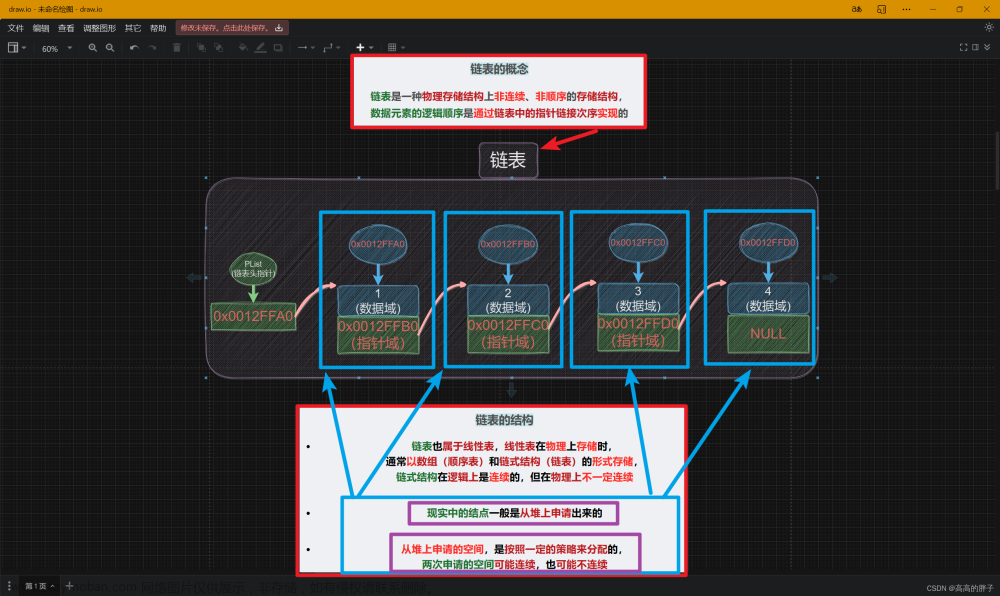
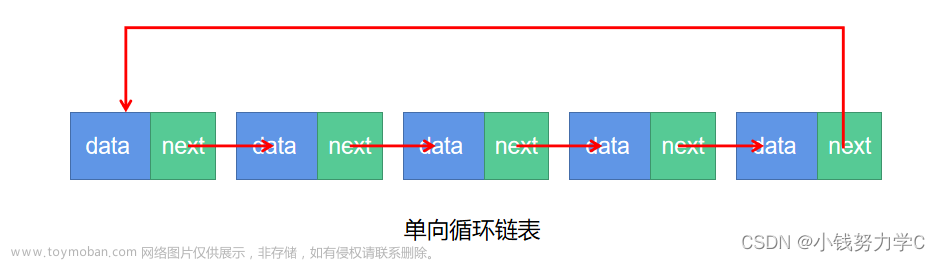
单向循环链表接口设计
/**
* @file name: 单向循环链表接口设计
* @brief :设计单向循环链表,实现各种功能函数并测试
* @author ni456xinmie@163.com
* @date 2024/04/23
* @version 1.0
* @property
* @note
* CopyRight (c) 2023-2024 ni456xinmie@163.com All Right Reseverd文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-856717.html
*/文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-856717.html
构造单向循环链表结构体
// 指的是单向循环链表中的结点有效数据类型,用户可以根据需要进行修改
typedef int DataType_t;
// 构造单向循环链表的结点,链表中所有结点的数据类型应该是相同的
typedef struct CircularLinkedList
{
DataType_t data; // 结点的数据域
struct CircularLinkedList *next; // 结点的指针域
} CircLList_t;
创建一个空单向循环链表并初始化
CircLList_t *CircLList_Create()
{
// 1.创建一个头结点并对头结点申请内存
CircLList_t *Head = (CircLList_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(CircLList_t));
if (NULL == Head)
{
perror("Calloc memory for Head is Failed");
exit(-1);
}
// 2.对头结点进行初始化,头结点是不存储数据域,指针域指向自身,体现“循环”思想
Head->next = Head;
return Head; // 3.把头结点的地址返回即可
}
创建新的结点,并对新结点进行初始化
CircLList_t *CircLList_NewNode(DataType_t data)
{
// 1.创建一个新结点并对新结点申请内存
CircLList_t *New = (CircLList_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(CircLList_t));
if (NULL == New)
{
perror("Calloc memory for NewNode is Failed");
return NULL;
}
// 2.对新结点的数据域和指针域进行初始化
New->data = data;
New->next = NULL;
return New;
}
功能函数:从首节点进行插入元素
bool CircLList_HeadInsert(CircLList_t *Head, DataType_t data)
{
CircLList_t *new = CircLList_NewNode(data);
CircLList_t *tmp = Head->next;
if (Head->next == Head) // empty list
{
Head->next = new;
new->next = new;
return true;
}
while (tmp->next != Head->next) // normal situation,find the last node
tmp = tmp->next;
new->next = Head->next;
Head->next = new;
tmp->next = new;
return true;
}
功能函数:从尾部插入新元素
bool CircLList_TailInsert(CircLList_t *Head, DataType_t data)
{
CircLList_t *new = CircLList_NewNode(data);
if (Head->next == Head) // judge is the null
{
Head->next = new;
new->next = new;
return true;
}
CircLList_t *tmp;
while (tmp->next != Head->next) // when the normal situation,find the last node
tmp = tmp->next;
tmp->next = new;
new->next = Head->next;
return true;
}
功能函数:从指定位置插入新元素
bool CircLList_DestInsert(CircLList_t *Head, DataType_t destval, DataType_t data)
{
CircLList_t *tmp = Head->next;
DataType_t i = Head->data;
if (Head->next == Head) // judge the empty list
{
printf("The list is empty");
return false;
}
CircLList_t *new = CircLList_NewNode(data);
while (destval != tmp->data && tmp->next != Head->next)
{
tmp = tmp->next;
}
if (destval == tmp->data)
{
new->next = tmp->next;
