一、模块概述
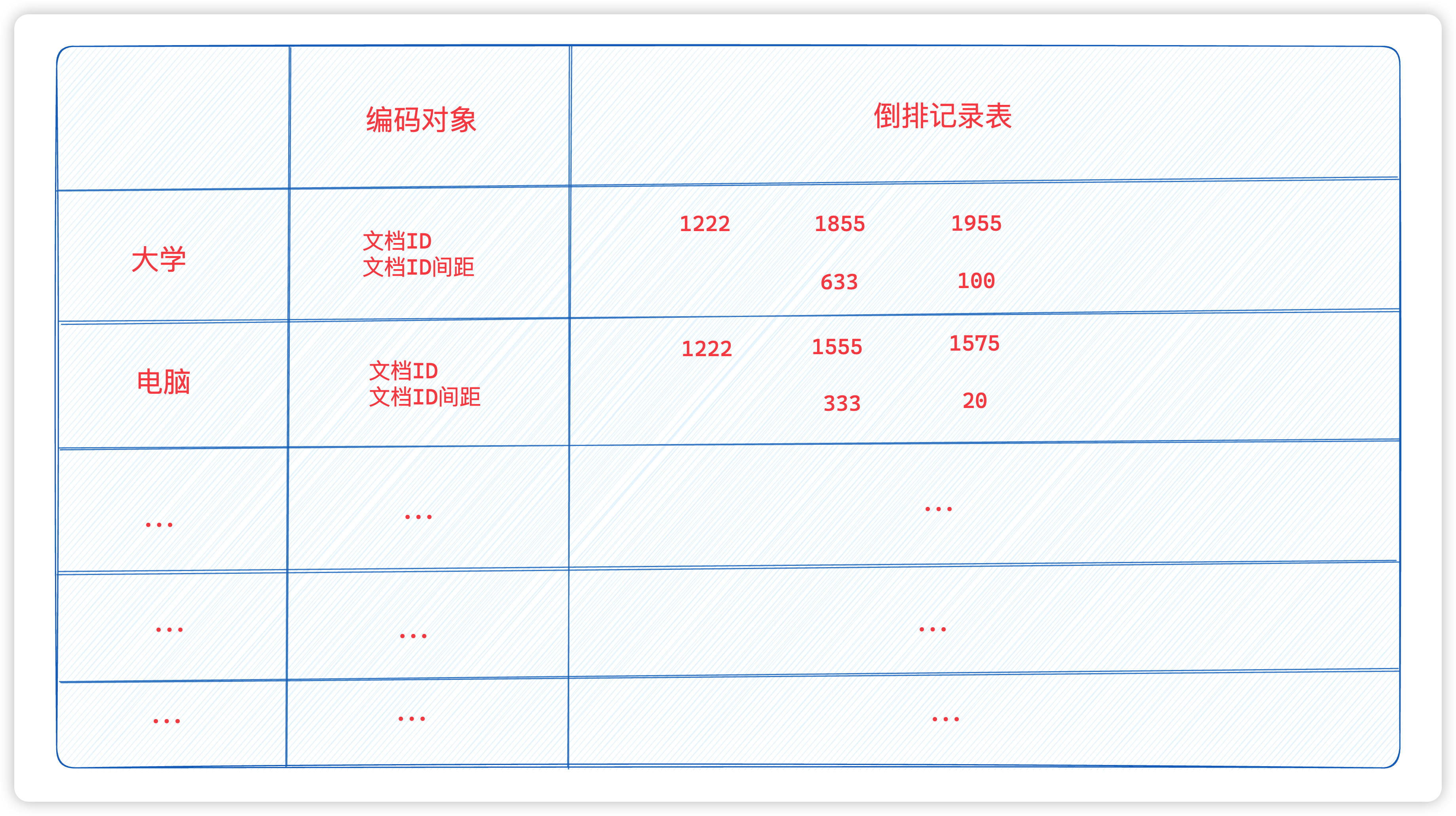
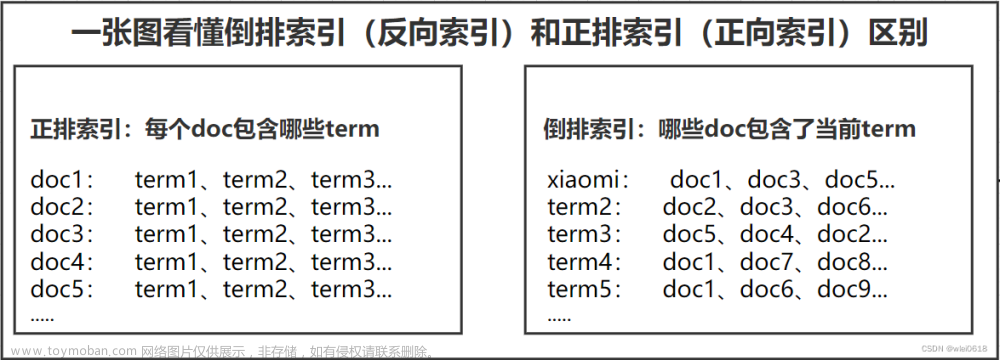
这个模块我们定义了一个名为Index的C++类,用于构建和维护一个文档索引系统。该系统采用单例模式确保只有一个索引实例,并使用正排索引和倒排索引来快速检索文档。正排索引存储了文档的基本信息,如标题、内容和URL,而倒排索引则根据关键词将文档分组。类中提供了构建索引、获取文档信息和获取倒排列表的方法。构建索引的过程涉及读取处理过的数据文件,解析文档数据,并根据文档内容构建索引。此外,我们还实现了简单的进度显示功能。整个索引系统的构建旨在提高文档检索的效率和准确性。
二、编写正排索引和倒排索引模块
✅安装 jsoncpp
🔴安装方法:sudo yum install -y jsoncpp-devel
✅Jieba分词库的安装
PS:我们要先在Linux机器上安装Jieba分词库链接:🔴 "结巴(Jieba)"中文分词的C++版本

1. 代码基本框架
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <mutex>
#include "util.hpp"
#include "log.hpp"
namespace ns_index {
// 定义文档信息结构体
struct DocInfo {
std::string title; // 文档的标题
std::string content; // 文档内容(去标签后)
std::string url; // 文档的URL
uint64_t doc_id; // 文档的唯一ID
};
// 定义倒排列表中的元素结构体
struct InvertedElem {
uint64_t doc_id; // 文档ID
std::string word; // 关键字
int weight; // 关键字权重
InvertedElem() : weight(0) {} // 默认构造函数,权重初始化为0
};
// 获取单例模式的实例
static Index* GetInstance() {
// 双重检查锁定模式,确保线程安全地获取单例
if (nullptr == instance) {
mtx.lock();
if (nullptr == instance) {
instance = new Index();
}
mtx.unlock();
}
return instance;
}
// 定义索引类Index
class Index {
private:
// 构造函数、拷贝构造函数和赋值操作符都设置为私有,防止被实例化
Index() {}
Index(const Index&) = delete;
Index& operator=(const Index&) = delete;
// 单例模式的实例指针
static Index* instance;
// 保护单例模式的互斥锁
static std::mutex mtx;
public:
// 析构函数
~Index() {}
// 根据关键字获取倒排拉链
InvertedList* GetInvertedList(const std::string& word) {
auto iter = inverted_index.find(word);
if (iter == inverted_index.end()) {
std::cerr << word << " have no InvertedList" << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
return &(iter->second);
}
};
// 初始化单例模式的实例指针为nullptr
Index* Index::instance = nullptr;
// 初始化互斥锁
std::mutex Index::mtx;
}
⭕代码分析
-
文档信息结构体 (
DocInfo):- 定义了存储文档信息的结构体,包括标题、内容、URL和文档ID。
-
倒排列表元素结构体 (
InvertedElem):- 定义了倒排列表中的元素结构体,包括文档ID、关键字和关键字权重。
-
单例模式的实现 (
Index类):-
Index类使用单例模式来确保整个程序中只有一个索引实例。 - 构造函数、拷贝构造函数和赋值操作符都是私有的,防止外部直接创建实例。
-
GetInstance方法用于获取索引实例,采用双重检查锁定模式来确保线程安全。 -
GetInvertedList方法用于根据关键字获取对应的倒排列表。
-
-
全局变量和互斥锁:
-
instance是一个静态指针,指向Index类的实例。 -
mtx是一个静态互斥锁,用于保护单例模式的实例创建过程。
