目录
一、SQL语句
1.1SQL语言分类
1.2查看数据库信息
1.3登录到你想登录的库
1.4查看数据库中的表信息
1.5显示数据表的结构(字段)
1.5.1数据表的结构
1.5.2常用的数据类型:
二、关系型数据库的四种语言
2.1DDL:数据定义语言,用于创建数据库对象,如库、表、索引等
2.1.1库的增删改查;
2.1.2.1创建数据库
2.1.2.2删除数据库
2.1.2表
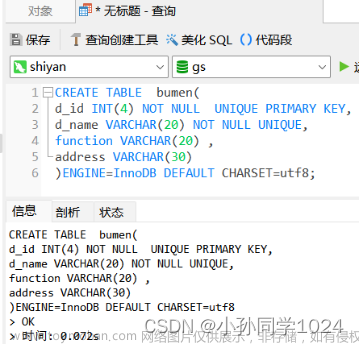
2.1.2.1创建表:
2.1.2.2删除表
方法一:drop table 表名;
方法二: drop table 库名.表名;
2.2DML 管理表中的数据记录 ---- 数据操纵语言,用于对表中的数据进行管理,用来插入、删除和修改数据库中的数据
2.2.1在 表 中insert(插入数据)
2.2.2update修改数据表
方法一:
方法二:
2.2.3delete删除数据表
2.3DQL查询数据记录 只有select
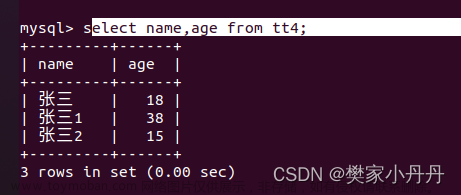
select * from ky66 limit 3; #只看头3行
select * from ky66 limit 2,3; #显示第2行后的前3行
2.4数据表高级操作
2.4.1清空表,删除表内的所有数据
2.4.2删除类型
2.4.3创建临时表
2.4.4克隆表
方法一:
方法二:
2.4DCL修改表名和表结构
2.4.1修改表名
2.4.2扩展表结构(增加字段)
2.4.3修改字段(列)名,添加唯一键
2.4.4删除字段
三、数据库用户管理
3.1新建用户
3.2查看用户信息
3.3重命名指定
3.4删除用户
3.5修改当前密码
3.6修改其他用户密码
3.7忘记root密码
①先修改配置文件,在mysqld块下添加skip-grant-tables;
②重启服务,直接用mysql免密登录数据库
③直接修改数据库的用户表中的对应密码数据;然后再返回配置文件,删除skip-grant-tables,然后重启服务
3.8修改密码
3.8.1Update修改密码
3.8.2直接修改
四、数据库用户授权
4.1给指定用户select权限
4.2使用Navicat图形化工具远程连接
1.没有授权之前
2.授权
4.3查看权限
4.4撤销权限
一、SQL语句
1.1SQL语言分类
DDL:数据定义语言,用于创建数据库对象,如库、表、索引等
DML :数据操纵语言,用于对表中的数据进行管理,用来插入、删除和修改数据库中的数据
DQL:数据查询语言,用于从数据表中查找符合条件的数据记录
DCL:数据控制语言,用于设置或者更改数据库用户或角色权限(数据控制语句,用于控制不通数据段直接的许可和访问级别的语句,这些语句定义了数据库、表、字段、用户的访问权限和安全级别,如COMMIT、ROLLBACK、GRANT、 REVOKE )
#DDL: Data Defination Language 数据定义语言
CREATE,DROP,ALTER#DML: Data Manipulation Language 数据操纵语言
INSERT,DELETE,UPDATE#DQL:Data Query Language 数据查询语言
SELECT
#DCL:Data Control Language 数据控制语言
GRANT,REVOKE,COMMIT,ROLLBACK
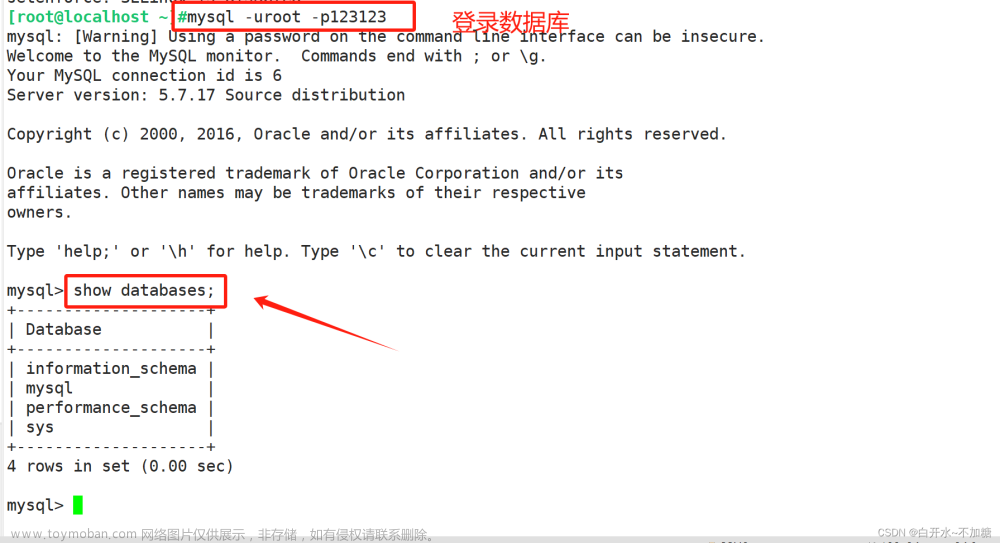
1.2查看数据库信息
show databases;
1.3登录到你想登录的库
use 数据库名

