增
# 有则修改,无则创建
put your_index_name/doc/id
{
"key":"value"
}
删
# 删除指定文档
delete your_index_name/doc/id
# 删除索引
delete your_index_name
改
修改指定文档属性
# - 修改时,不指定的属性会自动覆盖,只保留指定的属性(不正确的修改指定文档方式)
PUT test/doc/1
{
"name":"王计飞"
}
# - 使用POST命令,在id后面跟_update,要修改的内容放到doc文档(属性)中(正确的修改指定文档方式)
POST test/doc/1/_update { "doc":{ "desc":"生活就像 茫茫海上" } }
查
常用查询
ES(Elasticsearch)是一种基于Lucene的搜索引擎,支持各种查询语法,以下是常用的ES查询语法:
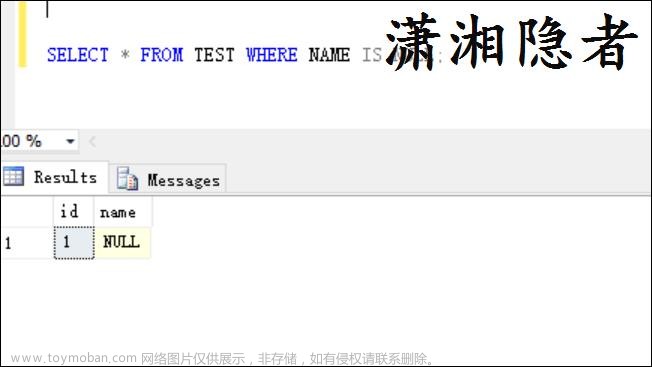
查询空字符串
因为空字符串在ES中也是一种数据类型,所以使用match或filter直接空串不能查出来,因此使用wildcard进行模糊匹配查询,"*"可以查询出非null、非空串和存在该字段的结果。
查询出没有该字段的文档
GET index名称/_count
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"exists": {
"field": "字段名称"
}
}
]
}
}
}
字段值为空字符串
GET index名称/_count
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"wildcard": {
"字段名称": {
"value": "*"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
字段值不为空字符串的文档
GET index名称/_count
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"字段名称": {
"value": "*"
}
}
}
}
1. Match Query:用于搜索指定字段中包含指定词条的文档。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "Elasticsearch"
}
}
}
2. Term Query:用于搜索指定字段中包含指定词条的文档,不会对词条进行分词。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": "Elasticsearch"
}
}
}
3. Range Query:用于搜索指定字段中符合指定范围的文档。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 18,
"lte": 30
}
}
}
}
4. Bool Query:用于组合多个查询条件,支持must、should、must_not和filter四种子查询。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "title": "Elasticsearch" }},
{ "match": { "content": "Java" }}
],
"should": [
{ "match": { "author": "John" }},
{ "match": { "author": "Jane" }}
],
"must_not": [
{ "match": { "status": "deleted" }}
],
"filter": [
{ "range": { "date": { "gte": "2020-01-01" }}}
]
}
}
}
5. Wildcard Query:用于搜索指定字段中符合通配符表达式的文档。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"title": "Elast*csearch"
}
}
}
6. Fuzzy Query:用于搜索指定字段中与指定词条相似的文档。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"title": {
"value": "Elastiksearch",
"fuzziness": "2"
}
}
}
}
7. Prefix Query:用于搜索指定字段中以指定前缀开头的文档。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"title": "Elast"
}
}
}
8. Match Phrase Query:用于搜索指定字段中包含指定短语的文档。
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": "Elasticsearch tutorial"
}
}
}
基本查询
查询某个索引所有的文档
GET /your_index_name/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
或
GET /your_index_name/_search
查询字符串搜索
GET test/doc/_search?q=name:wangfei
结构化查询(单字段查询,不能多字段组合查询)
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"name":"wang"
}
}
}
match 系列
1、match:返回所有匹配的分词。
2、match_all:查询全部。
3、match_phrase:短语查询,在match的基础上进一步查询词组,可以指定slop分词间隔。
4、match_phrase_prefix:前缀查询,根据短语中最后一个词组做前缀匹配,可以应用于搜索提示,但注意和max_expanions搭配。其实默认是50…
5、multi_match:多字段查询,使用相当的灵活,可以完成 match_phrase 和 match_phrase_prefix 的工作。
match_all (查询全部)
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all": {
}
}
}
match_phrase(短语查询)
# 匹配一整个词语
# 只用match,会单个字匹配
GET test1/doc/_search { "query":{ "match":{ "title":"中国" } } }
match_phrase_prefix(最左前缀查询)智能搜索–以什么开头
multi_match(多字段查询)
- multi_match是要在多个字段中查询同一个关键字 除此之外,mulit_match甚至可以当做match_phrase和match_phrase_prefix使用,只需要指定type类型即可
GET test2/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "beautiful",
"fields": [
"title",
"desc"
]
}
}
}
- 当设置属性 type:phrase 时 等同于 短语查询
GET test1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "中国",
"fields": [
"title"
],
"type": "phrase"
