❣博主主页: 33的博客❣
▶文章专栏分类: Java从入门到精通◀
🚚我的代码仓库: 33的代码仓库🚚
🫵🫵🫵关注我带你学更多数据结构的知识

1.前言
在上一篇文章中,博主已经分享了部分二叉树的经典习题,在这篇文章中,博主将继续和大家分享二叉树的经典习题。
2.二叉树经典习题
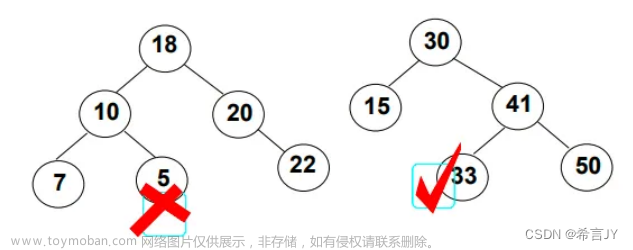
2.1公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先:OJ链接
解题思路
1.如果p,q分居在左子树和右子树,那么根节点root就是公共祖先
2.如果p,q在同一侧,若p是root,则返回p否则返回q
3.如果p,q在同一侧,但分居在一棵树的两侧,那么parent为公共祖先。
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root==null){
return null;
}
if(p==root||q==root){
return root;
}
//P、Q都不为root且不为空
TreeNode Left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode Right =lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(Left!=null&&Right!=null){
return root;
}
//Left与Rihet在一边
if (Left!=null){
return Left;
}
else{
//Right!=null或者Left==null&&Rightnull
return Right;
}
}
栈实现
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor2(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Stack<TreeNode> stackp=new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stackq=new Stack<>();
getpath(root,p,stackp);
getpath(root,q,stackq);
int sizep= stackp.size();
int sizeq=stackq.size();
int size=sizep-sizeq;
if (size>0){
while (size!=0){
stackp.pop();
size--;
}
}else {
while (size!=0){
stackq.pop();
size--;
}
}
while (!stackp.isEmpty()&&!stackq.isEmpty()){
TreeNode curp=stackp.pop();
TreeNode curq=stackq.pop();
if(curp.equals(curq)){
return curp;
}
}
return null;
}
public Boolean getpath(TreeNode root, TreeNode node, Stack<TreeNode> stack){
if(root==null||node==null){
return false;
}
stack.push(root);
if (root==node){
return true;
}
boolean Left=getpath(root.left,node,stack);
if (Left==true){
return true;
}
boolean Right=getpath(root.right,node,stack);
if (Right==true){
return true;
}
stack.pop();
return false;
}
2.2前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树:OJ链接
解题思路
1.根据前序遍历在中序遍历中找到根节点
2.中序遍历中,根的左边为左子树,根的右边为右子树
3.在根据前序遍历在中序中找到根节点,直到end的大于begin的左边
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
public int i=0;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int ib,int ie){
if(ib>ie){
return null;
}
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[i]);
int index=Find(preorder[i],inorder,ib,ie);
if (index==-1){
return null;
}
i++;
root.left=buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, ib, index-1);
root.right=buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, index+1, ie);
return root;
}
public int Find(int a,int[] arr,int ib,int ie){
for (int j=ib;j<=ie;j++){
if(arr[j]==a){
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
2.3后序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
后序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树:OJ链接
int post;
public TreeNode buildTree2(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
post=postorder.length-1;
return buildTreeChild2(inorder,postorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
public TreeNode buildTreeChild2(int[] inorder, int[] postorder,int ib,int ie) {
if(ib>ie){
return null;
}
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[post]);
int index=Find(postorder[post],inorder,ib,ie);
if (index==-1){
return null;
}
post--;
root.right=buildTreeChild2(inorder,postorder,index+1,ie);
root.left=buildTreeChild2(inorder,postorder,ib,index-1);
return root;
}
2.4二叉树创建字符串
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,请你采用前序遍历的方式,将二叉树转化为一个由括号和整数组成的字符串:OJ链接
解题思路
1.先遍历左边,如果左子树不为空:+(+左子树+),如果左子树为空:判断右子树是否为空,如果不为空+()
2.遍历右子树,如果右子树不为空:+(+左子树+),如果右子树为空return
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder =new StringBuilder();
tree2str(root,stringBuilder);
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
public void tree2str(TreeNode root,StringBuilder stringBuilder) {
if(root==null){
return ;
}
stringBuilder.append(root.val);
if(root.left!=null){
stringBuilder.append("(");
tree2str(root.left,stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.append(")");
}else {
//root.left==null
if(root.right!=null){
stringBuilder.append("()");
}else {
//root.left==null &&root.left==null
return ;
}
}
if(root.right!=null){
stringBuilder.append("(");
tree2str(root.right,stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.append(")");
}else {
//root.right==null
return;
}
}
2.5非递归前序遍历
解题思路
1.用栈来实现
2.前序遍历是根左右,我们先让根节点入栈.再一直向左遍历,当为空的时候就返回遍历右节点,如果右节点也为空,那么就出栈.
void preorder(TreeNode root){
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
if(root==null){
return;
}
TreeNode cur=root;
while (cur!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while (cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
System.out.println(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
cur=top.right;
}
}
2.6非递归中序遍历
解题思路
整体思路和前序遍历相似
1.用栈来实现
2.中序遍历是左根右,我们先让左节点入栈.再一直向左遍历,当为空的时候就出栈,返回父节点,再遍历右节点,如果右节点也为空,那么继续出栈.
void inorder(TreeNode root){
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
if(root==null){
return;
}
TreeNode cur=root;
while (cur!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while (cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
System.out.println(top.val+" ");
cur=top.right;
}
}
2.7非递归后序遍历
解题思路
整体思路和前序遍历相似
1.用栈来实现
2.中序遍历是左右根,我们先让左节点入栈.再一直向左遍历,当为空的时候需要判断右节点是否为空,如果右节点为空则出栈,如果右节点不为空那么遍历右节点.
3.但是我们需要注意的是:当右节点不为空遍历右节点的时候,可能造成死循环,所以我们需要定义一个值来表示最后一个被打印的节点。
void postorder(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
if(root==null){
return;
}
TreeNode cur=root;
TreeNode prev=null;
while (cur!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while (cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.peek();{
if (top.right==null||top.right==prev){
stack.pop();
System.out.println(top.val+" ");
prev=top;//标记被打印的节点
}else {
cur=top.right;
}
}
}
}
3.总结
博主整理的只是一部分二叉树的习题,在二叉树中,还有很多有趣的习题没和大家分享,感兴趣的同学可以自己去练习。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-859359.html
下期预告:优先级队列文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-859359.html
到了这里,关于【数据结构(八)下】二叉树经典习题的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!