1.4查看数据库中的表信息
use 数据库名 #登录到你想登录的库
show tables; #再查看表


show tables in mysql; 查看mysql数据库中的表

1.5显示数据表的结构(字段)
describe user; 可以缩写 desc user;

1.5.1数据表的结构

| Field | 字段名称 |
| type | 数据类型 |
| Null | 是否允许为空 |
| Key | 主键 |
| Default |
默认值 |
|
Extra |
Extra :扩展属性,例如:标志符列(标识了种子,增量/步长)1 2 |
主键是唯一的,但主键可以由多个字段构成
1.5.2常用的数据类型:
| int:整型 | 用于定义整数类型的数据 |
| float:单精度浮点4字节32位 | 准确表示到小数点后六位 |
| double:双精度浮点8字节64位 | |
| char:固定长度的字符类型 | 用于定义字符类型数据 |
| varchar:可变长度的字符类型 | |
| text | 文本 |
| image | 图片 |
| decimal(5,2):5个有效长度数字,小数点后面有2位 | 指定长度数组 |
char 假设可以放20字节,但是你放4个字节,他是占用20字节
varchar 假设可以放20字节,你放4个字节,就占用4个字节,它不占用磁盘空间
#Char如果存入数据的实际长度比指定长度要小,会补空格至指定长度,如果存入的数据的实际长度大于指定长度,低版本会被截取,高版本会报错
decimal(5,2):5个有效长度数字,小数点后面有2位
(一共有5个字符,小数点后面2个字符)
主键是唯一的,但主键可以由多个字段构成
扩展
MySQL数据库的数据文件存放在/usr/local/mysql/data目录下,每个数据库对应一个子目录,用于存储数据表文件。每个数据表对应为三个文件,扩展名分别为“.frm”、“.MYD”和“.MYI”。
MYD”文件是MyISAM存储引擎专用,存放MyISAM表的数据。每一个MyISAM表都会有一个“.MYD”文件与之对应,同样存放于所属数据库的文件夹下,和“.frm”文件在一起。
“.MYI”文件也是专属于 MyISAM 存储引擎的,主要存放 MyISAM 表的索引相关信息。对于 MyISAM 存储来说,可以被 cache 的内容主要就是来源于“.MYI”文件中。每一个MyISAM 表对应一个“.MYI”文件,存放于位置和“.frm”以及“.MYD”一样。
MyISAM 存储引擎的表在数据库中,每一个表都被存放为三个以表名命名的物理文件
(frm,myd,myi)。 每个表都有且仅有这样三个文件做为 MyISAM 存储类型的表的存储,也就是说不管这个表有多少个索引,都是存放在同一个.MYI 文件中。
另外还有“.ibd”和 ibdata 文件,这两种文件都是用来存放 Innodb 数据的,之所以有两种文件来存放 Innodb 的数据(包括索引),是因为Innodb的数据存储方式能够通过配置来决定是使用共享表空间存放存储数据,还是独享表空间存放存储数据。独享表空间存储 方式使用“.ibd”文件来存放数据,且每个表一个“.ibd”文件,文件存放在和 MyISAM 数据相同的位置。如果选用共享存储表空间来存放数据,则会使用 ibdata 文件来存放,所有表共同使用一个(或者多个,可自行配置)ibdata 文件。
二、关系型数据库的四种语言
- DDL:用于管理数据库对象(库、表、索引等)
- DML:用于管理表数据
- DQL:用于根据条件查询表数据
- DCL:用于管理用户和权限
2.1DDL:数据定义语言,用于创建数据库对象,如库、表、索引等
create、drop、alter
2.1.1库的增删改查;
create database 库名; ##创建库
drop database 库名; ##删除库
show databases; ##查看有哪些库
use 库名; ##切换库2.1.2.1创建数据库