}
}
}
- 当设置属性 type:phrase_prefix时 等同于 最左前缀查询
GET test2/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "bea",
"fields": [
"desc"
],
"type": "phrase_prefix"
}
}
}
排序查询
倒排
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
升序
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
]
}
分页查询
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"name": "wang"
}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 1
}
bool 查询 (must、should)
bool 查询总结
must:与关系,相当于关系型数据库中的 and。
should:或关系,相当于关系型数据库中的 or。
must_not:非关系,相当于关系型数据库中的 not。
filter:过滤条件。
range:条件筛选范围。
gt:大于,相当于关系型数据库中的 >。
gte:大于等于,相当于关系型数据库中的 >=。
lt:小于,相当于关系型数据库中的 <。
lte:小于等于,相当于关系型数据库中的 <=。
must
(must字段对应的是个列表,也就是说可以有多个并列的查询条件,一个文档满足各个子条件后才最终返回)
单条件查询
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"name": "wangfei"
}
}
]
}
}
}
多条件组合查询
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"name": "wanggfei"
}
},
{
"match": {
"age": 25
}
}
]
}
}
}
should
(只要符合其中一个条件就返回)
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"name": "wangjifei"
}
},
{
"match": {
"age": 27
}
}
]
}
}
}
must_not
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"name": "wangjifei"
}
},
{
"match": {
"age": 27
}
}
]
}
}
}
filter
(条件过滤查询,过滤条件的范围用range表示gt表示大于、lt表示小于、gte表示大于等于、lte表示小于等于)
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"name": "wangjifei"
}
}
],
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 10,
"lt": 27
}
}
}
}
}
}
查询结果过滤
GET test3/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "顾"
}
},
"_source": ["name","age"]
}
>>查询结果
{
"took" : 58,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test3",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"name" : "顾老二",
"age" : 30
}
}
]
}
}
查询结果高亮显示 (默认高亮显示)
GET test3/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "顾老二"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"name": {}
}
}
}
>>查询结果
{
"took" : 216,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.8630463,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test3",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.8630463,
"_source" : {
"name" : "顾老二",
"age" : 30,
"from" : "gu",
"desc" : "皮肤黑、武器长、性格直",
"tags" : [
"黑",
"长",
"直"
]
},
"highlight" : {
"name" : [
"<em>顾</em><em>老</em><em>二</em>"
]
}
}
]
}
}
精确查询与模糊查询
term 和 match 的区别是:
match 经过分词,用于模糊查询,可以查看某个字段值中的部分词
term 不经过分词,只能匹配到完整的字段值,用于精确查询
#### 准备数据
PUT w1
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties":{
"t1":{
"type": "text"
},
"t2": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
PUT w1/doc/1
{
"t1": "hi single dog",
"t2": "hi single dog"
}
# t1类型为text,会经过分词,match查询时条件也会经过分词,所以下面两种查询都能查到结果
GET w1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"t1": "hi single dog"
}
}
}
GET w1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"t1": "hi"
}
}
}
# t2类型为keyword类型,不会经过分词,match查询时条件会经过分词,所以只能当值为"hi single dog"时能查询到
GET w1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"t2": "hi"
}
}
}
GET w1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"t2": "hi single dog"
}
}
}
# t1类型为text,会经过分词,term查询时条件不会经过分词,所以只有当值为"hi"时能查询到
GET w1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"t1": "hi single dog"
}
}
}
GET w1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"t1": "hi"
}
}
}
# t2类型为keyword类型,不会经过分词,term查询时条件不会经过分词,所以只能当值为"hi single dog"时能查询到
GET w1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"t2": "hi single dog"
