什么是Promise Pool

Map-like, concurrent promise processing for Node.js.
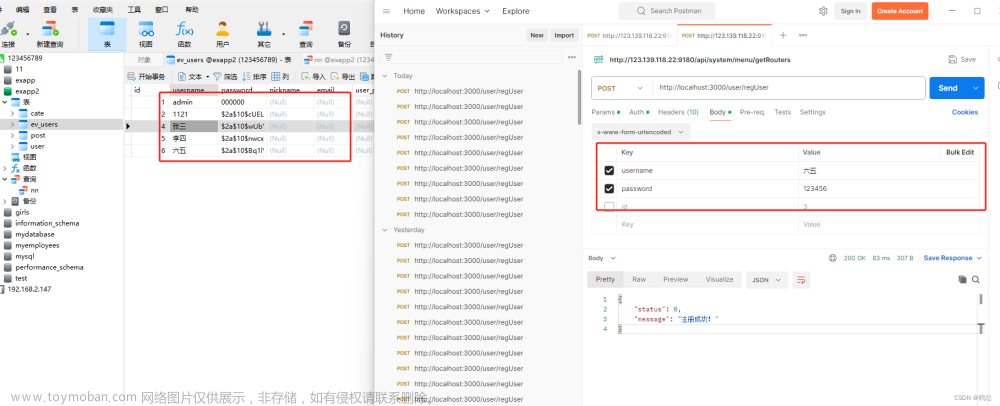
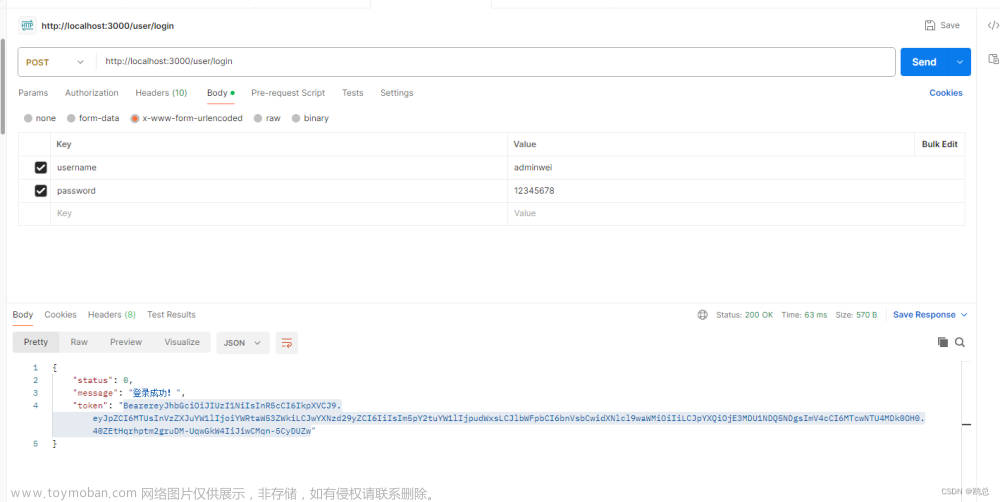
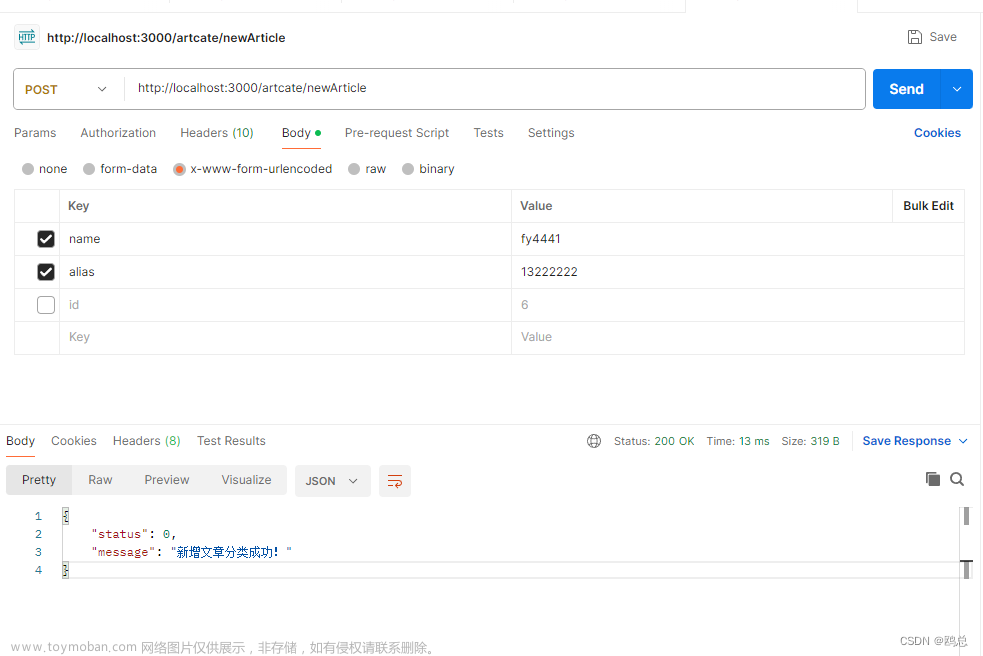
Promise-Pool是一个用于管理并发请求的JavaScript库,它可以限制同时进行的请求数量,以避免过多的请求导致服务器压力过大。使用Promise-Pool可以方便地实现对多个异步操作的并发控制。
Promise Pool “承诺池” 包允许您批量运行许多承诺。
承诺池确保并发处理任务的最大数量。
承诺池中的每个任务都是其他任务,这意味着一旦一个任务完成,池就开始处理下一个任务。
此处理可确保了为您的任务进行最佳的批处理。
Promise Pool - NPMJS
@supercharge/promise-pool - npm (npmjs.com)https://www.npmjs.com/package/@supercharge/promise-pool
Promise Pool - Document
Promise Poolhttps://superchargejs.com/docs/3.x/promise-pool
怎么使用PromisePool
Install 安装
so easy , just install it
npm i @supercharge/promise-poolUsage用例
Using the promise pool is pretty straightforward. The package exposes a class and you can create a promise pool instance using the fluent interface.