2.1.2.2删除数据库
drop database 库名; #删除库 谨慎!!!

2.1.2表
2.1.2.1创建表:
use 库名; ##先切换库
create table 表名 (字段1 数据类型 [约束属性],字段1 数据类型 [约束属性],.....); ##创建数据表结构
create table 表名 (字段1 数据类型,字段1 数据类型 ,....[约束属性]);
drop table 表名;
drop table [库名.]表名;
##删除表 谨慎!!
desc [库名.]表名;
##查询表结构 以表格形式显示
show create table [库名.]表名;
##以命令的形式显示表结构创建新的表 CREATE TABLE 表名 (字段1 数据类型,字段2 数据类型[,...][,PRIMARY KEY (主键名)]); #主键一般选择能代表唯一性的字段不允许取空值(NULL),一个表只能有一个主键

create table ky66 (id int not null,name char(10) not null,score decimal(4,2),passwd char(48) default'',primary key (id));
2.1.2.2删除表
方法一:drop table 表名;

方法二: drop table 库名.表名;

2.2DML 管理表中的数据记录 ---- 数据操纵语言,用于对表中的数据进行管理,用来插入、删除和修改数据库中的数据
insert(插入数据) 、update(修改、更新数据表)、delete(删除)
insert into [库名.]表名(字段1,字段2,....)values(字段1的值,字段2的值,....)
insert into [库名.]表名 values(所有字段的值 一一对应);
##添加数据记录
update [库名.]表名 set 字段名=字段值 where 条件表达式 [and/or 条件表达式2];
##修改数据的值
delete from [库名.]表名 where 条件表达式 [and/or 条件表达式2];
##删除数据的值
delete from [库名.]表名;
##清空数据表,只剩表结构2.2.1在 表 中insert(插入数据)
insert into ky66 (id,name,score,passwd) values(1,'xw',90,password('123123'));
select * from ky66; 查看表ky66
2.2.2update修改数据表
update ky66 set score='96' where name='xw';
修改 表名 得分 条件判断 name 方法一:

方法二:
update ky66 set score='88' where id='2';
2.2.3delete删除数据表
delete from ky66 where name='xw'; #删除xw这一条数据
不带where条件的语句 表示删除表中所有记录
delete from 表名; 删除表中数据

删除库很危险,一般只能删除表中数据
2.3DQL查询数据记录 只有select
select * from [库名.]表名;
##查看表中的所有字段对应的所有值
select 字段1,字段2,... from [库名.]表名 where 条件表达式 [and/or 条件表达式2];
##查询某些字段 满足条件的数据
select * from [库名.]表名 limit N;
##查询前N行,包括第N行的数据
select * from [库名.]表名 limit N,M;
##查询第N行以后,不包含第N行,后面M行的数据select name,score from ky66 where name='jian'; 只看jian的分数
select * from ky66 limit 3; #只看头3行
select * from ky66 limit 2,3; #显示第2行后的前3行
limit来做行数的查询