}
}
}
GET w1/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"t2": "hi"
}
}
}
- 查找多个精确值(terms)
#### 第一个查询方式
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"term": {
"age":27
}
},{
"term":{
"age":28
}
}
]
}
}
}
# 第二个查询方式
GET test/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"age": [
"27",
"28"
]
}
}
}
聚合查询 avg、max、min、sum
#### 数据准备
PUT zhifou/doc/1
{
"name":"顾老二",
"age":30,
"from": "gu",
"desc": "皮肤黑、武器长、性格直",
"tags": ["黑", "长", "直"]
}
PUT zhifou/doc/2
{
"name":"大娘子",
"age":18,
"from":"sheng",
"desc":"肤白貌美,娇憨可爱",
"tags":["白", "富","美"]
}
PUT zhifou/doc/3
{
"name":"龙套偏房",
"age":22,
"from":"gu",
"desc":"mmp,没怎么看,不知道怎么形容",
"tags":["造数据", "真","难"]
}
PUT zhifou/doc/4
{
"name":"石头",
"age":29,
"from":"gu",
"desc":"粗中有细,狐假虎威",
"tags":["粗", "大","猛"]
}
PUT zhifou/doc/5
{
"name":"魏行首",
"age":25,
"from":"广云台",
"desc":"仿佛兮若轻云之蔽月,飘飘兮若流风之回雪,mmp,最后竟然没有嫁给顾老二!",
"tags":["闭月","羞花"]
}
GET zhifou/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
- 需求1、查询from是gu的人的平均年龄。
GET zhifou/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"from": "gu"
}
},
"aggs": {
"my_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"_source": ["name", "age"]
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 83,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 3,
"max_score" : 0.6931472,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "zhifou",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 0.6931472,
"_source" : {
"name" : "石头",
"age" : 29
}
},
{
"_index" : "zhifou",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"name" : "顾老二",
"age" : 30
}
},
{
"_index" : "zhifou",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"name" : "龙套偏房",
"age" : 22
}
}
]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_avg" : {
"value" : 27.0
}
}
}
###### 上例中,首先匹配查询from是gu的数据。在此基础上做查询平均值的操作,这里就用到了聚合函数,其语法被封装在aggs中,而my_avg则是为查询结果起个别名,封装了计算出的平均值。那么,要以什么属性作为条件呢?是age年龄,查年龄的什么呢?是avg,查平均年龄。
##### 如果只想看输出的值,而不关心输出的文档的话可以通过size=0来控制
GET zhifou/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"from": "gu"
}
},
"aggs":{
"my_avg":{
"avg": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size":0,
"_source":["name","age"]
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 35,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 3,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_avg" : {
"value" : 27.0
}
}
}
- 需求2、查询年龄的最大值
GET zhifou/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"my_max": {
"max": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0,
"_source": ["name","age","from"]
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 10,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_max" : {
"value" : 30.0
}
}
}
- 需求3、查询年龄的最小值
GET zhifou/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"my_min": {
"min": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0,
"_source": ["name","age","from"]
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_min" : {
"value" : 18.0
}
}
}
- 需求4、查询符合条件的年龄之和
GET zhifou/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"from": "gu"
}
},
"aggs": {
"my_sum": {
"sum": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0,
"_source": ["name","age","from"]
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 3,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"my_sum" : {