使用promise pool承诺池非常简单。该包公开了一个类,您可以使用流畅的接口创建一个承诺池实例。
Here’s an example using a concurrency of 2:
import { PromisePool } from '@supercharge/promise-pool'
const users = [
{ name: 'Marcus' },
{ name: 'Norman' },
{ name: 'Christian' }
]
const { results, errors } = await PromisePool
.withConcurrency(2)
.for(users)
.process(async (userData, index, pool) => {
const user = await User.createIfNotExisting(userData)
return user
})The promise pool uses a default concurrency of 10
默认是十个线程,请按照自己的实际情况(业务+架构)处理
在以下示例中,我们创建了一个包含5个worker的线程池。然后,我们向线程池添加了10个任务。线程池会并发执行这些任务,但最多只能有5个任务同时运行。当一个任务完成时,线程池会自动分配下一个任务给空闲的worker。
const PromisePool = require('promise-pool');
// 创建一个包含5个worker的线程池
const pool = new PromisePool(5, (task) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 模拟一个耗时操作
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Task completed:', task);
resolve();
}, 1000);
});
});
// 添加任务到线程池
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
pool.addTask(i).then(() => {
console.log('Task finished:', i);
}).catch((err) => {
console.error('Error:', err);
});
}
//zhengkai.blog.csdn.netManually Stop the Pool 手工停止
You can stop the processing of a promise pool using the pool instance provided to the .process() and .handleError() methods. Here’s an example how you can stop an active promise pool from within the .process() method:
await PromisePool
.for(users)
.process(async (user, index, pool) => {
if (condition) {
return pool.stop()
}
// processes the `user` data
})You may also stop the pool from within the .handleError() method in case you need to:
import { PromisePool } from '@supercharge/promise-pool'
await PromisePool
.for(users)
.handleError(async (error, user, pool) => {
if (error instanceof SomethingBadHappenedError) {
return pool.stop()
}
// handle the given `error`
})
.process(async (user, index, pool) => {
// processes the `user` data
})Bring Your Own Error Handling
The promise pool allows for custom error handling. You can take over the error handling by implementing an error handler using the .handleError(handler).
If you provide an error handler, the promise pool doesn’t collect any errors. You must then collect errors yourself.
Providing a custom error handler allows you to exit the promise pool early by throwing inside the error handler function. Throwing errors is in line with Node.js error handling using async/await.