select * from 表名\G #以列表方式竖向显示 一般用的比较多

insert into插入数据
update修改/更新 数据 delete 删除数据
select *(代表所有字段) 也可以以单独的字段或多个字段查询
对应条件判断where
limit来做行数的查询 只显示所需行(显示前两行 limit2)
2.4数据表高级操作
2.4.1清空表,删除表内的所有数据
方法一:
delete from yyy3;
#DELETE清空表后,返回的结果内有删除的记录条目;
DELETE 工作时是一行一行的删除记录数据的;如果表中有自增长字段,使用DELETE FROM 删除
所有记录后,再次新添加的记录会从原来最大的记录ID后面继续自增写入记录。
方法二:
truncate table test01;
#TRUNCATE清空表后,没有返回被删除的条目: TRUNCATE 工作时是将表结构按原样重新建立,
因此在速度上TRUNCATE会比DELETE清空表快;使用TRUNCATE TABLE 清空表内数据后,
ID会从1开始重新记录
2.4.2删除类型
drop table table_name
1)属于DDL
2)不可回滚(无法恢复)
3)不可带where
4)表内容和结构删除
5)删除速度快truncate table table_name
1)属于DDL
2)不可回滚
3)不可带where
4)表内容删除
5)删除速度快
delete from table_name
1)属于DML
2)可回滚(可恢复)
3)可带where
4)表结构在,表内容要看where执行的情况
5)册删除速度慢,需要逐行删除不再需要一张表的时候,用drop
想删除部分数据行时候,用delete,并且带上where子句
保留表而删除所有数据的时候用truncate#删除速度drop> truncate > delete文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842991.html
安全性delete 最好 使用它哦
2.4.3创建临时表
create temporary table temp(id int primary key,name varchar(20),age int);
create temporary table 表名 (....);
临时表跟普通表一样可以进行增删改查,但是show tables是查不到的;
临时表只能在当前会话中有效,退出当前会话或在其它会话中,临时表都会失效临时建立的表,用于保存一些临时数据,不会长期存在
临时表创建成功之后,使用SHOWTABLES命令是看不到创建的临时表的,临时表会在连接退出后被销毁。
如果在退出连接之前,也可以可执行增删改查等操作,比如使用DROP TABLE语句手动直接删除临时表。
PS:无法创建外键
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE 表名 (字段1 数据类型,字段2 数据类型[, ...]
[, PRIMARY KEY (主键名)]);
sql 写入——》数据表中—》先把数据保存在内存中—》写入到磁盘
insert into info ——》info这张表,会先复制一份表数据到内存里面,给我们进行修改
---》敲完回车之后,确定提交了,才会写入数据表中—》再保存在磁盘里面
create table test01—》只会保存在内存中,在数据库退出连接之前的所有操作,都是在内存中进行的,不会保存在磁盘里面,退出连接后,临时表会释放掉
示例:
create temporary table xxx (
id int(4) zerofill primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(10) not null,
cardid int(18) not null unique key,
hobby varchar(50));
insert into xxx values (1,'zhangsan',123456,'running');
select * from test03;
show tables;
quit
select * from test03;
#int(4) zerofill:表示若数值不满4位数,则前面用"0"填充,例0001
#auto_increment:表示此字段为自增长字段,即每条记录自动递增1,默认从1开始递增;
自增长字段数据不可以重复;自增长字段必须是主键;如添加的记录数据没有指定此字段的值且
添加失败也会自动递增一次
#unique key:表示此字段唯一键约束,此字段数据不可以重复:一张表中只能有一个主键,但是一张表中可以有多个唯一键
#not null:表示此字段不允许为NULL
create temporary table ky55 (id int(6) zerofill primary key auto_increment,name varchar(16) not null,cardid int(18) not null unique key,hobby varchar(60),dianhua int(11));
#创建临时表#int(4) zerofill:表示若数值不满4位数,则前面用"0"填充,例0001
#auto_increment:表示此字段为自增长字段,即每条记录自动递增1,默认从1开始递增;
自增长字段数据不可以重复;自增长字段必须是主键;如添加的记录数据没有指定此字段的值且
添加失败也会自动递增一次
#unique key:表示此字段唯一键约束,此字段数据不可以重复:一张表中只能有一个主键,但是一张表中可以有多个唯一键
#not null:表示此字段不允许为NULL



临时表,做测试用的
2.4.4克隆表
##方法一:
create table 新表 like 旧表; #克隆表结构
insert into 新表 (select * from 旧表); #克隆表数据 可以实现表结构和表数据与旧表都一致
##方法二:
create table 新表 (select * from 旧表); #表数据和旧表一致,表结构和旧表不一定一致克隆表
create table yyy2 like yyy; #复制格式,通过LIKE方法,复制yyy表结构生成yyy2表
insert into yyy2 select * from yyy; #备份内容克隆表,将数据表的数据记录生成到新的表中
CREATE TABLE test02 (SELECT * from test); #复制test 表数据到test02中
示例:
show create table test02\G #获取数据表的表结构、索引等信息
SELECT * from test02;
方法一:
create table 新表 like 旧表; #克隆表结构
insert into 新表 (select * from 旧表); #克隆表数据#可以实现表结构和表数据与旧表都一致,一摸一样


