shape[0]
for xi, (x, log_) in enumerate(zip(prediction, logits)): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
log_ = log_[xc[xi]]
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
l = labels[xi]
v = torch.zeros((len(l), nc + 5), device=x.device)
v[:, :4] = l[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(l)), l[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5, None], j[:, None].float()), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float()), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
log_ = log_[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
logits_output[xi] = log_[i]
assert log_[i].shape[0] == x[i].shape[0]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
print(f'WARNING: NMS time limit {time_limit}s exceeded')
break # time limit exceeded
return output, logits_output
@staticmethod
def yolo_resize(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True):
return letterbox(img, new_shape=new_shape, color=color, auto=auto, scaleFill=scaleFill, scaleup=scaleup)
def forward(self, img):
prediction, logits, _ = self.model(img, augment=False)
prediction, logits = self.non_max_suppression(prediction, logits, self.confidence, self.iou_thresh,
classes=None,
agnostic=self.agnostic)
self.boxes, self.class_names, self.classes, self.confidences = [[[] for _ in range(img.shape[0])] for _ in
range(4)]
for i, det in enumerate(prediction): # detections per image
if len(det):
for *xyxy, conf, cls in det:
# 返回整数
bbox = [int(b) for b in xyxy]
self.boxes[i].append(bbox)
self.confidences[i].append(round(conf.item(), 2))
cls = int(cls.item())
self.classes[i].append(cls)
if self.names is not None:
self.class_names[i].append(self.names[cls])
else:
self.class_names[i].append(cls)
return [self.boxes, self.classes, self.class_names, self.confidences], logits
def preprocessing(self, img):
if len(img.shape) != 4:
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
im0 = img.astype(np.uint8)
img = np.array([self.yolo_resize(im, new_shape=self.img_size)[0] for im in im0])
img = img.transpose((0, 3, 1, 2))
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(self.device)
img = img / 255.0
return img
yolov5_object_detector.py的代码如下:
import numpy as np
import torch
from models.experimental import attempt_load
from utils.general import xywh2xyxy
from utils.dataloaders import letterbox
import cv2
import time
import torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
from utils.metrics import box_iou
class YOLOV5TorchObjectDetector(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
model_weight,
device,
img_size,
names=None,
mode='eval',
confidence=0.45,
iou_thresh=0.45,
agnostic_nms=False):
super(YOLOV5TorchObjectDetector, self).__init__()
self.device = device
self.model = None
self.img_size = img_size
self.mode = mode
self.confidence = confidence
self.iou_thresh = iou_thresh
self.agnostic = agnostic_nms
self.model = attempt_load(model_weight, inplace=False, fuse=False)
self.model.requires_grad_(True)
self.model.to(device)
if self.mode == 'train':
self.model.train()
else:
self.model.eval()
# fetch the names
if names is None:
self.names = ['your dataset classname']
else:
self.names = names
# preventing cold start
img = torch.zeros((1, 3, *self.img_size), device=device)
self.model(img)
@staticmethod
def non_max_suppression(prediction, logits, conf_thres=0.3, iou_thres=0.45, classes=None, agnostic=False,
multi_label=False, labels=(), max_det=300):
"""Runs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference and logits results
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls] and pruned input logits (n, number-classes)
"""
nc = prediction.shape[2] - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
# Settings
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
time_limit = 10.0 # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
t = time.time()
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6), device=prediction.device)] * prediction.shape[0]
logits_output = [torch.zeros((0, nc), device=logits.device)] * logits.shape[0]
# logits_output = [torch.zeros((0, 80), device=logits.device)] * logits.shape[0]
for xi, (x, log_) in enumerate(zip(prediction, logits)): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
log_ = log_[xc[xi]]
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
l = labels[xi]
v = torch.zeros((len(l), nc + 5), device=x.device)
v[:, :4] = l[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(l)), l[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5, None], j[:, None].float()), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float()), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
log_ = log_[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
logits_output[xi] = log_[i]
