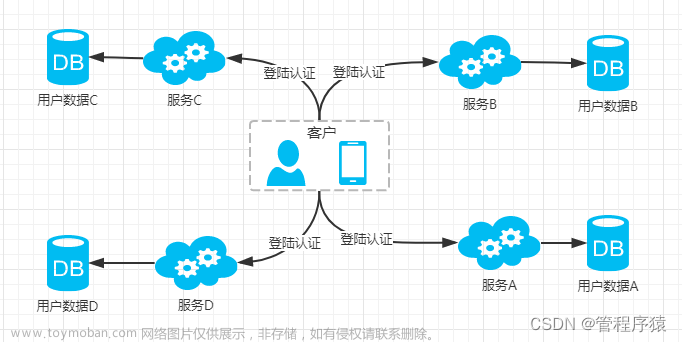
什么是 2FA(双因素身份验证)?
双因素身份验证(2FA)是一种安全系统,要求用户提供两种不同的身份验证方式才能访问某个系统或服务。国内普遍做短信验证码这种的用的比较少,不过在国外的网站中使用双因素身份验证的还是很多的。用户通过使用验证器扫描二维码,就能在app上获取登录的动态口令,进一步加强了账户的安全性。
主要步骤
pom.xml中增加依赖
<!-- 用于SecureKey生成 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-codec</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-codec</artifactId>
<version>1.15</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 二维码依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.iherus</groupId>
<artifactId>qrext4j</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
用户表中增加secretKey列
为用户绑定secretKey字段,用以生成二维码及后期校验
工具类
谷歌身份验证器工具类
/**
* 谷歌身份验证器工具类
*/
public class GoogleAuthenticator {
/**
* 时间前后偏移量
* 用于防止客户端时间不精确导致生成的TOTP与服务器端的TOTP一直不一致
* 如果为0,当前时间为 10:10:15
* 则表明在 10:10:00-10:10:30 之间生成的TOTP 能校验通过
* 如果为1,则表明在
* 10:09:30-10:10:00
* 10:10:00-10:10:30
* 10:10:30-10:11:00 之间生成的TOTP 能校验通过
* 以此类推
*/
private static int WINDOW_SIZE = 0;
/**
* 加密方式,HmacSHA1、HmacSHA256、HmacSHA512
*/
private static final String CRYPTO = "HmacSHA1";
/**
* 生成密钥,每个用户独享一份密钥
*
* @return
*/
public static String getSecretKey() {
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
byte[] bytes = new byte[20];
random.nextBytes(bytes);
Base32 base32 = new Base32();
String secretKey = base32.encodeToString(bytes);
// make the secret key more human-readable by lower-casing and
// inserting spaces between each group of 4 characters
return secretKey.toUpperCase();
}
/**
* 生成二维码内容
*
* @param secretKey 密钥
* @param account 账户名
* @param issuer 网站地址(可不写)
* @return
*/
public static String getQrCodeText(String secretKey, String account, String issuer) {
String normalizedBase32Key = secretKey.replace(" ", "").toUpperCase();
try {
return "otpauth://totp/"
+ URLEncoder.encode((!StringUtils.isEmpty(issuer) ? (issuer + ":") : "") + account, "UTF-8").replace("+", "%20")
+ "?secret=" + URLEncoder.encode(normalizedBase32Key, "UTF-8").replace("+", "%20")
+ (!StringUtils.isEmpty(issuer) ? ("&issuer=" + URLEncoder.encode(issuer, "UTF-8").replace("+", "%20")) : "");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
/**
* 获取验证码
*
* @param secretKey
* @return
*/
public static String getCode(String secretKey) {
String normalizedBase32Key = secretKey.replace(" ", "").toUpperCase();
Base32 base32 = new Base32();
byte[] bytes = base32.decode(normalizedBase32Key);
String hexKey = Hex.encodeHexString(bytes);
long time = (System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000) / 30;
String hexTime = Long.toHexString(time);
return TOTP.generateTOTP(hexKey, hexTime, "6", CRYPTO);
}
/**
* 检验 code 是否正确
*
* @param secret 密钥
* @param code code
* @param time 时间戳
* @return
*/
public static boolean checkCode(String secret, long code, long time) {
Base32 codec = new Base32();
byte[] decodedKey = codec.decode(secret);
// convert unix msec time into a 30 second "window"
// this is per the TOTP spec (see the RFC for details)
long t = (time / 1000L) / 30L;
// Window is used to check codes generated in the near past.