方法二:
create table 新表 (select * from 旧表); #表数据和旧表一致,表结构和旧表不一定一致


克隆表 两种
第一种 迁移表 表的结构 属性 约束 数据
第二种 备份数据 表的复制内容(数据)
2.4DCL修改表名和表结构
ALTER TABLE 旧表名 RENAME 新表名;
示例:
ALTER TABLE zzz RENAME yyy;
ALTER TABLE yyy RENAME zzz;
2.4.1修改表名

alter table ky89 rename ky92;

2.4.2扩展表结构(增加字段)
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD address varchar(50) default '地址不详';
#default '地址不详':表示此字段设置默认值为地址不详,可与NOT NULL配合使用
ALTER TABLE yyy ADD address varchar(50) NOT NULL default '地址不详';
alter table ky92 add address varchar(70) default 'shanghailu';
2.4.3修改字段(列)名,添加唯一键
ALTER TABLE 表名 CHANGE 旧列名 新列名 数据类型 [unique key];
unique key:唯一键(特性:唯一,但可以为空,空值只允许出现一次)
Primary key:唯一且非空(主键一般选择能代表唯一性的字段不允许取空值(NULL),一个表只能有一个主键。)
alter table 表名 change name xingmin varchar(15) unique key;
ALTER TABLE yyy CHANGE name user_name varchar(10) unique key;
#CHANGE可修改字段名、数据类型、约束等所有项。
ALTER TABLE 表名 modify column 字段名 类型。
数据库中表 字段是varchar(30),修改类型可以用(谨慎修改类型,可能会导致原有数据出错)
2.4.4删除字段
格式:
ALTER TABLE 表名 DROP 字段名;

alter修改 表 字段
①rename修改表名
②ADD 表结构扩展字段
③change 修改表结构的字段 类型modify
④drop 删除 字段
##案列扩展
use school;
create table if not exists info (
id int(4) zerofill primary key auto_increment, #指定主键的第二种方式
name varchar(10) not null,
cardid int(18) not null unique key,
hobby varchar(50));
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#if not exists:表示检测要创建的表是否已存在,如果不存在就继续创建
#int(4) zerofill:表示若数值不满4位数,则前面用"0"填充,例0001
#auto_increment:表示此字段为自增长字段,即每条记录自动递增1,默认从1开始递增;
自增长字段数据不可以重复;自增长字段必须是主键;如添加的记录数据没有指定此字段的值且
添加失败也会自动递增一次
#unique key:表示此字段唯一键约束,此字段数据不可以重复:一张表中只能有一个主键,但是一张表中可以有多个唯一键
#not null:表示此字段不允许为NULL
三、数据库用户管理
use mysql 库
3.1新建用户
CREATE USER '用户名'@'来源地址' [IDENTIFIED BY [PASSWORD] '密码'];
'用户名':指定将创建的用户名.
'来源地址':指定新创建的用户可在哪些主机上登录,可使用IP地址、网段、主机名的形式,本地用户可用localhost,允许任意主机登录
可用通配符%
'密码':若使用明文密码,直接输入'密码',插入到数据库时由Mysql自动加密;
若使用加密密码,需要先使用SELECT PASSWORD('密码');获取密文,再在语句中添PASSWORD '密文';
若省略“IDENTIFIED BY"部分,则用户的密码将为空(不建议使用)
CREATE USER 'user1'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123456';
SELECT PASSWORD('abc123');
CREATE USER 'user2'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY PASSWORD '*6BB4837EB74329105EE4568DDA7DC67ED2CA2AD9';
mysql> use mysql;
Database changed
mysql> select * from user\G #查看用户信息 所有创建后的user用户信息均在user表里
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Host: localhost
User: root
Select_priv: Y
Insert_priv: Y
Update_priv: Y
Delete_priv: Y
Create_priv: Y
Drop_priv: Y
Reload_priv: Y
Shutdown_priv: Y
Process_priv: Y
File_priv: Y
Grant_priv: Y
References_priv: Y
Index_priv: Y
Alter_priv: Y
Show_db_priv: Y
Super_priv: Y
Create_tmp_table_priv: Y
Lock_tables_priv: Y
Execute_priv: Y
Repl_slave_priv: Y
Repl_client_priv: Y
Create_view_priv: Y
Show_view_priv: Y
Create_routine_priv: Y
Alter_routine_priv: Y
Create_user_priv: Y
Event_priv: Y
Trigger_priv: Y
Create_tablespace_priv: Y
ssl_type:
ssl_cipher:
x509_issuer:
x509_subject:
max_questions: 0
max_updates: 0
max_connections: 0
max_user_connections: 0
plugin: mysql_native_password
authentication_string: *E56A114692FE0DE073F9A1DD68A00EEB9703F3F1
password_expired: N
password_last_changed: 2024-03-19 19:27:52
password_lifetime: NULL
account_locked: N
*************************** 2. row ***************************
Host: localhost
User: mysql.sys
Select_priv: N
Insert_priv: N
Update_priv: N
Delete_priv: N
Create_priv: N
Drop_priv: N
Reload_priv: N
Shutdown_priv: N
Process_priv: N
File_priv: N
Grant_priv: N
References_priv: N
Index_priv: N
Alter_priv: N
Show_db_priv: N
Super_priv: N
Create_tmp_table_priv: N
Lock_tables_priv: N
Execute_priv: N
Repl_slave_priv: N
Repl_client_priv: N
Create_view_priv: N
Show_view_priv: N
Create_routine_priv: N
Alter_routine_priv: N
Create_user_priv: N
Event_priv: N
Trigger_priv: N
Create_tablespace_priv: N
ssl_type:
ssl_cipher:
x509_issuer:
x509_subject:
max_questions: 0
max_updates: 0
max_connections: 0
max_user_connections: 0
plugin: mysql_native_password
authentication_string: *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE
password_expired: N
password_last_changed: 2024-03-19 19:25:59
password_lifetime: NULL
account_locked: Y
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> 
create user 'jian'@'localhost' identified by 'abc123';