assert log_[i].shape[0] == x[i].shape[0]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
print(f'WARNING: NMS time limit {time_limit}s exceeded')
break # time limit exceeded
return output, logits_output
@staticmethod
def yolo_resize(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True):
return letterbox(img, new_shape=new_shape, color=color, auto=auto, scaleFill=scaleFill, scaleup=scaleup)
def forward(self, img):
prediction, logits, _ = self.model(img, augment=False)
prediction, logits = self.non_max_suppression(prediction, logits, self.confidence, self.iou_thresh,
classes=None,
agnostic=self.agnostic)
self.boxes, self.class_names, self.classes, self.confidences = [[[] for _ in range(img.shape[0])] for _ in
range(4)]
for i, det in enumerate(prediction): # detections per image
if len(det):
for *xyxy, conf, cls in det:
# 返回整数
bbox = [int(b) for b in xyxy]
self.boxes[i].append(bbox)
self.confidences[i].append(round(conf.item(), 2))
cls = int(cls.item())
self.classes[i].append(cls)
if self.names is not None:
self.class_names[i].append(self.names[cls])
else:
self.class_names[i].append(cls)
return [self.boxes, self.classes, self.class_names, self.confidences], logits
def preprocessing(self, img):
if len(img.shape) != 4:
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
im0 = img.astype(np.uint8)
img = np.array([self.yolo_resize(im, new_shape=self.img_size)[0] for im in im0])
img = img.transpose((0, 3, 1, 2))
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(self.device)
img = img / 255.0
return img
3、更改model/yolo.py
①修改Detect类中的forward函数
def forward(self, x):
z = [] # inference output
logits_ = [] # 修改---1
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv
bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85)
x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
if not self.training: # inference
if self.dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]:
self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i)
logits = x[i][..., 5:] # 修改---2
if isinstance(self, Segment): # (boxes + masks)
xy, wh, conf, mask = x[i].split((2, 2, self.nc + 1, self.no - self.nc - 5), 4)
xy = (xy.sigmoid() * 2 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (wh.sigmoid() * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, conf.sigmoid(), mask), 4)
else: # Detect (boxes only)
xy, wh, conf = x[i].sigmoid().split((2, 2, self.nc + 1), 4)
xy = (xy * 2 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy
wh = (wh * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh
y = torch.cat((xy, wh, conf), 4)
z.append(y.view(bs, self.na * nx * ny, self.no))
logits_.append(logits.view(bs, -1, self.no - 5)) # 修改---3
# return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1),) if self.export else (torch.cat(z, 1), x)
return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), torch.cat(logits_, 1), x) # 修改---4
6、运行main_gradcam.py
参数列表可以自己进行修改。
# Arguments
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--model-path', type=str, default="yolov5s.pt", help='Path to the model')
parser.add_argument('--img-path', type=str, default='data/images/bus.jpg', help='input image path')
parser.add_argument('--output-dir', type=str, default='runs/result17', help='output dir')
parser.add_argument('--img-size', type=int, default=640, help="input image size")
parser.add_argument('--target-layer', type=str, default='model_17_cv3_act',
help='The layer hierarchical address to which gradcam will applied,'
' the names should be separated by underline')
parser.add_argument('--method', type=str, default='gradcam', help='gradcam method')
parser.add_argument('--device', type=str, default='cuda', help='cuda or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--no_text_box', action='store_true',
help='do not show label and box on the heatmap')
args = parser.parse_args()
--model-path:要用于检测图片的网络权重路径,要用修改过的v5权重生成热力图需要修改这里。
3、本博的重点:如何生成修改后的v5网络的热力图
1、修改训练类别名。
在main_gradcam.py中 names是存放训练类别的字典,yolov5s.pt是训练coco的80个类别,因此这里放的是coco的类别名,训练自己的权重要换成自己的数据集类别名。

2、修改生成的热力图的网络层
代码中target_layers是生成热力图的目标层。这里是Neck中输出的3层C3
target_layers = ['model_17_cv3_act', 'model_20_cv3_act', 'model_23_cv3_act']

读取网络层采用字典类型,‘model_17_cv3_act’ 分别对应self.model中模型数据、模块索引、模块名、模块中的网络层。
我们debug看看,把断点打到models/gradcam.py的
target_layer = find_yolo_layer(self.model, layer_name)
Evaluate一下self.model。

可以看到在模型中C3模块在第17层,和配置文件yolov5s.yaml中的层数是一样的,模块名字是cv3,模块中的网络层数是act层,也就是激活函数层,一般都是选择在激活函数层后面生成热力图。

因此,要查看自己训练的权重的热力图,首先要根据自己网络的配置文件来寻找网络层。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842720.html
重要提示:因为target_layers层是根据关键点+下划线的方式寻找网络层的,修改yolov5的模块是最好不要在网络层的名字中带下划线_,否则会无法找到网络层,又需要重头训练权重。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842720.html
target_layers = ['model_17_cv3_act', 'model_20_cv3_act', 'model_23_cv3_act']
到了这里,关于yolov5热力图生成和修改的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!