"value" : 81.0
}
}
}
分组查询
- 需求: 要查询所有人的年龄段,并且按照1520,2025,25~30分组,并且算出每组的平均年龄。
GET zhifou/doc/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"age_group": {
"range": {
"field": "age",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 15,
"to": 20
},
{
"from": 20,
"to": 25
},
{
"from": 25,
"to": 30
}
]
}
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 9,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"age_group" : {
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "15.0-20.0",
"from" : 15.0,
"to" : 20.0,
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "20.0-25.0",
"from" : 20.0,
"to" : 25.0,
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "25.0-30.0",
"from" : 25.0,
"to" : 30.0,
"doc_count" : 2
}
]
}
}
}
上例中,在aggs的自定义别名age_group中,使用range来做分组,field是以age为分组,分组使用ranges来做,from和to是范围
- 接下来,我们就要对每个小组内的数据做平均年龄处理。
GET zhifou/doc/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"age_group": {
"range": {
"field": "age",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 15,
"to": 20
},
{
"from": 20,
"to": 25
},
{
"from": 25,
"to": 30
}
]
},
"aggs": {
"my_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"age_group" : {
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "15.0-20.0",
"from" : 15.0,
"to" : 20.0,
"doc_count" : 1,
"my_avg" : {
"value" : 18.0
}
},
{
"key" : "20.0-25.0",
"from" : 20.0,
"to" : 25.0,
"doc_count" : 1,
"my_avg" : {
"value" : 22.0
}
},
{
"key" : "25.0-30.0",
"from" : 25.0,
"to" : 30.0,
"doc_count" : 2,
"my_avg" : {
"value" : 27.0
}
}
]
}
}
}
ES的聚合查询的总结:聚合函数的使用,一定是先查出结果,然后对结果使用聚合函数做处理
avg:求平均
max:最大值
min:最小值
sum:求和
mapping
mapping 是什么
映射,用于定义一个文档及其中的字段如何存储和索引
字段的数据类型
简单类型如文本(text)、关键字(keyword)、日期(data)、整形(long)、双精度>、(double)、布尔(boolean)或 ip。
可以是支持 JSON 的层次结构性质的类型,如对象或嵌套。
或者一种特殊类型,如 geo_point、geo_shape 或 completion。为了不同的目的,
以不同的方式索引相同的字段通常是有用的。例如,字符串字段可以作为全文搜索的文本字段进行索引,
也可以作为排序或聚合的关键字字段进行索引。或者,可以使用标准分析器、英语分析器和
法语分析器索引字符串字段。这就是多字段的目的。大多数数据类型通过 fields 参数支持多字段。
mappings 之 dynamic 的三种状态
ES 中的 mapping 用来定义索引中字段和字段属性。mapping 中的 dynamic 属性决定了新增字段的处理方式,它有三种状态:
- true (默认值)
当 dynamic 设置为 true 时,如果文档中出现新的字段,ES 会自动将这个字段添加到 mapping 定义中,并根据字段值自动识别其类型。
- false
当 dynamic 设置为 false 时,如果文档中出现新的字段,ES 不会自动将这个字段添加到 mapping, 而是忽略这个新增字段。
- strict
当 dynamic 设置为 strict 时,如果文档中出现新的字段,ES 不仅不会添加这个字段到 mapping, 还会抛出异常错误。
总的来说,dynamic 属性用来控制新增字段的处理模式:
- true 会自动添加字段
- false 会忽略新增字段
- strict 会报错
通过设置不同的 dynamic 状态,可以更好地管理索引的 mapping 定义和字段。这对控制数据结构非常重要。
##### 默认为动态映射
PUT test4
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
}
GET test4/_mapping
>>>查询结果
{
"test4" : {
"mappings" : {
"doc" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"sex" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
#####添加数据
PUT test4/doc/1
{
"name":"wangjifei",
"age":"18",
"sex":"不详"
}
#####查看数据
GET test4/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 8,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test4",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "wangjifei",
"age" : "18",
"sex" : "不详"
}
}
]
}
}
- 测试静态映射:当elasticsearch察觉到有新增字段时,因为dynamic:false的关系,会忽略该字段,但是仍会存储该字段。
#####创建静态mapping
PUT test5
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"dynamic":false,
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
}
#####插入数据
PUT test5/doc/1
{
"name":"wangjifei",