select authentication_string from user where user='jian';
3.2查看用户信息
创建后的用户保存在mysql 数据库的user表里
USE mysql;
SELECT User,authentication_string,Host from user; (如上图)
3.3重命名指定
RENAME USER 'zhangsan'@'localhost' TO 'lisi'@'localhost';

mysql> rename user 'jian'@'localhost' to 'zh'@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select authentication_string from user where user='zh';
+-------------------------------------------+
| authentication_string |
+-------------------------------------------+
| *6691484EA6B50DDDE1926A220DA01FA9E575C18A |
+-------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> 3.4删除用户
DROP USER 'lisi'@'localhost' ;
mysql> drop user 'zh'@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select authentication_string from user where user='zh';
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql>3.5修改当前密码
SET PASSWORD = PASSWORD('abc123');
mysql> set password = password('123123');
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit;
Bye
[root@localhost ~]#mysql -uroot -p123123
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 12
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> 
3.6修改其他用户密码
SET PASSWORD FOR 'user1'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('abc123T');

mysql> use mysql;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> create user 'cxk'@'localhost' identified by 'abc123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> set password for 'cxk'@'localhost' = password('123123');
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit
Bye
[root@localhost ~]#mysql -ucxk -p123123
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 13
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>3.7忘记root密码
修改/etc/my.cnf 配置文件,免密登陆mysql
vim /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
skip-grant-tables #添加,使登录mysql不使用授权表systemctl restart mysqld
mysql #直接登录
①先修改配置文件,在mysqld块下添加skip-grant-tables;
vim /etc/my.cof
[mysqld]
skip-grant-tables

②重启服务,直接用mysql免密登录数据库

③直接修改数据库的用户表中的对应密码数据;然后再返回配置文件,删除skip-grant-tables,然后重启服务


3.8修改密码
3.8.1Update修改密码
然后使用SQL语句修改密码
UPDATE mysql.user SET AUTHENTICATION_STRING = PASSWORD('abc123') where user='root';修改当前密码
SET PASSWORD = PASSWORD('abc123');修改其他用户密码
SET PASSWORD FOR 'user1'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('abc123T');
mysql> update mysql.user set authentication_string = password('abc123') where user='root';
Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 1
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit
Bye
[root@localhost ~]#vim /etc/my.cnf
[root@localhost ~]#sed -n '24p' /etc/my.cnf
#skip-grant-tables
[root@localhost ~]#mysql -uroot -pabc123
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 7
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> quit
Bye3.8.2直接修改
set password for root@localhost=password('123');