// You can use this value to tune how far you're willing to go.
long hash;
for (int i = -WINDOW_SIZE; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; ++i) {
try {
hash = verifyCode(decodedKey, t + i);
} catch (Exception e) {
// Yes, this is bad form - but
// the exceptions thrown would be rare and a static
// configuration problem
// e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
if (hash == code) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 根据时间偏移量计算
*
* @param key
* @param t
* @return
* @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException
* @throws InvalidKeyException
*/
private static long verifyCode(byte[] key, long t) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeyException {
byte[] data = new byte[8];
long value = t;
for (int i = 8; i-- > 0; value >>>= 8) {
data[i] = (byte) value;
}
SecretKeySpec signKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, CRYPTO);
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance(CRYPTO);
mac.init(signKey);
byte[] hash = mac.doFinal(data);
int offset = hash[20 - 1] & 0xF;
// We're using a long because Java hasn't got unsigned int.
long truncatedHash = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
truncatedHash <<= 8;
// We are dealing with signed bytes:
// we just keep the first byte.
truncatedHash |= (hash[offset + i] & 0xFF);
}
truncatedHash &= 0x7FFFFFFF;
truncatedHash %= 1000000;
return truncatedHash;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
String secretKey = getSecretKey();
System.out.println("secretKey:" + secretKey);
String code = getCode(secretKey);
System.out.println("code:" + code);
boolean b = checkCode(secretKey, Long.parseLong(code), System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("isSuccess:" + b);
}
}
}
二维码工具类
/**
* 验证码生成工具类
*/
public class TOTP {
private static final int[] DIGITS_POWER = {1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000, 10000000, 100000000};
/**
* This method uses the JCE to provide the crypto algorithm. HMAC computes a
* Hashed Message Authentication Code with the crypto hash algorithm as a
* parameter.
*
* @param crypto : the crypto algorithm (HmacSHA1, HmacSHA256, HmacSHA512)
* @param keyBytes : the bytes to use for the HMAC key
* @param text : the message or text to be authenticated
*/
private static byte[] hmac_sha(String crypto, byte[] keyBytes, byte[] text) {
try {
Mac hmac;
hmac = Mac.getInstance(crypto);
SecretKeySpec macKey = new SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, "RAW");
hmac.init(macKey);
return hmac.doFinal(text);
} catch (GeneralSecurityException gse) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(gse);
}
}
/**
* This method converts a HEX string to Byte[]
*
* @param hex : the HEX string
* @return: a byte array
*/
private static byte[] hexStr2Bytes(String hex) {
// Adding one byte to get the right conversion
// Values starting with "0" can be converted
byte[] bArray = new BigInteger("10" + hex, 16).toByteArray();
// Copy all the REAL bytes, not the "first"
byte[] ret = new byte[bArray.length - 1];
System.arraycopy(bArray, 1, ret, 0, ret.length);
return ret;
}
/**
* This method generates a TOTP value for the given set of parameters.
*
* @param key : the shared secret, HEX encoded
* @param time : a value that reflects a time
* @param returnDigits : number of digits to return
* @param crypto : the crypto function to use
* @return: a numeric String in base 10 that includes
*/
public static String generateTOTP(String key, String time, String returnDigits, String crypto) {
int codeDigits = Integer.decode(returnDigits);
String result = null;
// Using the counter
// First 8 bytes are for the movingFactor
// Compliant with base RFC 4226 (HOTP)
while (time.length() < 16) {
time = "0" + time;
}
// Get the HEX in a Byte[]
byte[] msg = hexStr2Bytes(time);
byte[] k = hexStr2Bytes(key);
byte[] hash = hmac_sha(crypto, k, msg);
// put selected bytes into result int
int offset = hash[hash.length - 1] & 0xf;
int binary = ((hash[offset] & 0x7f) << 24)
| ((hash[offset + 1] & 0xff) << 16)
| ((hash[offset + 2] & 0xff) << 8) | (hash[offset + 3] & 0xff);
int otp = binary % DIGITS_POWER[codeDigits];
result = Integer.toString(otp);
while (result.length() < codeDigits) {
result = "0" + result;
}
return result;
}
}
Service
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@Service
public class TwoFAService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 获取SecureKey
*/
public String getSecureKey(Integer userId) {
User user = userMapper.selectUserById(userId);
return user.getSecretKey();
}
/**
* 更新secureKey
*/
public Integer updateSecureKey(Integer userId, String secureKey) {
return userMapper.updateSecureKeyById(userId, secureKey);
}
/**
* 校验动态码
*/
public boolean chek2FACode(User user, String twoFACode) throws Exception {
String secretKey = user.getSecretKey();
// 没绑定设备就先验证通过
if(secretKey == null || secretKey.isEmpty()) {
return true;
} else {
if(twoFACode.isEmpty()) { throw new Exception("已绑定设备,请输入动态码"); }
boolean checkRes = GoogleAuthenticator.checkCode(secretKey, Long.parseLong(twoFACode), System.currentTimeMillis());
if(!checkRes) {
throw new Exception("动态码错误");
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
}
Controller
用户登录中增加两步验证:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-857589.html
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/mgr")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private LogService logService;
@Autowired
private TwoFAService twoFAService;
/**
* @Description: 用户登录
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/login", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public GlobalResult login(String userCode, String userPwd, String twoFACode) {
try {
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(userCode, userPwd);
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
subject.login(token);
// 2FA验证
User user = (User) subject.getPrincipal();
twoFAService.chek2FACode(user, twoFACode);
Log log = new Log();
.......