"age":"18",
"sex":"不详"
}
####条件查询
GET test5/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"sex": "不详"
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 9,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 0,
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}
#####查看所有数据
GET /test5/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test5",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "wangjifei",
"age" : "18",
"sex" : "不详"
}
}
]
}
}
- 测试严格映射:当elasticsearch察觉到有新增字段时,因为dynamic:strict 的关系,就会报错,不能插入成功。
#####创建严格mapping
PUT test6
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"dynamic":"strict",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
}
#####插入数据
PUT test6/doc/1
{
"name":"wangjifei",
"age":"18",
"sex":"不详"
}
>>>插入结果
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "strict_dynamic_mapping_exception",
"reason": "mapping set to strict, dynamic introduction of [sex] within [doc] is not allowed"
}
],
"type": "strict_dynamic_mapping_exception",
"reason": "mapping set to strict, dynamic introduction of [sex] within [doc] is not allowed"
},
"status": 400
}
小结: 动态映射(dynamic:true):动态添加新的字段(或缺省)。静态映射(dynamic:false):忽略新的字段。在原有的映射基础上,当有新的字段时,不会主动的添加新的映射关系,只作为查询结果出现在查询中。严格模式(dynamic:strict):如果遇到新的字段,就抛出异常。一般静态映射用的较多。就像 HTML 的 img 标签一样,src 为自带的属性,你可以在需要的时候添加 id 或者 class 属性。当然,如果你非常非常了解你的数据,并且未来很长一段时间不会改变,strict 不失为一个好选择。
ES 之 mappings 的 index 属性
- index属性默认为true,如果该属性设置为false,那么,elasticsearch不会为该属性创建索引,也就是说无法当做主查询条件。
PUT test7
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text",
"index": true
},
"age": {
"type": "long",
"index": false
}
}
}
}
}
####插入数据
PUT test7/doc/1
{
"name":"wangjifei",
"age":18
}
####条件查询数据
GET test7/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "wangjifei"
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 18,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test7",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"name" : "wangjifei",
"age" : 18
}
}
]
}
}
#####条件查询
GET test7/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"age": 18
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "query_shard_exception",
"reason": "failed to create query: {\n \"match\" : {\n \"age\" : {\n \"query\" : 18,\n \"operator\" : \"OR\",\n \"prefix_length\" : 0,\n \"max_expansions\" : 50,\n \"fuzzy_transpositions\" : true,\n \"lenient\" : false,\n \"zero_terms_query\" : \"NONE\",\n \"auto_generate_synonyms_phrase_query\" : true,\n \"boost\" : 1.0\n }\n }\n}",
"index_uuid": "fzN9frSZRy2OzinRjeMKGA",
"index": "test7"
}
],
"type": "search_phase_execution_exception",
"reason": "all shards failed",
"phase": "query",
"grouped": true,
"failed_shards": [
{
"shard": 0,
"index": "test7",
"node": "INueKtviRpO1dbNWngcjJA",
"reason": {
"type": "query_shard_exception",
"reason": "failed to create query: {\n \"match\" : {\n \"age\" : {\n \"query\" : 18,\n \"operator\" : \"OR\",\n \"prefix_length\" : 0,\n \"max_expansions\" : 50,\n \"fuzzy_transpositions\" : true,\n \"lenient\" : false,\n \"zero_terms_query\" : \"NONE\",\n \"auto_generate_synonyms_phrase_query\" : true,\n \"boost\" : 1.0\n }\n }\n}",
"index_uuid": "fzN9frSZRy2OzinRjeMKGA",
"index": "test7",
"caused_by": {
"type": "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason": "Cannot search on field [age] since it is not indexed."