承诺池允许自定义错误处理。
您可以通过使用.手柄错误(处理程序)实现错误处理程序来接管错误处理。
如果您提供了一个错误处理程序,则承诺池不会收集任何错误。
然后,您必须自己收集错误。
提供了一个自定义的错误处理程序,允许您通过抛出错误处理程序函数来提前退出承诺池。
抛出错误与Node.js错误处理使用异步/等待相一致。
import { PromisePool } from '@supercharge/promise-pool'
try {
const errors = []
const { results } = await PromisePool
.for(users)
.withConcurrency(4)
.handleError(async (error, user) => {
if (error instanceof ValidationError) {
errors.push(error) // you must collect errors yourself
return
}
if (error instanceof ThrottleError) { // Execute error handling on specific errors
await retryUser(user)
return
}
throw error // Uncaught errors will immediately stop PromisePool
})
.process(async data => {
// the harder you work for something,
// the greater you’ll feel when you achieve it
})
await handleCollected(errors) // this may throw
return { results }
} catch (error) {
await handleThrown(error)
}Callback for Started and Finished Tasks 开始和结束任务的回调
You can use the onTaskStarted and onTaskFinished methods to hook into the processing of tasks. The provided callback for each method will be called when a task started/finished processing:
您可以使用任务启动和任务完成的方法来连接到任务的处理中。
当任务启动/完成处理时,将调用为每个方法提供的回调:
import { PromisePool } from '@supercharge/promise-pool'
await PromisePool
.for(users)
.onTaskStarted((item, pool) => {
console.log(`Progress: ${pool.processedPercentage()}%`)
console.log(`Active tasks: ${pool.processedItems().length}`)
console.log(`Active tasks: ${pool.activeTasksCount()}`)
console.log(`Finished tasks: ${pool.processedItems().length}`)
console.log(`Finished tasks: ${pool.processedCount()}`)
})
.onTaskFinished((item, pool) => {
// update a progress bar or something else :)
})
.process(async (user, index, pool) => {
// processes the `user` data
})
You can also chain multiple onTaskStarted and onTaskFinished handling (in case you want to separate some functionality):
import { PromisePool } from '@supercharge/promise-pool'
await PromisePool
.for(users)
.onTaskStarted(() => {})
.onTaskStarted(() => {})
.onTaskFinished(() => {})
.onTaskFinished(() => {})
.process(async (user, index, pool) => {
// processes the `user` data
})Task Timeouts 超时设置
有时,配置一个任务必须完成处理的超时时间是很有用的。
一个超时的任务被标记为失败。
您可以使用与任务超时(<毫秒>)方法来配置任务的超时:
Sometimes it’s useful to configure a timeout in which a task must finish processing. A task that times out is marked as failed. You may use the withTaskTimeout(<milliseconds>) method to configure a task’s timeout:
import { PromisePool } from '@supercharge/promise-pool'
await PromisePool
.for(users)
.withTaskTimeout(2000) // milliseconds
.process(async (user, index, pool) => {
// processes the `user` data
})Notice: a configured timeout is configured for each task, not for the whole pool. The example configures a 2-second timeout for each task in the pool.
注意:为每个任务配置了一个已配置的超时,而不是为整个池。
该示例为池中的每个任务配置一个2秒的超时。
Correspond Source Items and Their Results 正确响应每个请求
有时,您希望处理后的结果与源项保持一致。
结果项在结果数组中的位置应该与其相关的源项相同。
使用使用对应结果方法来应用此行为:
Sometimes you want the processed results to align with your source items. The resulting items should have the same position in the results array as their related source items. Use the useCorrespondingResults method to apply this behavior:
import { setTimeout } from 'node:timers/promises'
import { PromisePool } from '@supercharge/promise-pool'
const { results } = await PromisePool
.for([1, 2, 3])
.withConcurrency(5)
.useCorrespondingResults()
.process(async (number, index) => {
const value = number * 2
return await setTimeout(10 - index, value)
})
/**
* source array: [1, 2, 3]
* result array: [2, 4 ,6]
* --> result values match the position of their source items
*/For example, you may have three items you want to process. Using corresponding results ensures that the processed result for the first item from the source array is located at the first position in the result array (=index 0). The result for the second item from the source array is placed at the second position in the result array, and so on …
例如,您可能有三个要处理的项目。
使用相应的结果可以确保从源数组中得到的第一个项的处理结果位于结果数组中的第一个位置(=索引0)。
来自源数组的第二个项的结果被放置在结果数组中的第二个位置,以此类推。
Return Values When Using Corresponding Results 在使用相应的结果时,请返回相应的值
The results array returned by the promise pool after processing has a mixed return type. Each returned item is one of this type:
- the actual value type: for results that successfully finished processing
-
Symbol('notRun'): for tasks that didn’t run -
Symbol('failed'): for tasks that failed processing
The PromisePool exposes both symbols and you may access them using
-
Symbol('notRun'): exposed asPromisePool.notRun -
Symbol('failed'): exposed asPromisePool.failed
处理后由承诺池返回的结果数组具有混合返回类型。
每个返回的项目都是以下类型之一:
实际值类型:对于成功完成处理的结果
符号(“notRun”):用于未运行的任务
符号(“failed”):用于处理失败的任务
承诺池公开了这两个符号,您可以使用
符号(“notRun”):公开为PromisePool.notRun
符号(“failed”):公开为PromisePool.failed
您可以对所有未运行或失败的任务重复处理:
You may repeat processing for all tasks that didn’t run or failed:
import { PromisePool } from '@supercharge/promise-pool'
const { results, errors } = await PromisePool
.for([1, 2, 3])
.withConcurrency(5)
.useCorrespondingResults()
.process(async (number) => {
// …
})
const itemsNotRun = results.filter(result => {
return result === PromisePool.notRun
})
const failedItems = results.filter(result => {
return result === PromisePool.failed
})When using corresponding results, you need to go through the errors array yourself. The default error handling (collect errors) stays the same and you can follow the described error handling section above.
当使用相应的结果时,您需要自己检查错误数组。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-849406.html
默认的错误处理(收集错误)保持不变,您可以按照上面描述的错误处理部分进行操作。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-849406.html
到了这里,关于Node.JS多线程PromisePool之promise-pool库实现的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!