[root@localhost ~]#systemctl stop firewalld
[root@localhost ~]#setenforce 0
setenforce: SELinux is disabled
[root@localhost ~]#vim /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
#skip-grant-tables #添加,使登录mysql不使用授权表
[root@localhost ~]#mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 3
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> flush privileges; #刷新
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> set password for root@localhost=password('123');
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit;
Bye
[root@localhost ~]#vim /etc/my.cnf
#skip-grant-tables #注释掉
[root@localhost ~]#systemctl restart mysqld.service #重启服务
[root@localhost ~]#mysql -uroot -p123
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 3
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>四、数据库用户授权
grant 提权
GRANT 权限列表 ON 数据库名.表名 TO '用户名'@'来源地址' [IDENTIFIED BY '密码'];
①权限列表:用于列出授权使用的各种数据库操作,以逗号进行分隔,如“select, insert, update”。使用"all"表示所有权限,可授权执行任何操作。
②数据库名.表名:用于指定授权操作的数据库和表的名称,其中可以使用通配符"*"。例如,使用“class.*"表示授权操作的对象为class数据库中的所有表。③用户名@来源地址’:用于指定用户名称和允许访问的客户机地址,即谁能连接、能从哪里连接。来源地址可以是域名、IP 地址,还可以使用“%”通配符,表示某个区域或网段内的所有地址,如“%.accp.com”、“192.168.48.%”等。 %表示所有
④IDENTIFIED BY:用于设置用户连接数据库时所使用的密码字符串。在新建用户时,若省略“IDENTIFIED BY”部分, 则用户的密码将为空。
授权用户权限是all privilege。这个all privilege都有哪些权限?all privilege权限如下:

4.1给指定用户select权限
示例:
#允许用户zhangsan在本地查询school数据库中所有表的数据记录,
但禁止查询其他数据库中的表的记录。
GRANT select ON school.* TO 'zhangsan'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'abc123';
[root@localhost ~]#mysql -uroot -p123123
ysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| nanjing |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show tables;
+-------------------+
| Tables_in_nanjing |
+-------------------+
| ky65 |
| ky66 |
| ky68 |
+-------------------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from ky66;
+----+------+-------+-------------------------------------------+
| id | name | score | passwd |
+----+------+-------+-------------------------------------------+
| 1 | xw | 90.00 | *E56A114692FE0DE073F9A1DD68A00EEB9703F3F1 |
| 2 | jiaw | 90.00 | *7A119ACFC9695992139D401AACE00F39F4C24012 |
+----+------+-------+-------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| nanjing |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> grant select ON nanjing.* to 'xw'@'localhost' identified by '123123'; #授权
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 2 warnings (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges; #刷新
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> quit;
Bye
[root@localhost ~]#mysql -uxw -p123123 #xw用户登录数据库
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 4
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| nanjing |
+--------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> use nanjing;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+-------------------+
| Tables_in_nanjing |
+-------------------+
| ky65 |
| ky66 |
| ky68 |
+-------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from ky66;
+----+------+-------+-------------------------------------------+
| id | name | score | passwd |
+----+------+-------+-------------------------------------------+
| 1 | xw | 90.00 | *E56A114692FE0DE073F9A1DD68A00EEB9703F3F1 |
| 2 | jiaw | 90.00 | *7A119ACFC9695992139D401AACE00F39F4C24012 |
+----+------+-------+-------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> drop tables ky66; #没有删除权限
ERROR 1142 (42000): DROP command denied to user 'xw'@'localhost' for table 'ky66'
mysql> 


4.2使用Navicat图形化工具远程连接
#允许用户lisi在所有终端远程连接mysql,并拥有所有权限。
GRANT ALL [PRIVILEGES] ON *.* TO 'lisi'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON kgc.* TO 'lisi'@'192.168.10.2' IDENTIFIED BY 'abc123';
1.没有授权之前


2.授权
[root@localhost ~]#mysql -uroot -p123123
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 6
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> grant all privileges on nanjing.* to 'xw'@'192.168.246.%' identified by '123123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> 
检测:


4.3查看权限
mysql -u root -pabc123
SHOW GRANTS FOR 用户名@来源地址;SHOW GRANTS FOR 'lisi'@'%';

[root@localhost ~]#mysql -uroot -p123123 #root用户登录
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 10
Server version: 5.7.17 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> show grants for 'xw'@'192.168.246.%'; #查看用户权限
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| Grants for xw@192.168.246.% |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
| GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'xw'@'192.168.246.%' |
| GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON "nanjing".* TO 'xw'@'192.168.246.%' |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show grants for 'xw'@'localhost'; #查看用户权限
+-------------------------------------------------+
| Grants for xw@localhost |
+-------------------------------------------------+
| GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'xw'@'localhost' |
| GRANT SELECT ON "nanjing".* TO 'xw'@'localhost' |
+-------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>4.4撤销权限
REVOKE 权限列表 ON 数据库名.表名 FROM 用户名@来源地址;
REVOKE ALL ON *.* FROM 'lisi'@'%';
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'lisi'@'%';
#USAGE权限只能用于数据库登陆,不能执行任何操作; USAGE权限不能被回收,即REVOKE不能删除用户。
flush privileges;

[root@localhost ~]#mysql -uroot -p123123
mysql> revoke all on nanjing.* from 'xw'@'192.168.246.%'; #撤销权限
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> show grants for 'xw'@'192.168.246.%';
+--------------------------------------------+
| Grants for xw@192.168.246.% |
+--------------------------------------------+
| GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'xw'@'192.168.246.%' |
+--------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit;
Bye
[root@localhost ~]#检测:

温故而知新:
1.查看数据库、数据表和表结构的操作
查看数据库show databases
查看数据表show tables
查看表结构describe 表名或desc 表名
2.创建库和表的操作及删除库和表的操作
创建库create database 库名
创建表create table 表名
删除库drop database 库名
删除表drop table 表名
3.数据表的增、删、改、查等操作
数据表增:Insert into 表名
数据表改:update表名 set 指定内容
数据表删:delete from 表名
数据表查:select(*、where、limit、\G)
数据表结构名称改:alter table 表名 rename 新名称
数据表扩展结构增:alter table 表名 add 扩展名
数据表字段内容改:alter table 表名 change 原结构字段名称 新结构字段名称
数据表字段内容删:alter table 表名 drop 指定结构字段
4.数据库表的清空表、临时表和克隆表操作
4.1清空表
delete from 表名
truncate table 表名
drop from 表名
4.2临时表
create temporary tabletablename
4.3克隆表
Like方法:create table 新表 like旧表------->insert into 新表 select *from旧表
Show create table方法:create table 新表(select * from 旧表)
5.数据库的用户授权相关操作
5.1数据库用户管理
新建用户:create user '用户名'@'localhost(或者指定IP)' identified by '密码'
重命名:rename user '旧用户名'@'localhost(或者指定IP)' to '新用户名'@'localhost(或者指定IP)'
删除用户:drop user '用户名'@'localhost(或者指定IP)'
修改当前密码:set password = password('密码')
修改其他用户密码:set password for '用户名'@'localhost' = password('新密码');
修改密码:update mysql.user set authentication_string = password('abc123') where user='root'
修改密码:flush privileges------>set password for root@localhost=password('123123')
5.2数据库授权
授权:grant 权限列表 ON 数据库名.表名 to '用户名'@'来源地址' identified by '密码'
查看权限:show grants '用户名'@'来源地址'
撤销权限:revoke 权限列表 on 数据库名.表名 from '用户名'@'来源地址'
删除类型
drop table table_name
1)属于DDL
2)不可回滚(无法恢复)
3)不可带where
4)表内容和结构删除
5)删除速度快truncate table table_name
1)属于DDL
2)不可回滚
3)不可带where
4)表内容删除
5)删除速度快
delete from table_name
1)属于DML
2)可回滚(可恢复)
3)可带where
4)表结构在,表内容要看where执行的情况
5)册删除速度慢,需要逐行删除不再需要一张表的时候,用drop
想删除部分数据行时候,用delete,并且带上where子句
保留表而删除所有数据的时候用truncate#删除速度drop> truncate > delete
安全性delete 最好 使用它哦文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-842991.html
到了这里,关于linux系统--------------mysql数据库管理的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!