}
}
}
]
},
"status": 400
}
5. ES 之 mappings 的copy_to属性
ES 中的 mappings 属性中,copy_to 属性用来将一个字段的内容拷贝到另一个字段中。
copy_to 属性指定将源字段的内容拷贝到目标字段。当源字段的值发生变化时,目标字段也会自动更新。
使用 copy_to 的好处是:
-
可以将一个字段内容标准化后拷贝到另一个字段,方便后续查询。例如可以将不规范的名称字段拷贝到规范后的名称字段。
-
可以将一个字段拆分后拷贝到多个目标字段,实现多字段查询。例如可以将姓名字段拆分后拷贝到姓和名字段。
-
可以提高搜索效率。例如拷贝文本字段到关键词字段后,可以使用关键词字段进行快速查询过滤。
设置 copy_to 属性需要指定源字段和目标字段。目标字段不会存储实际值,只是源字段值的拷贝。这对规范数据结构和提高查询效率很有帮助。
所以,copy_to 属性可以让 ES 更好地管理索引结构,实现复杂的数据转换和提升查询性能。
PUT test8
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"dynamic":false,
"properties": {
"first_name":{
"type": "text",
"copy_to": "full_name"
},
"last_name": {
"type": "text",
"copy_to": "full_name"
},
"full_name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
#####插入数据
PUT test8/doc/1
{
"first_name":"tom",
"last_name":"ben"
}
PUT test8/doc/2
{
"first_name":"john",
"last_name":"smith"
}
#####查询所有
GET test8/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 2,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test8",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "john",
"last_name" : "smith"
}
},
{
"_index" : "test8",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "tom",
"last_name" : "ben"
}
}
]
}
}
#####条件查询
GET test8/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"first_name": "tom"
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test8",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "tom",
"last_name" : "ben"
}
}
]
}
}
######条件查询
GET test8/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"full_name": "ben"
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test8",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "tom",
"last_name" : "ben"
}
}
]
}
}
上例中,我们将first_name和last_name都复制到full_name中。并且使用full_name查询也返回了结果
- 既要查询tom还要查询smith该怎么办?
GET test8/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"full_name": {
"query": "tom smith",
"operator": "or"
}
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 2,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test8",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "john",
"last_name" : "smith"
}
},
{
"_index" : "test8",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "tom",
"last_name" : "ben"
}
}
]
}
}
operator参数为多个条件的查询关系也可以是and
- 上面的查询还可以简写成一下:
GET test8/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"full_name": "tom smith"
}
}
}
- copy_to还支持将相同的属性值复制给不同的字段。
PUT test9
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"dynamic":false,
"properties": {
"first_name":{
"type": "text",
"copy_to": ["full_name1","full_name2"]
},
"last_name": {
"type": "text",
"copy_to": ["full_name1","full_name2"]
},
"full_name1": {
"type": "text"
},
"full_name2":{
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
####插入数据
PUT test9/doc/1
{
"first_name":"tom",
"last_name":"ben"
}
PUT test9/doc/2
{
"first_name":"john",
"last_name":"smith"
}
####条件查询
GET test9/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"full_name1": "tom smith"
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 7,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 2,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test9",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "john",
"last_name" : "smith"
}
},
{
"_index" : "test9",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "tom",
"last_name" : "ben"
}
}
]
}
}
#####条件查询
GET test9/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"full_name2": "tom smith"
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 7,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 2,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test9",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "john",
"last_name" : "smith"
}
},
{
"_index" : "test9",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"first_name" : "tom",
"last_name" : "ben"
}
}
]
}
}
full_name1 full_name2两个字段都可以查出来
6. ES 之mappings的对象属性
ES 中的 mappings 属性允许定义对象类型的字段。对象字段可以包含多个子字段,这对于一些复杂类型的文档来说很有用。
对象字段的定义方式是:
"对象字段名": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"子字段1":{
"type": "类型"
},
"子字段2":{
"type": "类型"
}
}
}
对象字段的主要属性如下:
-
type: 必须设置为"object", 表示这是一个对象类型。
-
properties: 用于定义对象内的子字段。key 为子字段名,value 定义子字段类型。
-
enabled: 默认 true, 表示是否启用该对象字段的动态添加模式。
使用对象字段可以更好地表示复杂类型的文档结构,比如用户信息包含姓名、地址等多个子字段,就可以定义为一个对象。
对象字段支持嵌套对象,可以定义多层次的复杂结构。这比单独定义每个子字段更加直观和易于管理。
对象字段也支持其他 mappings 常用属性,如 analyzer、format 等。它让 ES 能更好地处理和查询结构化文档数据。
- 首先先看看ES自动创建的mappings
PUT test10/doc/1
{
"name":"wangjifei",
"age":18,
"info":{
"addr":"北京",
"tel":"18500327026"
}
}
GET test10
>>>查询结果
{
"test10" : {
"aliases" : { },
"mappings" : {
"doc" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"info" : {
"properties" : {
"addr" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"tel" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
},
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"creation_date" : "1570975011394",
"number_of_shards" : "5",
"number_of_replicas" : "1",
"uuid" : "YvMGDHxkSri0Lgx6GGXiNw",
"version" : {
"created" : "6080299"
},
"provided_name" : "test10"
}
}
}
}
- 现在如果要以info中的tel为条件怎么写查询语句呢?