-
总体来说,上面的代码展示了一个索引系统的基础框架,包括文档信息的存储结构和单例模式的索引管理。
2. 正排索引的建立
// 定义宏常量
#define NUM 101
// 正排索引存储文档信息
std::vector<DocInfo> forward_index;
// 根据文档ID获取文档信息
DocInfo* GetForwardIndex(uint64_t doc_id) {
if (doc_id >= forward_index.size()) {
std::cerr << "doc_id out of range, error!" << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
return &forward_index[doc_id];
}
// 构建索引,输入为处理完毕的数据文件路径
bool BuildIndex(const std::string& input) {
// 打开输入文件
std::ifstream in(input, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);
if (!in.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "sorry, " << input << " open error" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 读取文件行并构建索引
std::string line;
int count = 0;
std::string bar(NUM, ' '); // 创建进度条
bar[1] = '=';
while (std::getline(in, line)) {
DocInfo* doc = BuildForwardIndex(line);
if (nullptr == doc) {
continue;
}
BuildInvertedIndex(*doc);
count++;
// 显示进度
if (count % 86 == 0) {
int cnt = count / 86 + 1;
bar[cnt] = '=';
std::cout << "成功建立索引进度: " << bar << " [" << cnt << "%]" << "\r";
std::cout.flush();
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return true;
}
// 私有辅助函数,用于构建正排索引
DocInfo* BuildForwardIndex(const std::string& line) {
// 分割字符串为标题、内容和URL
std::vector<std::string> results;
const std::string sep = "\3"; // 行内分隔符
ns_util::StringUtil::Split(line, &results, sep);
if (results.size() != 3) {
return nullptr;
}
// 创建文档信息并添加到正排索引
DocInfo doc;
doc.title = results[0];
doc.content = results[1];
doc.url = results[2];
doc.doc_id = forward_index.size();
// 插入到正排索引的vector
forward_index.push_back(std::move(doc));
return &forward_index.back();
}
⭕代码分析
-
forward_index是一个std::vector,用于存储所有文档的正排索引信息。 -
GetForwardIndex函数通过文档ID从正排索引中检索文档信息。如果文档ID超出范围,则返回空指针并打印错误信息。 -
BuildIndex函数用于从数据文件中读取文档数据并构建索引。它打开输入文件,逐行读取并处理每一行,构建正排索引和倒排索引,并显示进度条。 -
BuildForwardIndex函数是一个私有辅助函数,用于构建单个文档的正排索引条目。它将输入行分割为标题、内容和URL,创建一个DocInfo对象,并将其添加到forward_index向量中。
3. 倒排索引的建立
// 定义宏常量
#define X 10
#define Y 1
// 倒排索引存储关键字到倒排列表的映射
std::unordered_map<std::string, InvertedList> inverted_index;
// 定义倒排列表的类型为InvertedElem元素的向量