tmp->next = new;
return true;
}
else
{
printf("There is no destval\n");
return false;
}
}
功能函数:遍历打印链表
bool CircLList_Print(CircLList_t *Head)
{
// 对单向循环链表的头结点的地址进行备份
CircLList_t *Phead = Head;
// 判断当前链表是否为空,为空则直接退出
if (Head->next == Head)
{
printf("current linkeflist is empty!\n");
return false;
}
// 从首结点开始遍历
while (Phead->next)
{
// 把头结点的直接后继作为新的头结点
Phead = Phead->next;
// 输出头结点的直接后继的数据域
printf("data = %d\n", Phead->data);
// 判断是否到达尾结点,尾结点的next指针是指向首结点的地址
if (Phead->next == Head->next)
{
break;
}
}
return true;
}
功能函数:删除首节点
bool CircLList_HeadDel(CircLList_t *Head)
{
// 对单向循环链表的头结点的地址进行备份
CircLList_t *Phead = Head->next;
CircLList_t *tmp = Head->next;
if (Head->next == Head) // 判断当前链表是否为空,为空则直接退出
{
printf("current linkeflist is empty!\n");
return false;
}
while (tmp->next != Head->next) // find the last node
tmp = tmp->next;
tmp->next = Phead->next;
Head->next = Phead->next;
Phead->next = NULL;
free(Phead);
return true;
}
功能函数:删除尾部节点
bool CircLList_TailDel(CircLList_t *Head)
{
CircLList_t *tmpFormer;
CircLList_t *tmp = Head->next;
if (Head->next == Head) // 判断当前链表是否为空,为空则直接退出
{
printf("current linkeflist is empty!\n");
return false;
}
while (tmp->next != Head->next) // find the last node
{
tmpFormer = tmp;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
tmpFormer->next = Head->next;
tmp->next = NULL;
free(tmp);
return true;
}
功能函数:删除指定位置的节点
bool CircLList_MidDel(CircLList_t *Head, DataType_t destval)
{
CircLList_t *tmpFormer;
CircLList_t *tmp = Head->next;
if (Head->next == Head) // 判断当前链表是否为空,为空则直接退出
{
printf("current linkeflist is empty!\n");
return false;
}
while (tmp->data != destval && tmp->next != Head->next) // find the specific node
{
tmpFormer = tmp;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
if (tmp->data == destval)
{
tmpFormer->next = tmp->next;
tmp->next = NULL;
free(tmp);
return true;
}
else
{
printf("The is no destival\n");
return false;
}
}
主函数,调用并测试各功能函数
int main()
{
CircLList_t *H = CircLList_Create();
CircLList_HeadInsert(H, 10);
CircLList_HeadInsert(H, 20);
CircLList_HeadInsert(H, 30);
CircLList_TailInsert(H, 30);
CircLList_TailInsert(H, 40);
CircLList_DestInsert(H, 30, 15);
CircLList_Print(H);
puts("");
CircLList_HeadDel(H);
CircLList_Print(H);
puts("");
CircLList_TailDel(H);
CircLList_Print(H);
puts("");
CircLList_MidDel(H, 12);
CircLList_Print(H);
return 0;
}
到了这里,关于单向循环链表接口设计(C语言)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!







![[Collection与数据结构] 链表与LinkedList (一):链表概述与单向无头非循环链表实现](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/04/858484-1.png)