GET test10/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"info.tel": "18500327026"
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 5,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test10",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"name" : "wangjifei",
"age" : 18,
"info" : {
"addr" : "北京",
"tel" : "18500327026"
}
}
}
]
}
}
info既是一个属性,也是一个对象,我们称为info这类字段为对象型字段。该对象内又包含addr和tel两个字段,如上例这种以嵌套内的字段为查询条件的话,查询语句可以以字段点子字段的方式来写即可
7. ES之mappings的settings 设置
- 在创建一个索引的时候,我们可以在settings中指定分片信息:
PUT test11
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
},
"settings": {
"number_of_replicas": 1,
"number_of_shards": 5
}
}
number_of_shards是主分片数量(每个索引默认5个主分片),而number_of_replicas是复制分片,默认一个主分片搭配一个复制分片。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842856.html
8. ES 之mappings的ignore_above参数
- ignore_above参数仅针对于keyword类型有用
# 这样设置是会报错的
PUT test12
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text",
"ignore_above":5
}
}
}
}
}
>>>显示结果
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason": "Mapping definition for [name] has unsupported parameters: [ignore_above : 5]"
}
],
"type": "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason": "Failed to parse mapping [doc]: Mapping definition for [name] has unsupported parameters: [ignore_above : 5]",
"caused_by": {
"type": "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason": "Mapping definition for [name] has unsupported parameters: [ignore_above : 5]"
}
},
"status": 400
}
##### 正确的打开方式
PUT test12
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above":5
}
}
}
}
}
PUT test12/doc/1
{
"name":"wangjifei"
}
##### 这样查询能查出结果
GET test12/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test12",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "wangjifei"
}
}
]
}
}
######这样查询不能查询出结果
GET test12/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "wangjifei"
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 0,
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}
上面的例子证明超过ignore_above设定的值后会被存储但不会建立索引文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842856.html
- 那么如果字符串的类型是text时能用ignore_above吗,答案是能,但要特殊设置:
PUT test13
{
"mappings": {
"doc":{
"properties":{
"name1":{
"type":"keyword",
"ignore_above":5
},
"name2":{
"type":"text",
"fields":{
"keyword":{
"type":"keyword",
"ignore_above": 10
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
PUT test13/doc/1
{
"name1":"wangfei",
"name2":"wangjifei hello"
}
##### 能查出来
GET test13/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test13",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name1" : "wangfei",
"name2" : "wangjifei hello"
}
}
]
}
}
##### 通过name1 字段查不出来,因为设置的是keyword类型 限制了5个字符的长度,
##### 存储的值超过了最大限制
GET test13/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name1": "wangfei"
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 0,
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}
##### 通过name2 字段能查出来,虽然限制了5个字符的长度,存储的值超过了最大限制,但是,
##### 当字段类型设置为text之后,ignore_above参数的限制就失效了。(了解就好,意义不大)
GET test13/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name2": "wangjifei"
}
}
}
>>>查询结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.2876821,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "test13",
"_type" : "doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.2876821,
"_source" : {
"name1" : "wangfei",
"name2" : "wangjifei hello"
}
}
]
}
}
到了这里,关于ES kibana常用语法---增删改查的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!