typedef std::vector<InvertedElem> InvertedList;
// 私有辅助函数,用于构建倒排索引
bool BuildInvertedIndex(const DocInfo& doc) {
// 分词并统计词频
struct word_cnt {
int title_cnt;
int content_cnt;
word_cnt() : title_cnt(0), content_cnt(0) {}
};
// 用来暂存词频的映射表
std::unordered_map<std::string, word_cnt> word_map;
// 对标题进行分词
std::vector<std::string> title_words;
ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(doc.title, &title_words);
// 对标题进行词频统计
for (std::string s : title_words) {
boost::to_lower(s); // 将单词转换为小写
word_map[s].title_cnt++; // 如果存在就增加计数,否则创建新条目
}
// 对文档内容进行分词
std::vector<std::string> content_words;
ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(doc.content, &content_words);
// 对内容进行词频统计
for (std::string s : content_words) {
boost::to_lower(s);
word_map[s].content_cnt++;
}
// 构建倒排列表
for (const auto& word_pair : word_map) {
InvertedElem item;
item.doc_id = doc.doc_id;
item.word = word_pair.first;
// 计算权重,标题中的词乘以X,内容中的词乘以Y
item.weight = X * word_pair.second.title_cnt + Y * word_pair.second.content_cnt;
// 获取对应关键字的倒排列表,并添加新的倒排元素
InvertedList& inverted_list = inverted_index[word_pair.first];
inverted_list.push_back(std::move(item));
}
return true;
}
⭕代码分析
-
定义数据结构:
-
DocInfo结构体定义了文档信息,包括标题、内容、URL和唯一的文档ID。 -
InvertedElem结构体定义了倒排列表中的元素,包括文档ID、关键字和权重。 -
InvertedList类型定义为std::vector<InvertedElem>,表示一个倒排列表,包含多个InvertedElem元素。
-
-
构建正排索引:
-
forward_index是一个std::vector<DocInfo>,用于存储所有文档的正排索引信息。 -
GetForwardIndex函数通过文档ID从正排索引中检索文档信息。
-
-
构建倒排索引:
-
inverted_index是一个std::unordered_map<std::string, InvertedList>,用于存储关键字到倒排列表的映射。 -
BuildInvertedIndex函数用于根据文档信息构建倒排索引。它首先对文档的标题和内容进行分词,然后统计每个词在标题和内容中出现的次数(词频)。 - 每个分词后的词都会被转换为小写,以便进行不区分大小写的搜索。
- 为每个词创建一个
InvertedElem对象,并根据其在标题和内容中的出现次数计算权重。 - 将
InvertedElem对象添加到inverted_index中对应关键字的倒排列表中。
-
-
处理文本数据:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-850250.html
-
BuildIndex函数打开并读取输入文件,该文件包含处理完毕的文档数据。 - 对文件中的每一行数据,使用
BuildForwardIndex函数构建正排索引条目,并调用BuildInvertedIndex函数构建倒排索引。 - 在构建索引的过程中,显示进度条以指示索引构建的进度。
-
整体来说,上面这段代码展示了如何从文本数据中提取文档信息,并构建正排索引和倒排索引,以便在搜索引擎中快速检索相关文档。通过倒排索引,可以有效地根据关键字找到所有相关文档,提高搜索效率。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-850250.html