}
}
}
两步验证的Controler文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-857589.html
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/2fa")
public class TwoFAController {
@Autowired
private TwoFAService twoFAService;
/**
* 生成二维码信息对象
*/
@GetMapping("/getQrcode")
public QrCodeResponse getQrcode(@RequestParam("userId") Integer userId, @RequestParam("userCode") String userCode, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
try {
String secretKey = twoFAService.getSecureKey(userId);
QrCodeResponse qrCodeResponse = new QrCodeResponse();
if(secretKey == null || secretKey.isEmpty()) {
secretKey = GoogleAuthenticator.getSecretKey();
qrCodeResponse.setBind(false);
// userMapper.updateSecureKeyById(userId, secretKey);
} else {
qrCodeResponse.setBind(true);
}
// 生成二维码内容
String qrCodeText = GoogleAuthenticator.getQrCodeText(secretKey, userCode, "suggest-mgr");
// 以流的形式返回生成二维码输出
// new SimpleQrcodeGenerator().generate(qrCodeText).toStream(response.getOutputStream());
BufferedImage image = new SimpleQrcodeGenerator().generate(qrCodeText).getImage();
// 将图片转换为Base64字符串
String base64Image = convertImageToBase64(image);
qrCodeResponse.setQrCodeText(secretKey);
qrCodeResponse.setBase64Image(base64Image);
return qrCodeResponse;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 处理异常
e.printStackTrace();
return null; // 或者返回适当的错误信息
}
}
/**
* 更新SecretKey
* @param userId
* @param secretKey
*/
@GetMapping("/updateSecretKey")
public void updateSecretKey(@RequestParam("userId") Integer userId, @RequestParam("secretKey") String secretKey) {
twoFAService.updateSecureKey(userId, secretKey);
}
/**
* 获取新的secretKey 重置用
* @param userId
* @param userCode
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/getNewSecretKey")
public QrCodeResponse getNewSecretKey(@RequestParam("userId") Integer userId, @RequestParam("userCode") String userCode, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
try {
String secretKey = secretKey = GoogleAuthenticator.getSecretKey();
QrCodeResponse qrCodeResponse = new QrCodeResponse();
qrCodeResponse.setBind(false);
// 生成二维码内容
String qrCodeText = GoogleAuthenticator.getQrCodeText(secretKey, userCode, "xxx-site");
BufferedImage image = new SimpleQrcodeGenerator().generate(qrCodeText).getImage();
// 将图片转换为Base64字符串
String base64Image = convertImageToBase64(image);
qrCodeResponse.setQrCodeText(secretKey);
qrCodeResponse.setBase64Image(base64Image);
// 返回包含qrCodeText和Base64编码图片的信息
return qrCodeResponse;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 处理异常
e.printStackTrace();
return null; // 或者返回适当的错误信息
}
}
/**
* 将图片文件流转为base64
*/
private String convertImageToBase64(BufferedImage image) {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ImageIO.write(image, "png", baos);
byte[] imageBytes = baos.toByteArray();
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(imageBytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 处理异常
return "";
}
}
static public class QrCodeResponse {
private String secretKey;
private String base64Image;
private boolean isBind;
public String getSecretKey() {
return secretKey;
}
public void setSecretKeyt(String secretKey) {
this.secretKey = secretKey;
}
public String getBase64Image() {
return base64Image;
}
public void setBase64Image(String base64Image) {
this.base64Image = base64Image;
}
public boolean isBind() {
return isBind;
}
public void setBind(boolean bind) {
isBind = bind;
}
}
}
常用2FA验证工具
- Google Authenticator: google play, apple store
- Microsoft Authenticator: google play , apple store
- AuthenticatorPro(开源):https://github.com/jamie-mh/AuthenticatorPro
到了这里,关于SpringBoot项目添加2FA双因素身份认证的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!