三、整体代码
⭕index.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <mutex>
#include "util.hpp"
#include "log.hpp"
#define NUM 101
#define X 10
#define Y 1
namespace ns_index {
// 定义文档信息结构体
struct DocInfo {
std::string title; // 文档的标题
std::string content; // 文档内容(去标签后)
std::string url; // 文档的URL
uint64_t doc_id; // 文档的唯一ID
};
// 定义倒排列表中的元素结构体
struct InvertedElem {
uint64_t doc_id; // 文档ID
std::string word; // 关键字
int weight; // 关键字权重
InvertedElem() : weight(0) {} // 默认构造函数,权重初始化为0
};
// 倒排拉链储存列表
typedef std::vector<InvertedElem> InvertedList;
// 定义索引类Index
class Index {
private:
// 正排索引存储文档信息
std::vector<DocInfo> forward_index;
// 倒排索引存储关键字到倒排列表的映射
std::unordered_map<std::string, InvertedList> inverted_index;
// 构造函数、拷贝构造函数和赋值操作符都设置为私有,防止被实例化
Index() {}
Index(const Index&) = delete;
Index& operator=(const Index&) = delete;
// 单例模式的实例指针
static Index* instance;
// 保护单例模式的互斥锁
static std::mutex mtx;
public:
// 析构函数
~Index() {}
// 获取单例模式的实例
static Index* GetInstance() {
// 双重检查锁定模式,确保线程安全地获取单例
if (nullptr == instance) {
mtx.lock();
if (nullptr == instance) {
instance = new Index();
}
mtx.unlock();
}
return instance;
}
// 根据文档ID获取文档信息
DocInfo* GetForwardIndex(uint64_t doc_id) {
if (doc_id >= forward_index.size()) {
std::cerr << "doc_id out of range, error!" << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
return &forward_index[doc_id];
}
// 根据关键字获取倒排拉链
InvertedList* GetInvertedList(const std::string& word) {
auto iter = inverted_index.find(word);
if (iter == inverted_index.end()) {
std::cerr << word << " have no InvertedList" << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
return &(iter->second);
}
// 构建索引,输入为处理完毕的数据文件路径
bool BuildIndex(const std::string& input) {
// 打开输入文件
std::ifstream in(input, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);
if (!in.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "sorry, " << input << " open error" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 读取文件行并构建索引
std::string line;
int count = 0;
std::string bar(NUM, ' '); // 创建进度条
bar[1] = '=';
while (std::getline(in, line)) {
DocInfo* doc = BuildForwardIndex(line);
if (nullptr == doc) {
continue;
}
BuildInvertedIndex(*doc);
count++;
// 显示进度
if (count % 86 == 0) {
int cnt = count / 86 + 1;
bar[cnt] = '=';
std::cout << "成功建立索引进度: " << bar << " [" << cnt << "%]" << "\r";
std::cout.flush();
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return true;
}
private:
// 私有辅助函数,用于构建正排索引
DocInfo* BuildForwardIndex(const std::string& line) {
// 分割字符串为标题、内容和URL
std::vector<std::string> results;
const std::string sep = "\3"; // 行内分隔符
ns_util::StringUtil::Split(line, &results, sep);
if (results.size() != 3) {
return nullptr;
}
// 创建文档信息并添加到正排索引
DocInfo doc;
doc.title = results[0];
doc.content = results[1];
doc.url = results[2];
doc.doc_id = forward_index.size();
//插入到正排索引的vector
forward_index.push_back(std::move(doc));
return &forward_index.back();
}
// 私有辅助函数,用于构建倒排索引
bool BuildInvertedIndex(const DocInfo& doc) {
// 分词并统计词频
struct word_cnt{
int title_cnt;
int content_cnt;
word_cnt():title_cnt(0), content_cnt(0){}
};
std::unordered_map<std::string, word_cnt> word_map; //用来暂存词频的映射表
//对标题进行分词
std::vector<std::string> title_words;
ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(doc.title, &title_words);
//对标题进行词频统计
for(std::string s : title_words){
boost::to_lower(s); //需要统一转化成为小写
word_map[s].title_cnt++; //如果存在就获取,如果不存在就新建
}
//对文档内容进行分词
std::vector<std::string> content_words;
ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(doc.content, &content_words);
//对内容进行词频统计
for(std::string s : content_words){
boost::to_lower(s);
word_map[s].content_cnt++;
}
// 构建倒排列表
for (const auto& word_pair : word_map) {
InvertedElem item;
item.doc_id = doc.doc_id;
item.word = word_pair.first;
item.weight = X * title_cnt.title_cnt + Y * content_cnt.content_cnt;
InvertedList& inverted_list = inverted_index[word_pair.first];
inverted_list.push_back(std::move(item));
}
return true;
}
};
// 初始化单例模式的实例指针为nullptr
Index* Index::instance = nullptr;
// 初始化互斥锁
std::mutex Index::mtx;
}
到了这里,关于BoostCompass(建立正排索引和倒排索引模块)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!